
The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish that includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, trevallies, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only family within that order but molecular and anatomical studies indicate that there is a close relationship between this family and the five former Perciform families which make up the Carangiformes.

Diplomystus is an extinct genus of freshwater and marine clupeomorph fish distantly related to modern-day extant herrings, anchovies, and sardines. It is known from the United States, China, and Lebanon from the Late Cretaceous to the middle Eocene. Many other clupeomorph species from around the world were also formerly placed in the genus, due to it being a former wastebasket taxon. It was among the last surviving members of the formerly-diverse order Ellimmichthyiformes, with only its close relative Guiclupea living for longer.

Scomber is a genus of ray-finned fish in the family Scombridae living in the open ocean found in Atlantic, Indian and Pacific Ocean. The genus Scomber and the genus Rastrelliger comprise the tribe Scombrini, known as the "true mackerels". These fishes have an elongated body, highly streamlined, muscular and agile. The eyes are large, the head is elongated, with a big mouth provided with teeth. They have two triangular dorsal fins, with some stabilizing fins along the caudal peduncle. The basic color is blue-green with a silvery white belly and a darker back, usually black mottled.

Bathysoma is an extinct genus of marine lampriform ray-finned fish from the early-mid Paleocene. It contains a single species, B. lutkeni from Sweden. Its fossils are common in exposures of the Danian København Limestone Formation at Limhamns kalkbrott, one of the largest quarries in northern Europe. A single specimen is also known from an erratic boulder from the Selandian Lellinge Greensand Formation of southern Sweden.

Exellia is a genus of extinct spadefish that lived in the Tethys Ocean during the early Paleogene. The adult form is shaped akin to a large spadefish or a short dolphinfish, with very large pelvic fins, and a long dorsal fin starting from in front of the eyes to near the base of the caudal peduncle. The juvenile form resembles a juvenile drumfish, with the dorsal fin forming a long crest on top of the head.

Avitoluvarus is a genus of extinct louvar that lived in the Peri-Tethys Sea during the early Paleogene. The first specimens were found from the Danata Formation Lagerstätten, of the Ypresian age of Turkmenistan, where they were originally thought to be smaller or juvenile individuals of the true louvar, Luvarus necopinatus. These specimens were later reexamined, and determined to be a separate genus comprising two species.

Turkmenidae is an extinct family of lamprids from the Paleogene of the west-central Asia, in what was formerly the Peri-Tethys Ocean. They were small, disk-shaped fish that bore a strong resemblance to their closest living relatives, the opahs.

Trachicaranx tersus is an extinct primitive, pompano-like jack fish from what is now Turkmenistan. It lived in an ocean upwelling with its relative, Archaeus oblongus during the Thanetian epoch of the late Paleocene. Some incomplete fossil specimens were once identified as being a separate species, "Uylyaichthys eugeniae."
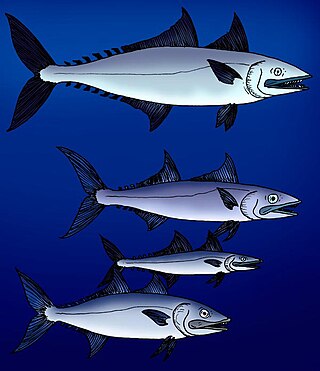
Euzaphlegidae is a family of extinct escolar-like ray-finned fish closely related to the snake mackerels. Fossils of euzaphlegids are found from Paleocene to Late Miocene-aged marine strata of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains, India, Iran, Turkmenistan, Italy, and Southern California.

Oligolophotes is an extinct genus of fish from the Early Oligocene of the bank of Belaya River in Adygea, the Caucasus Mountains. There is one species, Oligolophotes fragosus, known from the holotype that is estimated to have measured 122 mm (4.8 in) in body length.
Aulorhamphus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived from the early to middle Eocene. It contains four species known from the Early Eocene of Italy and the Middle Eocene of Russia. It was an aulorhamphid, an extinct family of syngnathiform fishes.
Berycomorus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish that lived during the late Eocene epoch. It contains a single species, B. firdoussi, from the Pabdeh Formation of Iran.

Balistomorphus is an extinct genus of prehistoric triggerfish during the early Oligocene epoch in what is now Canton Glarus, Switzerland. It inhabited the marine environment of the Tethys Ocean.
Aluvarus praeimperialis is an extinct ray-finned fish, known from two headless larval fossil specimens found in the Pabdeh Formation, a Late Eocene stratum from the Priabonian epoch, of what is now Iran. A. praeimperialis was originally thought to be a luvar, described as "Luvarus praeimperialis", as it was thought to be a predecessor to the modern luvar. A later reexamination of the specimens showed that they were too incomplete to demonstrate such a conclusion and had no clear exclusive shared traits with luvar, and were renamed "Aluvarus", meaning "not luvar" or "different than luvar". However, some authorities still retain it as a luvar.
Caprovesposus is an extinct, prehistoric surgeonfish that inhabited the Paratethys Sea during the Oligocene. It is known from a single species, C. parvus, from what is now the North Caucasus, Russia. Potential specimens are known from the Miocene of Egypt, but these are poorly preserved and this attribution is uncertain.

Palimphyes is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish known from the Paleogene period. It was a euzaphlegid, an extinct family of scombroid fish related to the escolars and snake mackerels.
Caucasichthys is an extinct genus of perciform bony fish which existed in Russia during the middle Eocene epoch. It is known from the Gorny Luch locality of northern Caucasus. It was first named by Alexandre F. Bannikov, Giorgio Carnevale and N. V. Parin in 2011 and the type species is Caucasichthys kumaensis. The generic name comes from Caucas, from Caucasus and ichthys, fish. The specific name is derived from the Kuma Horizon, where the fossils were found.
The Danata Formation is an earliest Eocene to Middle Eocene sedimentary succession located in Turkmenistan. It is mostly famous for its fish-bearing horizons (Ichthyofauna). The formation for example crops out in the Kopet Dag mountain range in the border region of Turkmenistan and Iran. It was deposited in a far northeastern arm of the Tethys Sea.
The Matt Formation is an Early Oligocene-aged marine geological formation that outcrops in the Glarus Alps of the Canton of Glarus, Switzerland. It is most notable for its fossiliferous slates found near Engi, known as the Engi slates, Glarner Schiefer or Glarner Fischschiefer, which contain the well-preserved fossils of fishes, birds, and sea turtles. The metamorphization of the rock has led to many of the fossils appearing somewhat distorted.
Hemingwaya is an extinct genus of billfish in the monotypic family Hemingwayidae that lived during the earliest Eocene epoch, approximately 56 to 55 million years ago. It contains a single species, H. sarissa. Members of this family are characterized by their elongated, spear-like bills, a feature that defines modern billfish such as swordfish and marlins. It is known from the Danata Formation of Turkmenistan, which represented a far eastern inland arm of the Tethys Ocean, and was deposited in the earliest Eocene shortly after the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum. The genus name honors famed author Ernest Hemingway, who prominently featured a marlin in his 1952 novella The Old Man and the Sea, while the species name "sarissa" originates from the Greek word for "spear".















