Wolf spiders are members of the family Lycosidae, named for their robust and agile hunting skills and excellent eyesight. They live mostly in solitude, hunt alone, and usually do not spin webs. Some are opportunistic hunters, pouncing upon prey as they find it or chasing it over short distances; others wait for passing prey in or near the mouth of a burrow. Wolf spiders resemble nursery web spiders, but wolf spiders carry their egg sacs by attaching them to their spinnerets, while the Pisauridae carry their egg sacs with their chelicerae and pedipalps. Two of the wolf spider's eight eyes are large and prominent; this distinguishes them from nursery web spiders, whose eyes are all of roughly equal size. This can also help distinguish them from the similar-looking grass spiders.

Cheiracanthium inclusum, alternately known as the black-footed yellow sac spider or the American yellow sac spider, was formerly classified as a true sac spider, and then placed in the family Miturgidae, but now belongs to family Cheiracanthiidae. It is a rather small pale yellow species that is indigenous to the Americas. It is often found living in the foliage of forests and gardens but also can inhabit human homes. Despite common beliefs of necrosis, Cheiracanthium bites cause only localized swelling. C. inclusum is closely related to Cheiracanthium mildei, an introduced species native to Europe which is similar in appearance and natural history and can also be found in North American homes.

Huntsman spiders, members of the family Sparassidae, catch their prey by hunting rather than in webs. They are also called giant crab spiders because of their size and appearance. Larger species sometimes are referred to as wood spiders, because of their preference for woody places. In southern Africa the genus Palystes are known as rain spiders or lizard-eating spiders. Commonly, they are confused with baboon spiders from the Mygalomorphae infraorder, which are not closely related.

Nursery web spiders (Pisauridae) are a family of araneomorph spiders first described by Eugène Simon in 1890. Females of the family are known for building special nursery webs. When their eggs are about to hatch, a female spider builds a tent-like web, places her egg sac inside, and stands guard outside, hence the family's common name. Like wolf spiders, however, nursery web spiders are roaming hunters that do not use webs for catching prey.

Deinopidae, also known as net casting spiders, is a family of cribellate spiders first described by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1850. It consists of stick-like elongated spiders that catch prey by stretching a web across their front legs before propelling themselves forward. These unusual webs will stretch two or three times their relaxed size, entangling any prey that touch them. The posterior median eyes have excellent night vision, allowing them to cast nets accurately in low-light conditions. These eyes are larger than the others, and sometimes makes these spiders appear to only have two eyes. Ogre-faced spiders (Deinopis) are the best known genus in this family. The name refers to the perceived physical similarity to the mythological creature of the same name. This family also includes the humped-back spiders (Menneus).

Austracantha is a genus of spider with a single species, Austracantha minax, commonly known as the jewel spider or the Christmas spider. It is a member of the family Araneidae and is endemic to Australia. They are relatively small spiders, reaching a maximum total body length of only around 12 mm (0.47 in) for females, and 5 mm (0.20 in) for males. Their abdomen has six distinctive projections ("spines") that makes them easy to identify. They are predominantly a shiny black, with variable white, yellow, and orange patterns. Melanistic forms also occur during autumn. They are facultatively gregarious, and can be found in large aggregations of overlapping orb webs. They feed on small flying insects that get entangled in their webs. They are harmless to humans, though the webs can be a nuisance for bushwalkers. They are most abundant during the summer months.

The spider species Tegenaria domestica, commonly known as the barn funnel weaver in North America and the domestic house spider in Europe, is a member of the funnel-web family Agelenidae.

Steatoda grossa, commonly known as the cupboard spider, the dark comb-footed spider, the brown house spider, or the false widow or false black widow, is a common species of spider in the genus Steatoda.

The black house spider or common black spider is a common species of cribellate Australian spider, introduced to New Zealand,Japan and South Africa. A closely related species, Badumna longinqua, the grey house spider, has a similar distribution, but has also been introduced to the Americas.
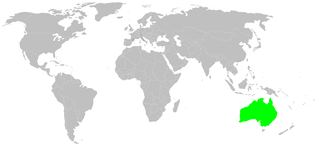
Phryganoporus candidus, also known as the foliage web spider, is a small, subsocial jumping spider endemic to Australia. On average, they are 6–10 mm long and are a mottled brown colour, covered in silvery grey hair. They typically reside in arid and semi-arid locations, building their nests in various trees, bushes, and other plant-life. They have a mutualistic relationship with Acacia ligulata, and therefore prefer to build their nests in these trees.

Sidymella rubrosignata is a species of crab spiders found in Australia. It is a common spider, often seen on Dianella plants.

Uliodon is a genus of spiders endemic to New Zealand and possibly Australia. They are commonly referred to as vagrant spiders. Vagrant spiders vary in colour from dark brown to almost black, they typically have a body length of 20mm and a 50mm leg span. When alive, the interior of the male's pedipalp are brightly coloured.

Rugathodes sexpunctatus is a minute species of spider in the family Theridiidae, the cobweb or tangle-web spiders. This family includes the medically important genus Latrodectus—the widow spiders. The species in the genus Rugathodes are too small to be dangerous to humans. Very little is known about most species in this genus.

Cyrtophora exanthematica are tent spiders common in tropical Asia and Australia. They are commonly known as double-tailed tent spiders because of the pair of blunt projections at the end of their abdomens. They are harmless to humans.

Palystes is a genus of huntsman spiders, commonly called rain spiders or lizard-eating spiders, occurring in Africa, India, Australia, and the Pacific. The most common and widespread species is P. superciliosus, found in South Africa, home to 12 species in the genus. The name Palystes is derived from either the Latin palaestes or the Greek palaistes, meaning "wrestler". The genus was first described by Ludwig Carl Christian Koch in 1875.

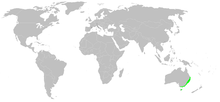
Argiope radon is a species of orb web spider native to Australia. It is found in tropical areas of the Northern Territory, Western Australia and Queensland. It is commonly known as the Northern St Andrew's cross spider.

Arbanitis robertsi is a species of tube-dwelling spider in the family Idiopidae found in and near rainforests in New South Wales and Queensland, Australia. A mid to large sized spider which builds a tube of web that extends from the burrow. The tube is attached to rocks, tree ferns or the base of trees. Thousands of these tubes were recorded by Sid Jackson in November 1922 at the south eastern end of Wallis Lake. "Up to three feet long, and half an inch wide". Situated on damp ground, close to freshwater streams.

Arachnura feredayi, the tailed forest spider or scorpion-tailed spider, is endemic to New Zealand. It is known for the distinctive tapering body shape in females, which are also much larger than males, and for producing vertical columns of egg sacs in their webs.

Asianopis is a genus of Asian net-casting spiders first described by Y. J. Lin, L. Shao and A. Hänggi in 2020.

Salsa fuliginata, commonly known as the sooty orbweaver, is a orb-weaver spider in the genus Salsa. The species is found throughout southeastern Australia and New Zealand.