
Farmington is a town in Hartford County in the Farmington Valley area of central Connecticut in the United States. The town is part of the Capitol Planning Region. The population was 26,712 at the 2020 census. It sits 10 miles west of Hartford at the hub of major I-84 interchanges, 20 miles south of Bradley International Airport and two hours by car from New York City and Boston. It is home to the world headquarters of several large corporations including Otis Elevator Company, United Technologies, and Carvel. The northwestern section of Farmington is a suburban neighborhood called Unionville.

United States v. Schooner Amistad, 40 U.S. 518 (1841), was a United States Supreme Court case resulting from the rebellion of Africans on board the Spanish schooner La Amistad in 1839. It was an unusual freedom suit that involved international diplomacy as well as United States law. The historian Samuel Eliot Morison described it in 1969 as the most important court case involving slavery before being eclipsed by that of Dred Scott in 1857.
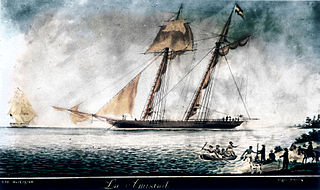
La Amistad was a 19th-century two-masted schooner owned by a Spaniard colonizing Cuba. It became renowned in July 1839 for a slave revolt by Mende captives who had been captured and sold to European slave traders and illegally transported by a Portuguese ship from West Africa to Cuba, in violation of European treaties against the Atlantic slave trade. Spanish plantation owners Don José Ruiz and Don Pedro Montes bought 53 captives in Havana, Cuba, including four children, and were transporting them on the ship to their plantations near Puerto Príncipe. The revolt began after the schooner's cook jokingly told the slaves that they were to be "killed, salted, and cooked." Sengbe Pieh unshackled himself and the others on the third day and started the revolt. They took control of the ship, killing the captain and the cook. Three Africans were also killed in the melee.

The Farmington Canal, also known as the New Haven and Northampton Canal, was a major private canal built in the early 19th century to provide water transportation from New Haven into the interior of Connecticut, Massachusetts and beyond. Its Massachusetts segment was known as the Hampshire and Hampden Canal. With the advent of railroads, it was quickly converted to a railroad in the mid-19th century and in recent years has been converted to a multi-use trail after being abandoned for years.

Hill–Stead Museum is a Colonial Revival house and art museum set on a large estate at 35 Mountain Road in Farmington, Connecticut. It is best known for its French Impressionist masterpieces, architecture, and stately grounds. The property was designated a National Historic Landmark as a nationally significant example of Colonial Revival architecture, built in 1901 to designs that were the result of a unique collaboration between Theodate Pope Riddle, one of the United States' first female architects, and the renowned firm of McKim, Mead & White. The house was built for Riddle's father, Alfred Atmore Pope, and the art collection it houses was collected by Pope and Riddle.

The William H. Seward House Museum is a historic house museum at 33 South Street in Auburn, New York. Built about 1816, the home of William H. Seward (1801–72), who served as a New York state senator, the governor of New York, a U.S. senator, a presidential candidate, and then Secretary of State under presidents Abraham Lincoln and Andrew Johnson. The house was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1964, and added to the National Register of Historic Places on October 15, 1966. It is now maintained by nonprofit organization as a museum dedicated to Seward's legacy.

The Farmington Historic District encompasses a 275-acre (111 ha) area of the town center of Farmington, Connecticut. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1972. The area roughly corresponds to the section of Route 10 between Route 4 and U.S. Route 6, and includes 115 buildings, primarily residences, built before 1835. The district includes several National Historic Landmarks, include Hill-Stead, the Austin F. Williams Carriagehouse and House, the First Church of Christ, Congregational, and the Stanley-Whitman House.

The First Church of Christ, Congregational, also known as First Church 1652 is a historic church at 75 Main Street in Farmington, Connecticut. Built in 1771, this Greek Revival church was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1975 for its role in sheltering the Amistad Africans before their return to Africa.

The Stanley-Whitman House is a historic house museum at 37 High Street in Farmington, Connecticut. Built ca 1720, it is one of the oldest houses in Farmington. A well-preserved saltbox with post-medieval construction features, it was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1960 and National Register of Historic Places when the registry opened in 1966.

