Related Research Articles

The Polikarpov I-153 Chaika was a late 1930s Soviet biplane fighter. Developed as an advanced version of the I-15 with a retractable undercarriage, the I-153 fought in the Soviet-Japanese combats in Mongolia and was one of the Soviets' major fighter types in the early years of the Second World War. Three I-153s are still flying.

The Arsenal VG 90 was a French carrier-based jet-engined interceptor developed in the late 1940s. It was intended to compete for an Aéronavale contract and first flew in 1949. It set a speed record for a French aircraft the following year, but both of the completed prototypes were destroyed in fatal crashes and the program was cancelled in 1952 before the third prototype was finished. The Aéronavale contract was eventually awarded to a license-built British aircraft. The remains of the last VG 90 were scrapped in 1978.

The Fauvel AV.36 was a single-seat tailless glider designed in France in the 1950s by Charles Fauvel. Although the "AV" in AV.36 stands for Aile Volante, it was not a true flying wing: it featured two large fins mounted on stubby tailbooms extending back from the wing's trailing edge, and accommodated the pilot within a stubby fuselage. The aircraft was designed to be quickly disassembled for road transport, with the nose detaching, and the fins able to fold back against the trailing edge of the wing. A refined version with a slightly longer wingspan, the AV.361 was introduced in 1960.

The Breda Ba.27 was a fighter produced in Italy in the 1930s, used by the Chinese Nationalist Air Force in the Second Sino-Japanese War.
The Dewoitine D.33 was a single-engine low-wing monoplane aircraft built by the Dewoitine Company. It is remembered for setting a long-distance record on its first flight in 1930.

The Farman F.50 was a French twin-engined night bomber designed and built by Farman as a replacement for the single-engined Voisin pusher biplanes in service with the French Air Force.

The DFW C.IV, DFW C.V, DFW C.VI, and DFW F37 were a family of German reconnaissance aircraft first used in 1916 in World War I. They were conventionally configured biplanes with unequal-span unstaggered wings and seating for the pilot and observer in tandem, open cockpits. Like the DFW C.II before them, these aircraft seated the gunner to the rear and armed him with a machine gun on a ring mount. Compared to preceding B- and C-class designs by DFW, however, the aerodynamics of the fuselage were more refined, and when coupled with more powerful engines, resulted in a machine with excellent performance.

The Lioré et Olivier LeO 7 was a French bomber escort biplane designed and built by Lioré et Olivier for the French Air Force.
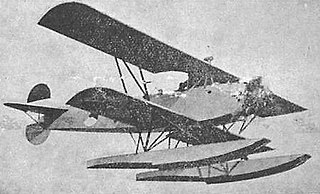
The Fokker C.VII-W was a reconnaissance seaplane built in the Netherlands in the late 1920s. Sharing elements of the highly successful C.V design, the C.VII-W was a conventional, single-bay biplane with wings of unequal span braced with N-struts. The undercarriage consisted of a standard twin-pontoon arrangement, and the fin and rudder continued through to the ventral side of the fuselage, creating a cruciform tail. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, open cockpits. The wing structure was wooden with fabric and plywood covering, and the fuselage was of steel tube construction with fabric covering.

The Fokker C.XI-W was a reconnaissance seaplane designed to operate from warships that was produced in the Netherlands in the mid-1930s. It was the result of a Royal Netherlands Navy specification of 1935 requesting such an aircraft. Fokker's response was a conventional single-bay biplane with staggered wings of unequal span braced by N-struts. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, open cockpits, and the undercarriage consisted of twin pontoons. The wings were of wooden construction with plywood and fabric covering, and the fuselage was of steel tube, also covered with fabric.
The Fokker CXIV-W was a reconnaissance seaplane produced in the Netherlands in the 1930s. It was a conventional, single-bay biplane with staggered wings of unequal span braced by N-struts. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, open cockpits, and the undercarriage consisted of twin pontoons. 11 of the 24 examples produced were stationed in the Dutch East Indies. These were later joined by 12 aircraft that had escaped to the UK following the German invasion of the Netherlands in 1940. All C.XIVs were destroyed during the Japanese invasion of the Dutch East Indies.

The Hannover CL.II was an escort fighter, produced in Germany during World War I, designed in response to a 1917 requirement by the Idflieg for such a machine to protect reconnaissance aircraft over enemy territory. It was a compact biplane of largely conventional configuration with single-bay staggered wings of unequal span. The fuselage was a thin plywood paneled, wooden monocoque design, very similar to the style of fuselage in Robert Thelen's Albatros series of single-seat fighters.

The Hanriot HD.14 was a military trainer aircraft produced in large numbers in France during the 1920s. It was a conventional, two-bay biplane with unstaggered wings of equal span. The pilot and instructor sat in tandem, open cockpits, and the fuselage was braced to the lower wing with short struts. The main units of the fixed tailskid undercarriage were divided, each unit carrying two wheels, and early production examples also had anti-noseover skids projecting forwards as well.

The LVG C.V was a reconnaissance aircraft produced in large numbers in Germany during World War I.

The Macchi M.18 was a flying boat designed by Alessandro Tonini and produced by Macchi in Italy in the early 1920s. Originally planned as a passenger aircraft, it entered production as a bomber before eventually being offered on the civil market that it was originally intended for.

The Potez IX was an early airliner produced in France in the 1920s, a further development of the SEA IV that Henry Potez had co-designed during the First World War.

The Potez 53 was a French low-wing enclosed cockpit single-seat cantilever monoplane racing aircraft built by Potez to specifically to compete in the 1933 Coupe Deutsch de la Meurthe race, which it won outright.
The Bréguet Br 900 Louisette was a short-span, single-seat competition sailplane built in France in the 1940s. It set some French gliding records but was unsuccessful at the international level. Only six production aircraft were built.
The Lioré et Olivier LeO 8, Lioré et Olivier LeO 8-Cau 2 or Lioré et Olivier LeO 8 CAN 2 was a French two seat, parasol wing monoplane night fighter and reconnaissance aircraft, built in 1923.
The Caudron C.99 was a French light bomber and reconnaissance aircraft. The only example flew with different engines in the mid-1920s.
References
- ↑ de Narbonne 2008, p. 79
- de Narbonne, Roland (July 2008). "Juillet 1948, dans l'aéronautique française: Trop vite, trop tôt, le NC 211 "Cormoran"". Le Fana de l'Aviation (in French). No. 464. pp. 76–79.
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 81.
- World Aircraft Information Files. London: Bright Star Publishing. pp. File 889 Sheet 81.