Many countries and territories have installed significant solar power capacity into their electrical grids to supplement or provide an alternative to conventional energy sources. Solar power plants use one of two technologies:

Solar power in Australia is a fast growing industry. As of April 2022, Australia's over 3.12 million solar PV installations had a combined capacity of 26,093 MW photovoltaic (PV) solar power, of which at least 4,342 MW were installed in the preceding 12 months. In 2019, 59 solar PV projects with a combined capacity of 2,881 MW were either under construction, constructed or due to start construction having reached financial closure. Solar accounted for 9.9% of Australia's total electrical energy production in 2020.

Solar power in India is a fast developing industry as part of the renewable energy in India. The country's solar installed capacity was 57.705 GW as of 30 June 2022.
For solar power, South Asia has the ideal combination of both high solar insolation and a high density of potential customers.
Financial incentives for photovoltaics are incentives offered to electricity consumers to install and operate solar-electric generating systems, also known as photovoltaics (PV).
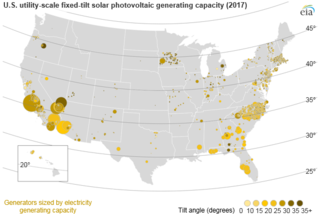
Solar power includes utility-scale power plants as well as local distributed generation, mostly from rooftop photovoltaics and increasingly from community solar arrays. From January through December 2021, utility-scale solar power generated 114.7 terawatt-hours (TWh), or 2.79% of all generated electrical energy in the United States. During the same time period total solar generation, including estimated small-scale photovoltaic generation, was 163.7 TWh.

Solar power in California includes utility-scale solar power plants as well as local distributed generation, mostly from rooftop photovoltaics. It has been growing rapidly because of high insolation, community support, declining solar costs, and a Renewable Portfolio Standard which requires that 33% of California's electricity come from renewable resources by 2020, and 60% by 2030. Much of this is expected to come from solar power via photovoltaic facilities or concentrated solar power facilities.

Solar power in Arizona has the potential to, according to then-Governor Janet Napolitano, make Arizona "the Persian Gulf of solar energy". In 2012, Arizona had 1,106 MW of photovoltaic (PV) solar power systems, and 6 MW of concentrated solar power (CSP), bringing the total to over 1,112 megawatts (MW) of solar power. As an example, the Solana Generating Station, a 280 MW parabolic trough solar plant, when commissioned in 2013, was the largest parabolic trough plant in the world and the first U.S. solar plant with molten salt thermal energy storage.

India is world's 3rd largest consumer of electricity and world's 3rd largest renewable energy producer with 38% of energy capacity installed in the year 2020 coming from renewable sources. Ernst & Young's (EY) 2021 Renewable Energy Country Attractiveness Index (RECAI) ranked India 3rd behind USA and China. In November 2021, India had a renewable energy capacity of 150 GW consisting of solar, wind, small hydro power, bio-mass, large hydro, and nuclear. India has committed for a goal of 450 GW renewable energy capacity by 2030.

The energy sector in Hawaii has rapidly adopted solar power due to the high costs of electricity, and good solar resources, and has one of the highest per capita rates of solar power in the United States. Hawaii's imported energy costs, mostly for imported petroleum and coal, are three to four times higher than the mainland, so Hawaii has motivation to become one of the highest users of solar energy. Hawaii was the first state in the United States to reach grid parity for photovoltaics. Its tropical location provides abundant ambient energy.
The National Solar Mission is an initiative of the Government of India and State Governments to promote solar power. The mission is one of the several policies of the National Action Plan on Climate Change. The program was inaugurated as the Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission by former Prime Minister Manmohan Singh on 11 January 2010 with a target of 20 GW by 2022. This was later increased to 100 GW by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in the 2015 Union budget of India. India increased its utility solar power generation capacity by nearly 5 times from 2,650 MW on 26 May 2014 to 12,288.83 MW on 31 March 2017. The country added 9,362.65 MW in 2017–18, the highest of any year. The original target of 20 GW was surpassed in 2018, four years ahead of the 2022 deadline.

Solar power in Gujarat, a state of India, is a fast developing industry given that the large state is mostly arid. It was one of the first states to develop solar generation capacity in India.

A rooftop solar power system, or rooftop PV system, is a photovoltaic (PV) system that has its electricity-generating solar panels mounted on the rooftop of a residential or commercial building or structure. The various components of such a system include photovoltaic modules, mounting systems, cables, solar inverters and other electrical accessories.

A photovoltaic power station, also known as a solar park, solar farm, or solar power plant, is a large-scale grid-connected photovoltaic power system designed for the supply of merchant power. They are differentiated from most building-mounted and other decentralised solar power because they supply power at the utility level, rather than to a local user or users. The generic expression utility-scale solar is sometimes used to describe this type of project.

Solar power in Virginia on rooftops is estimated to be capable of providing 32.4% of electricity used in Virginia using 28,500 MW of solar panels. Installing solar panels provides a 6.8% return on investment in Virginia, and a 5 kW array would return a profit of $16,041 over its 25 year life.

Mahindra Susten Pvt. Ltd., formerly Mahindra EPC Services Pvt. Ltd. , is part of the USD 19 billion Mahindra Group. They are a portfolio company under the Cleantech arm of Mahindra Partners.

Vikram Solar Limited is an Indian company based in Kolkata, the largest solar module manufacturer in India with 2.5 GW module manufacturing capacity annually and the second-largest solar energy company in India by revenue. The company's primary business focus is manufacturing solar PV modules and also carries out engineering, procurement and construction services and operations & maintenance of solar power plants.
Jakson Group was established in the year 1947 as an electrical trading firm, today it is a diversified energy and Infrastructure company having expertise in Distributed Energy, Solar Solutions and Electrical EPC Solutions. Jakson is head quartered at Noida, Uttar Pradesh, India and has four state of the art manufacturing facilities for manufacturing of Generating Sets, Solar Modules and Battery Energy Storage Systems. The Company has more than 2500 persons working for the company and have a presence in India, SAARC, Middle East and African regions.

Adani Green Energy Limited (AGEL) is an Indian renewable energy company headquartered in Ahmedabad, Gujarat. It is owned by Indian conglomerate Adani Group. The company operates Kamuthi Solar Power Project, one of the largest solar photovoltaic plants in the world.