




An Antarctic oasis is a large area naturally free of snow and ice in the otherwise ice-covered continent of Antarctica.





An Antarctic oasis is a large area naturally free of snow and ice in the otherwise ice-covered continent of Antarctica.
In Antarctica there are, in addition to mountaintops and nunataks, other natural snow- and ice-free areas often referred to as "Antarctic oases" or "dry valleys". [1] [2] These areas are surrounded by the Antarctic ice sheet or, in coastal areas, are situated between the ice sheet and the Antarctic ice shelves.
Antarctic oases and dry valleys develop in areas with particular regional weather patterns and geography. These areas have very low humidity and precipitation. Although these areas are very cold, sufficient solar energy is absorbed by the ground to melt what little snow does fall, or else it is scoured or sublimated by katabatic winds, leaving the underlying rock exposed.
Despite usually extreme aridity, some plants, in the form of bryophytes and lichens, can survive in Antarctic oases.
The larger oases (with their respective areas) are:

The geography of Antarctica is dominated by its south polar location and, thus, by ice. The Antarctic continent, located in the Earth's southern hemisphere, is centered asymmetrically around the South Pole and largely south of the Antarctic Circle. It is washed by the Southern Ocean or, depending on definition, the southern Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. It has an area of more than 14.2 million km2. Antarctica is the largest ice desert in the world.

The McMurdo Dry Valleys are a row of largely snow-free valleys in Antarctica, located within Victoria Land west of McMurdo Sound. The Dry Valleys experience extremely low humidity and surrounding mountains prevent the flow of ice from nearby glaciers. The rocks here are granites and gneisses, and glacial tills dot this bedrock landscape, with loose gravel covering the ground. It is one of the driest places on Earth and is sometimes claimed to have not seen rain in nearly two million years, though this is highly unlikely and several anecdotal accounts of rainfall within the Dry Valleys exist.

The Transantarctic Mountains comprise a mountain range of uplifted rock in Antarctica which extends, with some interruptions, across the continent from Cape Adare in northern Victoria Land to Coats Land. These mountains divide East Antarctica and West Antarctica. They include a number of separately named mountain groups, which are often again subdivided into smaller ranges.

Lake Fryxell is a frozen lake 4.5 kilometres (2.8 mi) long, between Canada Glacier and Commonwealth Glaciers at the lower end of Taylor Valley in Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was mapped in the early 1900s and named during Operation Deep Freeze in the 1950s. There are several forms of algae living in the waters and a weather station located at the lake.
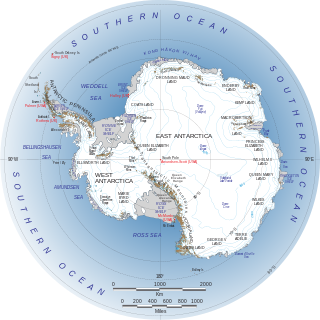
West Antarctica, or Lesser Antarctica, one of the two major regions of Antarctica, is the part of that continent that lies within the Western Hemisphere, and includes the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from East Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains and is covered by the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. It lies between the Ross Sea, and the Weddell Sea. It may be considered a giant peninsula, stretching from the South Pole towards the tip of South America.
Polar ecology is the relationship between plants and animals in a polar environment. Polar environments are in the Arctic and Antarctic regions. Arctic regions are in the Northern Hemisphere, and it contains land and the islands that surrounds it. Antarctica is in the Southern Hemisphere and it also contains the land mass, surrounding islands and the ocean. Polar regions also contain the subantarctic and subarctic zone which separate the polar regions from the temperate regions. Antarctica and the Arctic lie in the polar circles. The polar circles are imaginary lines shown on maps to be the areas that receives less sunlight due to less radiation. These areas either receive sunlight or shade 24 hours a day because of the earth's tilt. Plants and animals in the polar regions are able to withstand living in harsh weather conditions but are facing environmental threats that limit their survival.
Bunger Hills, also known as Bunger Lakes or Bunger Oasis, is a coastal range on the Knox Coast in Wilkes Land in Antarctica, consisting of a group of moderately low, rounded coastal hills, overlain by morainic drift and notably ice free throughout the year, lying south of the Highjump Archipelago. The reasoning behind the minute amount of ice in the area is still relatively unknown and remains under intense debate amongst scientists today.
The Vestfold Hills are rounded, rocky, coastal hills, 512 square kilometres (198 sq mi) in extent, on the north side of Sorsdal Glacier on the Ingrid Christensen Coast of Princess Elizabeth Land, Antarctica. The hills are subdivided by three west-trending peninsulas bounded by narrow fjords. Most of the hills range between 30 and 90 metres in height, with the highest summit reaching nearly 160 metres (520 ft).

East Antarctica, also called Greater Antarctica, constitutes the majority (two-thirds) of the Antarctic continent, lying primarily in the Eastern Hemisphere south of the Indian Ocean, and separated from West Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains. It is generally greater in elevation than West Antarctica, and includes the Gamburtsev Mountain Range in the center. The geographic South Pole is located within East Antarctica.

