Related Research Articles

The AMX-13 is a French light tank produced from 1952 to 1987. It served with the French Army, as the Char 13t-75 Modèle 51, and was exported to more than 26 other nations. Named after its initial weight of 13 tonnes, and featuring a tough and reliable chassis, it was fitted with an oscillating turret built by GIAT Industries with revolver-type magazines, which were also used on the Austrian SK-105 Kürassier. Including prototypes and export versions, over a hundred variants exist, including self-propelled guns, anti-aircraft systems, APCs, and ATGM versions.

Société Anonyme des Anciens Etablissements Hotchkiss et Compagnie was a French arms and, in the 20th century, automobile manufacturer first established by United States gunsmith Benjamin B. Hotchkiss. He moved to France and set up a factory, first at Viviez near Rodez in 1867, manufacturing arms used by the French in the Franco-Prussian War of 1870, then moving at Saint-Denis near Paris in 1875. It was merged into and succeeded by Thomson-CSF, now Thales Group.

The Automitrailleuse de Reconnaissance Renault Modèle 1933 was a French light cavalry tank developed during the Interbellum and used in the Second World War.

The Automitrailleuse de Reconnaissance Renault Modèle 35 Type ZT was a French light tank developed during the Interbellum and used in the Second World War. It was not intended to reconnoitre and report as its name suggests but was a light armoured combat vehicle, mostly without a radio and used as a support tank for the mechanised infantry.

The Renault R35, an abbreviation of Char léger Modèle 1935 R or R 35, was a French light infantry tank of the Second World War.

The AMC 34 was a French tank originally built for the French Army's cavalry units. Its production was cut short, and the few vehicles produced were out of service by the time of the Battle of France in the Second World War.

The AMX-32 was a French main battle tank developed by AMX and APX in the late 1970s during the Cold War as an export tank to fit in a specific market niche of nations with smaller defence budgets. While six prototypes were built, it failed to garner interest for foreign sales.

The Hotchkiss H35 or Char léger modèle 1935 H was a French cavalry tank developed prior to World War II. Despite having been designed from 1933 as a rather slow but well-armoured light infantry support tank, the type was initially rejected by the French Infantry because it proved difficult to steer while driving cross-country, and was instead adopted in 1936 by the French Cavalry arm.

The MAC mle 1931 machine gun, was a machine gun used in French tanks of the World War II era, as well as in fortifications such as the Maginot line. It is also sometimes known as the JM Reibel, from Jumelage de mitrailleuses, or Reibel twin-mounted guns and really refers to the specialized twin-mounting frame used in JM cloche cupolas on the Maginot Line fortifications, while MAC mle 1931 refers specifically to the gun. The JM twin-mounts were the standard emplacement for the mle 1931 in fixed fortifications, while tanks and other AFVs received single guns.

The Renault UE Chenillette is a light tracked armoured carrier and prime mover produced by France between 1932 and 1940.

The FCM 36 or Char léger Modèle 1936 FCM, was a light infantry tank that was designed for the French Army prior to World War II. It had a crew of two and was equipped with a short 37mm main armament and a 7.5mm coaxial machine gun.
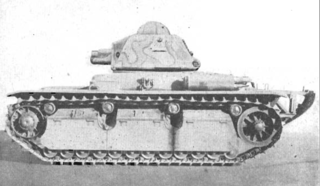
The Renault R40 or Char léger modèle 1935 R modifié 1939 was a French light infantry tank that was used early in World War II, an improvement of the Renault R35, of which it is often considered a variant.

The ARL 44 was a French heavy tank and tank destroyer, the development of which started just before the end of the Second World War. Only sixty of these tanks were ever completed, from 1949 onwards. The type proved to be unsatisfactory and only entered limited service. The tank was phased out in 1953.
The Char G1 was a French replacement project for the Char D2 medium tank. Several prototypes from different companies were developed from 1936 onwards, but not a single one had been fully completed at the time of the Fall of France in 1940. The projects represented some of the most advanced French tank design of the period and finally envisaged a type that would have been roughly equal in armament and mobility to later World War II standard tanks of other nations, such as the Soviet T-34 and the American M4 Sherman, but possessing several novel features, such as gun stabilisation, a semi-automatic loader and an optical rangefinder.

The 25 mm Hotchkiss anti-tank gun was a French anti-tank gun from the 1930s, built by the Hotchkiss arsenal, that saw service in the Spanish Civil War, the Second World War and the Indochina War.

The 47 mm APX anti-tank gun was a French anti-tank gun that saw service in the first years of the Second World War.

French development into tanks began during World War I as an effort to overcome the stalemate of trench warfare, and largely at the initiative of the manufacturers. The Schneider CA1 was the first tank produced by France, and 400 units were built. The French also experimented with various tank designs, such as the Frot-Laffly landship, Boirault machine and Souain experiment. Another 400 Saint-Chamond tanks were manufactured from April 1917 to July 1918 but they were underpowered and were of limited utility because the caterpillar tracks were too short for the tank's length and weight. The most significant French tank development during the war was the Renault FT light tank, which set the general layout for future tank designs and was used or redesigned by various military forces, including those of the United States.
The AMX 38 was a prototype French tank designed in 1937 at the AMX works. Designed as AMX's response to the 20-tonne tank programme intended to replace the aging Char D2, it was a faster and heavier alternative to Renault R35, in practice a cross-over between a light tank and medium tank.
The Ateliers de construction d'Issy-les-Moulineaux were born from the nationalization of the Renault factories in Issy-les-Moulineaux in 1936. They were specialized in the construction of armored vehicles for the French Army. The workshops were also known by the acronym AMX where A stands for Ateliers and MX stands for Moulineaux. Armored vehicles designed by Ateliers de construction d'Issy-les-Moulineaux had the acronym AMX in front of the name such as AMX-13, AMX-30.
References
- 1 2 "Atelier de construction de Puteaux. Hauts-de-Seine". data.bnf.fr (in French). data.bnf.fr. Retrieved 2 Feb 2020.
- ↑ "Saint-Ouen-la-Rouërie". histoirealasource (in French). histoirealasource. Retrieved 2 Feb 2020.
- ↑ "Le carré militaire de Puteaux" [The military square of Puteaux]. Souvenir Francais 92 (in French). Souvenir Francais 92. Retrieved 2 Feb 2020.
- ↑ Pasholok, Yuri. "AMX 38". yuripasholok.livejourna (in Russian). yuripasholok.livejourna. Retrieved 1 Feb 2020.