
North Kivu is a province bordering Lake Kivu in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Its capital is Goma. The 2020 population was estimated to be 8,147,400.

South Kivu is one of 26 provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Its capital is Bukavu.

The Interahamwe is a Hutu paramilitary organization active in the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Uganda. The Interahamwe was formed around 1990 as the youth wing of the National Republican Movement for Democracy and Development, the then-ruling party of Rwanda, and enjoyed the backing of the Hutu Power government. The Interahamwe, led by Robert Kajuga, were the main perpetrators of the Rwandan genocide, during which an estimated 500,000 to 1,000,000 Tutsi, Twa, and moderate Hutus were killed from April to July 1994, and the term "Interahamwe" was widened to mean any civilian militias or bands killing Tutsi.

Virunga National Park is a national park in the Albertine Rift Valley in the eastern part of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. It was created in 1925. In elevation, it ranges from 680 m (2,230 ft) in the Semliki River valley to 5,109 m (16,762 ft) in the Rwenzori Mountains. From north to south it extends approximately 300 km (190 mi), largely along the international borders with Uganda and Rwanda in the east. It covers an area of 8,090 km2 (3,120 sq mi).

The term Mai-Mai or Mayi-Mayi refers to any kind of community-based militia group active in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) that is formed to defend local communities and territory against other armed groups. Most were formed to resist the invasion of Rwandan forces and Rwanda-affiliated Congolese rebel groups, but some may have formed to exploit the war to their own advantage by looting, cattle rustling or banditry.

Goma is the capital and largest city of the North Kivu Province in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). It is located on the northern shore of Lake Kivu, next to the Rwandan city of Gisenyi. It shares its borders with Bukumu Chiefdom to the north, the Republic of Rwanda to the east, Masisi Territory to the west, and is flanked by Lake Kivu to the south. The city lies in the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift System, and lies only 13–18 km (8.1–11.2 mi) south of the active Nyiragongo Volcano. With an approximate area of approximately 75.72 square kilometers, the city has an estimated population of nearly 2 million people according to the 2022 census, while the 1984 estimate placed the number at 80,000.

The Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda is an armed rebel group active in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. As an ethnic Hutu group opposed to the ethnic Tutsi influence, the FDLR is one of the last factions of Rwandan rebels active in the Congo. It was founded through an amalgamation of other groups of Rwandan refugees in September 2000, including the former Army for the Liberation of Rwanda (ALiR), under the leadership of Paul Rwarakabije. It was active during the latter phases of the Second Congo War and the subsequent insurgencies in Kivu.

The Army for the Liberation of Rwanda was a rebel group largely composed of members of the Interahamwe and Armed Forces of Rwanda. Operating mostly in the eastern regions of the Democratic Republic of the Congo along the border with Rwanda, it carried out attacks throughout the Second Congo War against forces aligned with Rwanda and Uganda. In 2000, the ALiR agreed to merge with the Hutu resistance movement based in Kinshasa into the new Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR). ALiR was largely supplanted by the FDLR by 2001.
Congolese history in the 2000s has primarily revolved around the Second Congo War (1998–2003) and the empowerment of a transitional government.
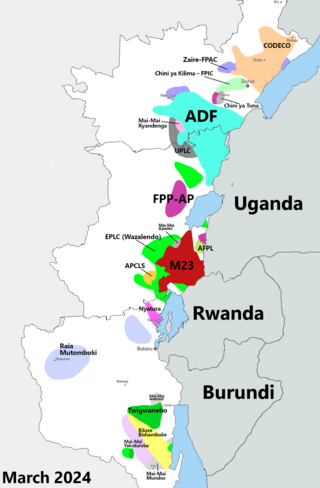
The Kivu conflict is an umbrella term for a series of protracted armed conflicts in the North Kivu and South Kivu provinces in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo which have occurred since the end of the Second Congo War. Including neighboring Ituri province, there are more than 120 different armed groups active in the eastern Democratic Republic of Congo. Currently, some of the most active rebel groups include the Allied Democratic Forces, the Cooperative for the Development of the Congo, the March 23 Movement, and many local Mai Mai militias. In addition to rebel groups and the governmental FARDC troops, a number of national and international organizations have intervened militarily in the conflict, including the United Nations force known as MONUSCO, and an East African Community regional force.

The Institut Congolais pour la Conservation de la Nature is a Congolese governmental partner tasked with the protection and conservation of the Virunga National Park and Kahuzi-Biega National Park, both UNESCO World Heritage Sites in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Members of the ICCN are charged with the overall protection of the parks and the endangered mountain gorilla. The ICCN works with various national and international NGO partners.

The 2008 Nord-Kivu campaign was an armed conflict in the eastern Nord-Kivu province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The upsurge of violence in the Kivu conflict saw heavy battles between the Democratic Republic of Congo's army, supported by the United Nations, and Tutsi militia under General Laurent Nkunda.

The National Congress for the Defence of the People is a political armed militia established by Laurent Nkunda in the Kivu region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo in December 2006. The CNDP was engaged in the Kivu conflict, an armed conflict against the military of the Democratic Republic of the Congo. In January 2009, the CNDP split and Nkunda was arrested by the Rwanda government. The remaining CNDP splinter faction, led by Bosco Ntaganda, was planned to be integrated into the national army.
Laurent Nkunda is a former General in the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and is the former warlord operating in the province of Nord-Kivu, sympathetic to Congolese Tutsis and the Tutsi-dominated government of neighbouring Rwanda. Nkunda, who is himself a Congolese Tutsi, commanded the former DRC troops of the 81st and 83rd Brigades of the DRC Army. He speaks English, French, Swahili, Kinyarwanda, Lingala and Kinande. On January 22, 2009, he was put under house arrest in Gisenyi when he was called for a meeting to plan a joint operation between the Congolese and Rwandan militaries.

The 2009 Eastern Congo offensive was a joint Congo-Rwanda military offensive against the Hutu Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR) rebel group descended from those groups that carried out the 1994 Rwanda genocide. Two operations were carried out: 'Kimia II' and 'Umoja Wetu.' 'Kimia' can be translated as 'calm.' "Umoja Wetu" is Swahili for "Our Unity".
Sylvestre Mudacumura was the overall commander of the military wing of the rebel Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR), known as the Forces Combattants Abacunguzi (FOCA).
iGorilla is a software application (app) that is designed for use with the internet and multimedia enabled smartphones iPhone or iPod Touch, which were created by Apple Inc. iGorilla is the first app to be dedicated to the protection of mountain gorillas and is evidence that organizations involved in wildlife conservation are using digital media technology to raise funds and awareness by communicating directly with people who are concerned about the planet’s biological heritage.

Rutshuru Territory is a territory in the North Kivu province of the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), with headquarters is the town of Rutshuru.

Bunyakiri is a town located in the high plateau of Kalehe Territory in the South Kivu Province in the eastern region of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Bunyakiri is nearby the Bulehe and Mulamba villages. It is mainly inhabited by Tembo, Havu, Twa and Hunde ethnic groups.
Events in the year 2021 in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.














