
The Rivulidae are a family of killifishes in the order Cyprinodontiformes. They are commonly known as rivulids, South American killifish or New World killifish. The latter names are slightly misleading, however, as they are neither restricted to South America, though most are in fact found there, nor are they the only killifishes from the Americas. Occasionally, they are still referred to as rivulines, a term dating back to when they were considered a subfamily of the Aplocheilidae.
Leptolebias marmoratus, the marbled pearlfish, annual tropical killifish or ginger pearlfish, is a species of killifish in the family Rivulidae. This threatened species is found in temporary channels within dense Atlantic rainforest, in the floodplains of rivers draining into the Baía de Guanabara, near the city of Rio de Janeiro in southeastern Brazil. It reaches up to 3 cm (1.2 in) in total length.

Leptolebias is a ray-finned fish genus of the killifish family Rivulidae. Like many of their relatives, they are rather ambiguously known as "pearlfish".

Rivulus is a genus of small freshwater fish in the Cyprinodontiformes family Rivulidae. It was traditionally considered to be the largest genus in its family; however, the genus's size is currently in dispute. Wilson J. E. Costa split this genus into several new genera in 2004 and 2011, leaving only a few Greater Antillean species in Rivulus itself. Despite being moved to other genera, some of the species retain the common name "rivulus", like the well-known mangrove rivulus. Shortly after the review by Costa, another review authored by J.H. Huber refuted the split, moving the proposed genera back in Rivulus and again making the genus the largest in the family Aplocheilidae.

Austrolebias is a genus of killifish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish live in temporary pools, swamps and streams in the Río de la Plata, Patos–Mirim and Mamoré basins in South America.
Llanolebias stellifer is a species of killifish in the family Rivulidae. It is endemic to the Llanos, a part of the Orinoco basin in Venezuela, where it lives in shallow temporary waters in forests. This annual killifish grows to a total length of 7.5 cm (3.0 in). It is the only known member of its genus, but it was formerly included in Rachovia.

Melanorivulus is a genus of South American freshwater fish in the family Rivulidae. Most species are endemic to the Río de la Plata, eastern Amazon, Tocantins–Araguaia and São Francisco basins in Brazil, but a few members of this genus range west into Bolivia, south into Paraguay and Argentina, and east to Parnaíba and Sergipe in northeastern Brazil. Only M. schuncki occurs north of the Amazon River. They inhabit shallow waters, generally 5–30 cm (2–12 in) deep, at the margins of streams in open or fairly open habitats like the Cerrado or Cerrado–Amazon transition. Many have tiny ranges and are seriously threatened.
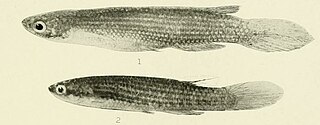
Anablepsoides is a genus of killifish in the family Rivulidae native to tropical South America and the Lesser Antilles. The majority are from the Amazon and Orinoco basins, as well as freshwater systems in the Guiana Shield, but a few species are from northern Venezuela, northeastern Brazil and the Lesser Antilles. Although largely restricted to lowlands, a few species occur in the lower East Andean foothills. They are mostly found in shallow fresh water swamps, streams, edges of rivers, ponds and pools, but a few may occur in brackish estuaries. They are able to jump over land and breathe air for short periods, allowing them to access isolated waters inhabited by few or no other fish. Several Anablepsoides species have small distributions and some are seriously threatened by habitat loss; the entire known range of A. xinguensis is in the area flooded by the Belo Monte Dam.
Atlantirivulus is a genus of fishes in the family Rivulidae. They are endemic to shallow swamps, creeks, streams and pools in the Atlantic Forest in southeastern Brazil, ranging from Rio de Janeiro to Santa Catarina. Several of the species are highly threatened, while others survive in well-protected reserves. A. janeiroensis was initially feared extinct, but has since been rediscovered in two reserves.

Laimosemion is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae from the Amazon basin and basins in the Guiana Shield in tropical South America. They mostly inhabit small streams, creeks, swamps and pools in lowlands, but locally occur to an altitude of 1,300 m (4,300 ft).

Moema is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish are mostly restricted to the Amazon basin in Bolivia, Brazil and Peru, but a few inhabit the upper Essequibo basin in Guyana, upper Orinoco basin in Venezuela and upper Paraguay basin in Brazil. They inhabit temporary waters, such as swamps or ponds, in primary forests. Once the water disappears, the adults die, but the eggs that have been laid in the bottom remain, only hatching after 3–10 months when the water returns. They rapidly reach adult size, but generally only live a few months after hatching, although captives can live longer.

Neofundulus is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish are endemic to the Paraguay, Guaporé, Mamoré and São Francisco basins in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay. They inhabit temporary waters, such as swamps or ponds, that typically are located in open habitats like grassland. Once the water disappears, the adults die, but the eggs that have been laid in the bottom remain, only hatching after several months when the water returns.
Papiliolebias is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish are endemic to seasonal pools in the Paraguay and upper Madeira river basins in northwestern Argentina, central and southeastern Bolivia, and western Paraguay.
Pterolebias is a genus of killifish from the family Rivulidae which are native to temporary swamps and ponds in South America. It includes two groups, which sometimes are regarded as separate genera: Pterolebias from the southern Amazon and Paraguay river basins, and Gnatholebias from the Orinoco river basin.
Rachovia is a genus of killifish from the family Rivulidae the species of which are endemic to the Orinoco, Maracaibo and Magdalena basins in Colombia and Venezuela, where they live in small temporary waters like ponds. They are small annual killifish that reach up to 6 cm (2.4 in) in total length. The name of this genus honours the German aquarist Arthur Rachow (1884–1960) who sent fish specimens to George S. Myers.
Renova oscari is a species of killifish from the family Rivulidae which is endemic to the Orinoco River basin of Venezuela. This annual killifish grows to a standard length of 4.7 cm (1.9 in). This species is the only known member of its genus. It is found in the aquarium trade. This species was described in 1995 by Jamie E. Thomerson and Donald Charles Taphorn Baechle with the type locality given as the southwestern edge of Isla Raton in the vicinity of the village of Sabanita, upper Río Orinoco. The specific name honours Oscar León Mata (1964-2018), a killifish collector, environmental engineer and curator of fish at Museo de Ciencias Naturales in Guanare.

Simpsonichthys is a genus of killifish from the family Rivulidae the species of which are endemic to temporary freshwater habitats like ponds in the upper Paraná, upper Araguaia, upper Jequitinhonha and São Francisco basins on the central Brazilian Plateau. They are small annual killifish that reach up to 5.5 cm (2.2 in) in standard length.
Trigonectes is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish are endemic to the Paraguay, upper Madeira and Tocantins basins in far northern Argentina, Bolivia, central Brazil and western Paraguay. They inhabit seasonal swamp, pools and similar habitats in open regions. Once the water disappears, the adults die, but the eggs that have been laid in the bottom remain, only hatching after several months when the water returns.
Xenurolebias is a genus of fish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish are endemic to temporary pools in the Atlantic forest near the coast in southeast Bahia and Espírito Santo, Brazil.

Spectrolebias is a genus of killifish in the family Rivulidae. These annual killifish are endemic to seasonal waters in the Paraguay, Tocantins–Araguaia, Xingu and Mamoré–Grande basins in Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay. Each species generally has a small distribution and some are seriously threatened by habitat loss; the entire known range of S. reticulatus is in the area flooded by the Belo Monte Dam.










