The medulla oblongata is a long stem-like structure located in the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. It is a cone-shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic (involuntary) functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure.

The brainstem is the posterior part of the brain, continuous with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem includes the midbrain, and the pons and medulla oblongata of the hindbrain. Sometimes the diencephalon, the caudal part of the forebrain, is included.

The spinothalamic tract is a sensory pathway from the skin to the thalamus. From the ventral posterolateral nucleus in the thalamus, sensory information is relayed upward to the somatosensory cortex of the postcentral gyrus.

The fourth ventricle is one of the four connected fluid-filled cavities within the human brain. These cavities, known collectively as the ventricular system, consist of the left and right lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, and the fourth ventricle. The fourth ventricle extends from the cerebral aqueduct to the obex, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).

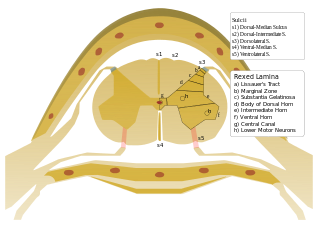
The dorsal root of spinal nerve is one of two "roots" which emerge from the spinal cord. It emerges directly from the spinal cord, and travels to the dorsal root ganglion. Nerve fibres with the ventral root then combine to form a spinal nerve. The dorsal root transmits sensory information, forming the afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.

In the spinal cord, the most lateral of the bundles of the ventral nerve roots is generally taken as a dividing line that separates the antero-lateral region into two parts: an anterior funiculus, between the anterior median fissure and the most lateral of the ventral nerve roots; and a lateral funiculus, between the exit of these roots and the posterolateral sulcus.

The most lateral of the bundles of the anterior nerve roots is generally taken as a dividing line that separates the anterolateral system into two parts. These are the anterior funiculus, between the anterior median fissure and the most lateral of the anterior nerve roots, and the lateral funiculus between the exit of these roots and the posterolateral sulcus.

The posterior median sulcus is the posterior end of the posterior median septum of neuroglia of the spinal cord. The septum varies in depth from 4 to 6 mm, but diminishes considerably in the lower part of the spinal cord.

The lateral spinothalamic tract, which is a part of the anterolateral system, is a bundle of afferent nerve fibers ascending through the white matter of the spinal cord, carrying sensory information to the brain. It carries pain, crude touch and temperature sensory information to the thalamus. It is composed primarily of fast-conducting, sparsely myelinated A delta fibers and slow-conducting, unmyelinated C fibers. These are secondary sensory neurons which have already synapsed with the primary sensory neurons of the peripheral nervous system in the posterior horn of the spinal cord.

The posterolateral tract is a small strand situated in relation to the tip of the posterior column close to the entrance of the posterior nerve roots. It is present throughout the spinal cord, and is most developed in the upper cervical regions.

The olfactory tract is a bundle of afferent nerve fibers from the mitral and tufted cells of the olfactory bulb that connects to several target regions in the brain, including the piriform cortex, amygdala, and entorhinal cortex. It is a narrow white band, triangular on coronal section, the apex being directed upward.

The posterior spinal artery arises from the vertebral artery in 25% of humans or the posterior inferior cerebellar artery in 75% of humans, adjacent to the medulla oblongata. It supplies the grey and white posterior columns of the spinal cord.
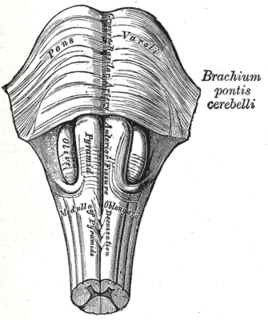
The medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts – known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limit of the pyramids is marked when the fibers cross (decussate).

The spinal veins are situated in the pia mater and form a minute, tortuous, venous plexus.

The anterolateral sulcus is a sulcus on the side of the medulla oblongata. The rootlets of cranial nerve XII emerge from this sulcus.
The spinoreticular tract is an ascending pathway in the white matter of the spinal cord, positioned closely to the lateral spinothalamic tract. The tract is from spinal cord—to reticular formation— to thalamus.
Anterolateral sulcus may refer to:
Anterolateral may refer to:
Sulcus of spinal cord may refer to:
The public domain consists of all the creative works to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable.

Gray's Anatomy is an English language textbook of human anatomy originally written by Henry Gray and illustrated by Henry Vandyke Carter. Earlier editions were called Anatomy: Descriptive and Surgical and Gray's Anatomy: Descriptive and Applied, but the book's name is commonly shortened to, and later editions are titled, Gray's Anatomy. The book is widely regarded as an extremely influential work on the subject, and has continued to be revised and republished from its initial publication in 1858 to the present day. The latest edition of the book, the 41st, was published in September 2015.