Related Research Articles

Amalaric was king of the Visigoths from 522 until his assassination. He was a son of king Alaric II and his first wife Theodegotha, daughter of Theoderic the Great.

Amalasuintha was a ruler of Ostrogothic Kingdom from 526 to 535. She ruled first as regent for her son Athalaric and thereafter as queen. Amalasuintha was highly educated and was praised by both Cassiodorus, and Procopius for her wisdom and her ability to speak three languages,.

The Ostrogoths were a Roman-era Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Gothic kingdoms within the Roman Empire, based upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century, having crossed the Lower Danube. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under the influence of the Amal dynasty, the family of Theodoric the Great.

Theodoricthe Great, also called Theodoric the Amal, was king of the Ostrogoths (475–526), and ruler of the independent Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy between 493 and 526, regent of the Visigoths (511–526), and a patrician of the Eastern Roman Empire. As ruler of the combined Gothic realms, Theodoric controlled an empire stretching from the Atlantic Ocean to the Adriatic Sea. Though Theodoric himself only used the title 'king' (rex), some scholars characterize him as a Western Roman Emperor in all but name, since he ruled large parts of the former Western Roman Empire, had received the former Western imperial regalia from Constantinople in 497, and was referred to by the title augustus by some of his subjects.
The 520s decade ran from January 1, 520, to December 31, 529.

Clovis was the first king of the Franks to unite all of the Frankish tribes under one ruler, changing the form of leadership from a group of petty kings to rule by a single king and ensuring that the kingship was passed down to his heirs. He is considered to have been the founder of the Merovingian dynasty, which ruled the Frankish kingdom for the next two centuries. Clovis is important in the historiography of France as "the first king of what would become France".

Theodoric is a Germanic given name. First attested as a Gothic name in the 5th century, it became widespread in the Germanic-speaking world, not least due to its most famous bearer, Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths.

Athalaric was the king of the Ostrogoths in Italy between 526 and 534. He was a son of Eutharic and Amalasuntha, the youngest daughter of Theoderic the Great, whom Athalaric succeeded as king in 526.

Chlothar I, sometime called "the Old", also anglicised as Clotaire, was a king of the Franks of the Merovingian dynasty and one of the four sons of Clovis I.
Foederati were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as foedus, with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the socii, but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign states, client kingdoms or barbarian tribes to which the empire provided benefits in exchange for military assistance. The term was also used, especially under the empire, for groups of "barbarian" mercenaries of various sizes who were typically allowed to settle within the empire.

The Battle of Tolbiac was fought between the Franks, who were fighting under Clovis I, and the Alamanni, whose leader is not known. The date of the battle has traditionally been given as 496, though other accounts suggest it may either have been fought earlier, in the 480s or early 490s, or later, in 506. The site of "Tolbiac", or "Tolbiacum", is usually given as Zülpich, North Rhine-Westphalia, about 60 km east of what is now the German-Belgian frontier. The Franks were successful at Tolbiac and established their dominance over the Alamanni.

Sigismund was King of the Burgundians from 516 until his death. He was the son of king Gundobad and Caretene. He succeeded his father in 516. Sigismund and his brother Godomar were defeated in battle by Clovis's sons, and Godomar fled. Sigismund was captured by Chlodomer, King of Orléans, where he was kept as a prisoner. Later he, his wife and his children were executed. Godomar then rallied the Burgundian army and won back his kingdom.
The Amali – also called Amals, Amalings or Amalungs – were a leading dynasty of the Goths, a Germanic people who confronted the Roman Empire during the decline of the Western Roman Empire. They eventually became the royal house of the Ostrogoths and founded the Ostrogothic Kingdom.

The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy, existed under the control of the Germanic Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
Theodemir or Thiudimer was king of the Ostrogoths of the Amal Dynasty, and father of Theoderic the Great. He had two "brothers" named Valamir and Videmir. Theodemir was Arian, while his wife Erelieva was Catholic and took the Roman Christian name Eusebia upon her baptism. In the beginning of Theodemir's reign, he ruled together with his brothers-in-law as vassals under Attila the Hun. Most likely settling for this arrangement after his older brother had only managed a rule lasting four years. He eventually consolidated the three Gothic regions in Pannonia under his rule after the death of Vidimir, and later inheriting the lands of the childless Valamir as well. He was married to Erelieva, with whom he had two children: Theoderic (454–526) and Amalafrida. When Theodemir died in 475, Theoderic succeeded him as king over a combined Ostrogothic kingdom.

Basina or Basine was remembered as a queen of Thuringia in the middle of the fifth century, by much later authors such as especially Gregory of Tours. However, because Gregory described her family's kingdom of Thuringia as being on the Gaulish or western side of the river Rhine, it is sometimes thought to be the Civitas Tungrorum, which is now Belgium.
Eutharic Cilliga was an Ostrogothic prince from Iberia who, during the early 6th century, served as Roman Consul and "son in weapons" alongside the Byzantine emperor Justin I. He was the son-in-law and presumptive heir of the Ostrogoth king Theoderic the Great but died in AD 522 at the age of 42 before he could inherit Theoderic's title. Theoderic claimed that Eutharic was a descendant of the Gothic royal house of Amali and it was intended that his marriage to Theoderic's daughter Amalasuintha would unite the Gothic kingdoms, establish Theoderic's dynasty and further strengthen the Gothic hold over Italy.
The Duchy of Thuringia was an eastern frontier march of the Merovingian kingdom of Austrasia, established about 631 by King Dagobert I after his troops had been defeated by the forces of the Slavic confederation of Samo at the Battle of Wogastisburg. It was recreated in the Carolingian Empire and its dukes were appointed by the king until it was absorbed by the Saxon dukes in 908. From about 1111/12 the territory was ruled by the Landgraves of Thuringia as Princes of the Holy Roman Empire. When Frederick IV, the last independent ruler of Thuringia died in 1440, the territory passed to his nephew, the saxon elector Frederick II.
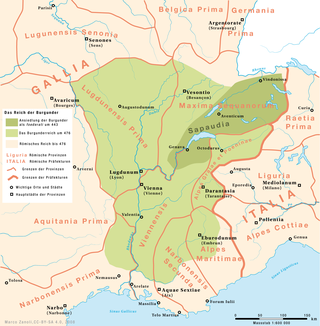
The Kingdom of the Burgundians or First Kingdom of Burgundy was established by Germanic Burgundians in the Rhineland and then in eastern Gaul in the 5th century.
Lantechildis was a Frankish noblewoman, the daughter of the Frankish king Childeric I (d. 481) and the Thuringian noblewoman Basina (d. 477). She was a sister of Clovis I. She is mentioned in Gregory of Tours and the Liber historiae Francorum.
References
- ↑ Previté-Orton, Charles William (1966). The Shorter Cambridge Medieval History. Cambridge University Press.
- 1 2 Deanesly, Margaret (1960). A History of Early Medieval Europe, 476-911. Methuen. p. 41.