Related Research Articles

Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases.
Legionella is a genus of pathogenic gram-negative bacteria that includes the species L. pneumophila, causing legionellosis including a pneumonia-type illness called Legionnaires' disease and a mild flu-like illness called Pontiac fever.
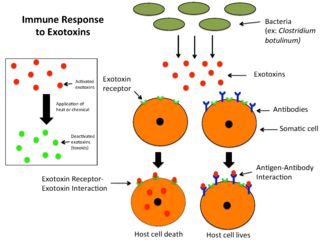
An exotoxin is a toxin secreted by bacteria. An exotoxin can cause damage to the host by destroying cells or disrupting normal cellular metabolism. They are highly potent and can cause major damage to the host. Exotoxins may be secreted, or, similar to endotoxins, may be released during lysis of the cell. Gram negative pathogens may secrete outer membrane vesicles containing lipopolysaccharide endotoxin and some virulence proteins in the bounding membrane along with some other toxins as intra-vesicular contents, thus adding a previously unforeseen dimension to the well-known eukaryote process of membrane vesicle trafficking, which is quite active at the host-pathogen interface.
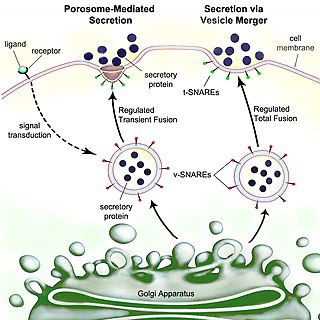
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structures embedded in the cell membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.

Legionella pneumophila is a thin, aerobic, pleomorphic, flagellated, non-spore-forming, Gram-negative bacterium of the genus Legionella. L. pneumophila is the primary human pathogenic bacterium in this group and is the causative agent of Legionnaires' disease, also known as legionellosis.
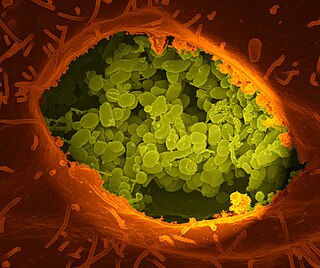
Coxiella burnetii is an obligate intracellular bacterial pathogen, and is the causative agent of Q fever. The genus Coxiella is morphologically similar to Rickettsia, but with a variety of genetic and physiological differences. C. burnetii is a small Gram-negative, coccobacillary bacterium that is highly resistant to environmental stresses such as high temperature, osmotic pressure, and ultraviolet light. These characteristics are attributed to a small cell variant form of the organism that is part of a biphasic developmental cycle, including a more metabolically and replicatively active large cell variant form. It can survive standard disinfectants, and is resistant to many other environmental changes like those presented in the phagolysosome.

In cell biology, a phagosome is a vesicle formed around a particle engulfed by a phagocyte via phagocytosis. Professional phagocytes include macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells (DCs).
Intracellular parasites are microparasites that are capable of growing and reproducing inside the cells of a host.

The gene EEA1 encodes for the 1400 amino acid protein, Early Endosome Antigen 1.

Adenylylation, more commonly known as AMPylation, is a process in which an adenosine monophosphate (AMP) molecule is covalently attached to the amino acid side chain of a protein. This covalent addition of AMP to a hydroxyl side chain of the protein is a posttranslational modification. Adenylylation involves a phosphodiester bond between a hydroxyl group of the molecule undergoing adenylylation, and the phosphate group of the adenosine monophosphate nucleotide. Enzymes that are capable of catalyzing this process are called AMPylators.

Protein numb homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUMB gene. The protein encoded by this gene plays a role in the determination of cell fates during development. The encoded protein, whose degradation is induced in a proteasome-dependent manner by MDM2, is a membrane-bound protein that has been shown to associate with EPS15, LNX1, and NOTCH1. Four transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.

26S proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 2, also as known as 26S Proteasome Regulatory Subunit Rpn1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PSMD2 gene.

F-box/LRR-repeat protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBXL2 gene.

Ankyrin-3 (ANK-3), also known as ankyrin-G, is a protein from ankyrin family that in humans is encoded by the ANK3 gene.

Inflammasomes are cytosolic multiprotein oligomers of the innate immune system responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses. Activation and assembly of the inflammasome promotes proteolytic cleavage, maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18), as well as cleavage of Gasdermin-D. The N-terminal fragment resulting from this cleavage induces a pro-inflammatory form of programmed cell death distinct from apoptosis, referred to as pyroptosis, and is responsible for secretion of the mature cytokines, presumably through the formation of pores in the plasma membrane.
Intracellular antibody-mediated degradation (IAMD) is a neutralization mechanism of intracellular antibody-mediated immunity whereby an effector protein, TRIM21, directs antibody bound virions to the proteasome where they are degraded. As yet, it has only been observed to act against the adenovirus but is likely to also be effective against other non-enveloped viruses.
Ubiquitin-associated (UBA) domains are protein domains that non-covalently interact with ubiquitin through protein-protein interactions. Ubiquitin is a small protein that is covalently linked to other proteins as part of intracellular signaling pathways, often as a signal for protein degradation. UBA domains are among the most common ubiquitin-binding domains.
Bacterial effectors are proteins secreted by pathogenic bacteria into the cells of their host, usually using a type 3 secretion system (TTSS/T3SS), a type 4 secretion system (TFSS/T4SS) or a Type VI secretion system (T6SS). Some bacteria inject only a few effectors into their host’s cells while others may inject dozens or even hundreds. Effector proteins may have many different activities, but usually help the pathogen to invade host tissue, suppress its immune system, or otherwise help the pathogen to survive. Effector proteins are usually critical for virulence. For instance, in the causative agent of plague, the loss of the T3SS is sufficient to render the bacteria completely avirulent, even when they are directly introduced into the bloodstream. Gram negative microbes are also suspected to deploy bacterial outer membrane vesicles to translocate effector proteins and virulence factors via a membrane vesicle trafficking secretory pathway, in order to modify their environment or attack/invade target cells, for example, at the host-pathogen interface.
Legionella jordanis is a Gram-negative bacterium from the genus Legionella which was isolated from the Jordan River in Bloomington, Indiana and from the sewage in DeKalb County, Georgia. L. jordanis is a rare human pathogen and can cause respiratory tract infections.

Nucleomodulins are a family of bacterial proteins that enter the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
References
- ↑ Christopher T. D. Price, Tasneem Al-Quadan, Marina Santic, Ilan Rosenshine, Yousef Abu Kwaik. Host Proteasomal Degradation Generates Amino Acids Essential for Intracellular Bacterial Growth. SCIENCE VOL 334 16 DECEMBER 2011
- ↑ Price C. T., Al-Khodor S., Al-Quadan T., Santic M., Habyarimana F., Kalia A., Kwaik Y. A. (2009). Molecular mimicry by an F-Box Effector of Legionella pneumophila hijacks a conserved polyubiquitination machinery within macrophages and protozoa. PLoS Pathog. 5, e1000704. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000704.