
The Ford Trimotor is an American three-engined transport aircraft. Production started in 1925 by the companies of Henry Ford and ended on June 7, 1933. A total of 199 Ford Trimotors were made. It was designed for the civil aviation market, but also saw service with military units.

The Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp is an aircraft engine of the reciprocating type that was widely used in American aircraft from the 1920s onward. It was the Pratt & Whitney aircraft company's first engine, and the first of the famed Wasp series. It was a single-row, nine-cylinder, air-cooled, radial design, and displaced 1,344 cubic inches (22 L); bore and stroke were both 5.75 in (146 mm). A total of 34,966 engines were produced.

The Pratt & Whitney R-1690 Hornet was a widely used American aircraft engine. Developed by Pratt & Whitney, 2,944 were produced from 1926 through 1942. It first flew in 1927. It was a single-row, 9-cylinder air-cooled radial design. Displacement was 1,690 cubic inches. It was built under license in Italy as the Fiat A.59. In Germany, the BMW 132 was a developed version of this engine. The R-1860 Hornet B was an enlarged version produced from 1929.

The Douglas Dolphin was an American amphibious flying boat. While only 58 were built, they served a wide variety of roles including private air yacht, airliner, military transport, and search and rescue.

The Bellanca Aircruiser and Airbus were high-wing, single-engine aircraft built by Bellanca Aircraft Corporation of New Castle, Delaware. The aircraft was built as a "workhorse" intended for use as a passenger or cargo aircraft. It was available with wheels, floats or skis. The aircraft was powered by either a Wright Cyclone or Pratt and Whitney Hornet engine. The Airbus and Aircruiser served as both commercial and military transports.

The Boeing 80 was an American airliner of the 1920s. A three-engined biplane, the Model 80 was built by the Boeing Airplane Company for Boeing's own airline, Boeing Air Transport, successfully carrying both airmail and passengers on scheduled services.

The Vought O2U Corsair was a 1920s biplane scout and observation aircraft. Made by Vought Corporation, the O2U was ordered by the United States Navy (USN) in 1927. Powered by a 400 hp (298 kW) Pratt & Whitney R-1340 Wasp engine, it incorporated a steel-tube fuselage structure and a wood wing structure with fabric covering. Many were seaplanes or amphibians.

The Fokker F-10 was an enlarged development of the Fokker F.VII airliner, built in the late 1920s by the Fokker Aircraft Corporation of America. It carried 12 passengers, four more than the F.VII, and had a larger wing and more powerful engines.

The Bellanca 31-40 Senior Pacemaker and its derivatives were a family of a six- and eight-seat utility aircraft built in the United States in the late 1930s. They were the final revision of the original late 1920s Wright-Bellanca WB-2 design. The model numbers used by Bellanca in this period reflected the wing area and engine horsepower, each divided by ten. Like their predecessors, these were high-wing braced monoplanes with conventional tailwheel undercarriage.

The Buhl AirSedan was a family of American civil cabin sesquiplane aircraft developed and manufactured by the Buhl Aircraft Company in the late 1920s. One example completed the first transcontinental non-stop roundtrip flight, made in 1929 by the CA-6 Spokane Sun-God, and the first Pope to have flown did so in a Buhl Airsedan.

The Consolidated Model 17 Fleetster was a 1920s American light transport monoplane aircraft built by the Consolidated Aircraft Corporation.

The Keystone LB-6 and LB-7 were 1920s American light bombers, built by the Keystone Aircraft company for the United States Army Air Corps, called Panther by the company, but adoption of the name was rejected by the U.S. Army.

The Fairchild Super 71 was a Canadian parasol-mounted high-wing monoplane cargo aircraft built by Fairchild Aircraft Ltd. (Canada). The Super 71 was an entirely new design that was one of the first purpose-built civilian bush planes for use in remote and northern locales in Canada.

The Stinson Detroiter was a six-seat cabin airliner for passengers or freight designed and built by the Stinson Aircraft Syndicate, later the Stinson Aircraft Corporation. Two distinct designs used the Detroiter name, a biplane and a monoplane.

The Spartan C4 is an American four-seat cabin monoplane designed and built by the Spartan Aircraft Company.

The Stearman 4 is an American commercial biplane that was manufactured in the 1920s by Stearman Aircraft. They were marketed at the time as fast and luxurious executive transports and mail planes for about US$16,000.

The Spartan C3 is an American three-seat open-cockpit utility biplane from the late 1920s.

The Hamilton H-45 and H-47 were six-passenger-seat, all-metal, high-wing monoplanes powered by single Pratt & Whitney radial engines. They were built for passenger and mail-carrying work in the US in the late 1920s.
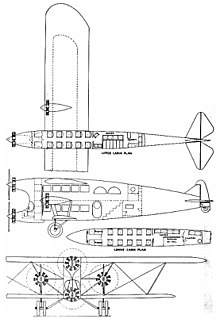
The Bach "Super Transport" was a design for a four-engined transport aircraft that was never built.

The Zenith Z-6 is a single engine biplane U.S. airliner built in the late 1920s. Its cabin, in the fuselage immediately behind its radial engine, holds five or six passengers depending on engine power. It is flown from an open cockpit further aft. Nine were completed and one has been restored to flight.





















