Related Research Articles

The Bantu languages are a language family of about 600 languages that are spoken by the Bantu peoples of Central, Southern, Eastern and Southeast Africa. They form the largest branch of the Southern Bantoid languages.

Niger–Congo is a hypothetical language family spoken over the majority of sub-Saharan Africa. It unites the Mande languages, the Atlantic-Congo languages, and possibly several smaller groups of languages that are difficult to classify. If valid, Niger-Congo would be the world's largest in terms of member languages, the third-largest in terms of speakers, and Africa's largest in terms of geographical area. It is generally considered to be the world's largest language family in terms of the number of distinct languages, just ahead of Austronesian, although this is complicated by the ambiguity about what constitutes a distinct language; the number of named Niger–Congo languages listed by Ethnologue is 1,540.
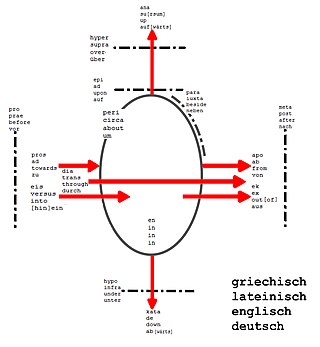
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix un- is added to the word happy, it creates the word unhappy. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.

Swahili, also known by its local name Kiswahili, is the native language of the Swahili people, who are found primarily in Kenya, Tanzania and Mozambique. It is a Bantu language, though Swahili has borrowed a number of words from foreign languages, particularly Arabic and Persian, but also words from Portuguese, English and German. Around forty percent of Swahili vocabulary consists of Arabic loanwords, including the name of the language. The loanwords date from the era of contact between Arab traders and the Bantu inhabitants of the east coast of Africa, which was also the time period when Swahili emerged as a lingua franca in the region. The number of Swahili speakers, be they native or second-language speakers, is estimated to be around 80 million.

Zulu, or isiZulu as an endonym, is a Southern Bantu language of the Nguni branch spoken in Southern Africa. It is the language of the Zulu people, with about 12 million native speakers, who primarily inhabit the province of KwaZulu-Natal of South Africa. Zulu is the most widely spoken home language in South Africa, and it is understood by over 50% of its population. It became one of South Africa's 11 official languages in 1994.
The Ganda language or Luganda is a Bantu language spoken in the African Great Lakes region. It is one of the major languages in Uganda and is spoken by more than 10 million Baganda and other people principally in central Uganda, including the capital Kampala of Uganda. Typologically, it is an agglutinative, tonal language with subject–verb–object word order and nominative–accusative morphosyntactic alignment.
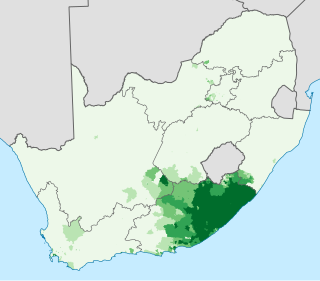
Xhosa, formerly spelled Xosa and also known by its local name isiXhosa, is a Nguni language and one of the official languages of South Africa and Zimbabwe. Xhosa is spoken as a first language by approximately 8.2 million people and as a second language by another 11 million, mostly in South Africa, particularly in Eastern Cape, Western Cape, Northern Cape and Gauteng, and also in parts of Zimbabwe and Lesotho. It has perhaps the heaviest functional load of click consonants in a Bantu language, with one count finding that 10% of basic vocabulary items contained a click.

The Swazi or siSwati language is a Bantu language of the Nguni group spoken in Eswatini and South Africa by the Swati people. The number of speakers is estimated to be in the region of 2.4 million. The language is taught in Eswatini and some South African schools in Mpumalanga, particularly former KaNgwane areas. Siswati is an official language of Eswatini, and is also one of the eleven official languages of South Africa.

Northern Ndebele, also called Ndebele, isiNdebele saseNyakatho, Zimbabwean Ndebele or North Ndebele, associated with the term Matabele, is a Bantu language spoken by the Northern Ndebele people which belongs to the Nguni group of languages.
Sesotho nouns signify concrete or abstract concepts in the language, but are distinct from the Sesotho pronouns.
Sesotho verbs are words in the language that signify the action or state of a substantive, and are brought into agreement with it using the subjectival concord. This definition excludes imperatives and infinitives, which are respectively interjectives and class 14 nouns.
The phonology of Sesotho and those of the other Sotho–Tswana languages are radically different from those of "older" or more "stereotypical" Bantu languages. Modern Sesotho in particular has very mixed origins inheriting many words and idioms from non-Sotho–Tswana languages.
This article presents a brief overview of the grammar of the Sesotho and provides links to more detailed articles.
Kwangali, or RuKwangali, is a Bantu language spoken by 85,000 people along the Kavango River in Namibia, where it is a national language, and in Angola. It is one of several Bantu languages of the Kavango which have click consonants; these are the dental clicks c and gc, along with prenasalization and aspiration.
Sukuma is a Bantu language of Tanzania, spoken in an area southeast of Lake Victoria between Mwanza, Shinyanga, and Lake Eyasi.
Zulu grammar is the way in which meanings are encoded into wordings in the Zulu language. Zulu grammar is typical for Bantu languages, bearing all the hallmarks of this language family. These include agglutinativity, a rich array of noun classes, extensive inflection for person, tense and aspect and a subject–verb–object word order.

Jita is a Bantu language of Tanzania, spoken on the southeastern shore of Lake Victoria/Nyanza and on the island of Ukerewe.
Ngurimi (Ngoreme) is a Bantu language of Tanzania. Ngoreme is spoken in the Serengeti District of the Mara Region of north-west Tanzania by some 55,000 people. There are two main dialects of Ngoreme - a northern dialect and a southern dialect - which maintain mutual intelligibility.
Proto-Bantu is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Bantu languages, a subgroup of the Southern Bantoid languages. It is thought to have originally been spoken in West/Central Africa in the area of what is now Cameroon. About 5,000 years ago, it split off from Proto-Southern Bantoid when the Bantu expansion began to the south and east. Two theories have been put forward about the way the languages expanded: one is that the Bantu-speaking people moved first to the Congo region and then a branch split off and moved to East Africa; the other is that the two groups split from the beginning, one moving to the Congo region, and the other to East Africa.
This article describes the grammar of the Old Irish language. The grammar of the language has been described with exhaustive detail by various authors, including Thurneysen, Binchy and Bergin, McCone, O'Connell, Stifter, among many others.