Princess Astrid Coast is a portion of the coast of Queen Maud Land, Antarctica, lying between 5° and 20° E. The entire coast is bordered by ice shelves. The region was discovered by Capt. H. Halvorsen of the Sevilla (ship) in March 1931 and in 1932 was named for Princess Astrid of Norway. The ice of the continental glacier is up to 4,000 meters thick in the interior. These thick glaciers are held in place by coastal mountain ranges. On the Princess Astrid Coast, some of the ice does flow through the mountains, spilling onto the relatively flat land on the Princess Astrid Coast. Also, the cold air spills over the mountains, creating very strong and persistent winds, which makes the snow scour off the tops of the glaciers leaving pale blue patches of bare ice. On top of the coastal line is the ice shelf, which is much smoother. The glacial ice floats on the sea surface which is beyond the chaotic surface of the sea ice which has been solidifying all winter long.

The Schirmacher Oasis is a 25 km (16 mi) long and up to 3 km (1.9 mi) wide ice-free plateau with more than 100 freshwater lakes. It is situated in the Schirmacher Hills on the Princess Astrid Coast in Queen Maud Land in East Antarctica and is, on average, 100 m (330 ft) above sea level. With an area of 34 km2 (13 sq mi), the Schirmacher Oasis ranks among the smallest Antarctic oases and is a typical polar desert.

Antarctica is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of 14,200,000 km2 (5,500,000 sq mi). Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of 1.9 km (1.2 mi).

Queen Maud Land is a roughly 2.7-million-square-kilometre (1.0-million-square-mile) region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addition, a small unclaimed area from 1939 was annexed in June 2015. Positioned in East Antarctica, it makes out about one-fifth of the continent, and is named after the Norwegian Queen Maud (1869–1938).

Norway has three dependent territories, all uninhabited and located in the Southern Hemisphere. Bouvet Island (Bouvetøya) is a sub-Antarctic island in the South Atlantic Ocean. Queen Maud Land is the sector of Antarctica between the 20th meridian west and the 45th meridian east. Peter I Island is a volcanic island located 450 kilometres (280 mi) off the coast of Ellsworth Land of continental Antarctica. Despite being unincorporated areas, neither Svalbard nor Jan Mayen is formally considered a dependency. While the Svalbard Treaty regulates some aspects of that Arctic territory, it acknowledges that the islands are part of Norway. Similarly, Jan Mayen is recognized as an integral part of Norway.

Jutulsessen is a nunatak in the Gjelsvik Mountains in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It is located in Princess Martha Coast, 235 kilometers (146 mi) from the King Haakon VII Sea. Jutulsessen is the site of the Norwegian research station Troll and the affiliated Troll Satellite Station, which has two radomes on top of the mountain. Troll Airfield is located in the vicinity.
Lake Burton, also known as Burton Lagoon, is a meromictic and saline lake in the Vestfold Hills of Princess Elizabeth Land in Eastern Antarctica. Princess Elizabeth Land, including the lake, is claimed by Australia as part of the Australian Antarctic Territory. The lake has a surface area of 1.35 km2 (0.52 sq mi), a volume of 9.69 million m3, a maximum depth of 18.3 metres (60 ft) and a mean depth of 7.16 metres (23.5 ft). The lake is named after H. R. Burton, a biologist working in the Vestfold Hills of Antarctica.
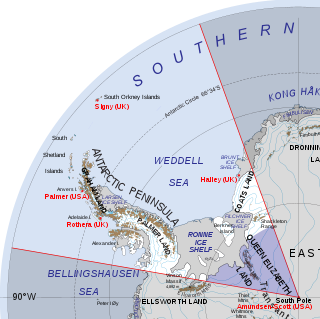
Queen Elizabeth Land is a portion of mainland Antarctica named by the government of the United Kingdom and claimed as part of the British Antarctic Territory. Situated south of Weddell Sea and between longitudes 20°W and 80°W, stretching from Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf to the South Pole. It is bordered by Zumberge Coast of Ellsworth Land to the West and by Hercules Inlet to the Northwest. To the Northeast, circle of latitude 82°S is the dividing line against Coats Land. The area of Queen Elizabeth Land was unnamed until 2012, though most of it was unofficially known as Edith Ronne Land in 1947–68 and includes areas claimed by the United Kingdom, Chile and Argentina.

A blue-ice area is an ice-covered area of Antarctica where wind-driven snow transport and sublimation result in net mass loss from the ice surface in the absence of melting, forming a blue surface that contrasts with the more common white Antarctic surface. Such blue-ice areas typically form when the movement of both air and ice are obstructed by topographic obstacles such as mountains that emerge from the ice sheet, generating particular climatic conditions where the net snow accumulation is exceeded by wind-driven sublimation and snow transports.