The Reverend George B. Hitchcock House is a historic house museum in Cass County, Iowa, near the city of Lewis. Built in 1856 by the Congregationalist minister George B. Hitchcock, it has features indicative of its use as a "station" on the Underground Railway, corroborated by documentary evidence of Hitchcock's involvement in the shelter and transport of escaped slaves. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 2006. It now houses a museum.

The John Johnson House is a National Historic Landmark in the Germantown section of Philadelphia, significant for its role in the antislavery movement and the Underground Railroad. It is located at 6306 Germantown Avenue and is a contributing property of the Colonial Germantown Historic District, which is also a National Historic Landmark. It is operated today as a museum open to the public.

The F. Julius LeMoyne House is a historic house museum at 49 East Maiden Street in Washington, Pennsylvania. Built in 1812, it was the home of Dr. Francis Julius LeMoyne (1798–1897), an antislavery activist who used it as a stop on the Underground Railroad. LeMoyne also assisted in the education of freed slaves after the American Civil War, founding the historically black LeMoyne–Owen College in Memphis, Tennessee. His house, now operated as a museum by the local historical society, was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1997. It is designated as a historic public landmark by the Washington County History & Landmarks Foundation.

Rokeby Museum is a historic farm property and museum at 4334 United States Route 7 in Ferrisburgh, Vermont. The 90-acre (36 ha) property includes a 1780s farmstead, and eight agricultural outbuildings with permanent exhibits. Hiking trails cover more than 50 acres (20 ha) of the grounds. Rokeby is open from mid-May to mid-October each year. The property was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1997 for its association with Rowland T. Robinson, a Quaker and ardent abolitionist who openly sheltered escaped slaves at Rokeby as part of the Underground Railroad. Robinson's extensive correspondence is an essential archive giving insight into the practices of abolitionists and the operations of the railroad.

The William C. Nell House, now a private residence, was a boarding home located in 3 Smith Court in the Beacon Hill neighbourhood of Boston, Massachusetts, opposite the former African Meeting House, now the Museum of African American History.

Wilson Bruce Evans House is a historic house at 33 East Vine Street in Oberlin, Ohio. Completed in 1856, it served a major stop on the Underground Railroad, with its builders, Wilson Bruce Evans and Henry Evans, participating the 1858 Oberlin-Wellington Rescue, a celebrated rescue of a slave. It was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1997.

The Nathan and Mary (Polly) Johnson properties are a National Historic Landmark at 17–19 and 21 Seventh Street in New Bedford, Massachusetts. Originally the building consisted of two structures, one dating to the 1820s and an 1857 house joined with the older one shortly after construction. They have since been restored and now house the New Bedford Historical Society. The two properties are significant for their association with leading members of the abolitionist movement in Massachusetts, and as the only surviving residence in New Bedford of Frederick Douglass. Nathan and Polly Johnson were free African-Americans who are known to have sheltered escaped slaves using the Underground Railroad from 1822 on. Both were also successful in local business; Nathan as a caterer and Polly as a confectioner.

The John P. Parker House is a historic house museum at 300 North Front Street in Ripley, Ohio. It was home to former slave and inventor John P. Parker (1827–1900) from 1853 to his death in 1900. Parker was an abolitionist and a well-documented conductor on the Underground Railroad, helping hundreds of escaped slaves. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980, and it was further designated a National Historic Landmark in 1997. It is now owned and managed by a local nonprofit organization as a museum about Parker's life and the abolitionist movement.

The Mount Pleasant Historic District encompasses the historic center of the village of Mount Pleasant, Ohio. Founded in 1803 by anti-slavery Quakers, the village was an early center of abolitionist activity and a well-known haven for fugitive slaves on the Underground Railroad. The village center is relatively little altered since the antebellum period. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Districts in 1974, and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 2005.

White Horse Farm, also known as the Elijah F. Pennypacker House, is a historic home and farm located in Schuylkill Township, Chester County, Pennsylvania. The original section was built around 1770. In the 19th century, it was the home of abolitionist Elijah F. Pennypacker and served as a station on the Underground Railroad. The farm was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1987.





















