
Trolling is a method of fishing where one or more fishing lines, baited with lures or bait fish, are drawn through the water at a consistent, low speed. This may be behind a moving boat, or by slowly winding the line in when fishing from a static position, or even sweeping the line from side-to-side, e.g. when fishing from a jetty. Trolling is used to catch pelagic fish such as salmon, mackerel and kingfish.

Angling is a fishing technique that uses a fish hook attached to a fishing line to tether individual fish in the mouth. The fishing line is usually manipulated via a fishing rod, although rodless techniques such as handlining also exist. Modern angling rods are usually fitted with a fishing reel that functions as a cranking device for storing, retrieving and releasing out the line, although Tenkara fishing and traditional cane pole fishing are two rod-angling methods that do not use any reel. The fish hook itself can be additionally weighted with a denser tackle called a sinker, and is typically dressed with an appetizing bait to attract and entice the fish into swallowing the hook, but sometimes an inedible fake/imitation bait with multiple attached hooks is used instead of a single hook with edible bait. Some type of bite indicator, such as a float, a bell or a quiver tip, is often used to relay underwater status of the hook to the surface and alert the angler of a fish's presence.

A fisherman or fisher is someone who captures fish and other animals from a body of water, or gathers shellfish.
Hemiramphidae is a family of fishes that are commonly called halfbeaks, spipe fish or spipefish. They are a geographically widespread and numerically abundant family of epipelagic fish inhabiting warm waters around the world. The halfbeaks are named for their distinctive jaws, in which the lower jaws are significantly longer than the upper jaws. The similar viviparous halfbeaks have often been included in this family.

Big-game fishing, also known as offshore sportfishing, offshore gamefishing or blue-water fishing, is a form of recreational fishing targeting large game fish, usually on a large body of water such as a sea or ocean.

Recreational fishing, also called sport fishing or game fishing, is fishing for leisure, exercise or competition. It can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is professional fishing for profit; or subsistence fishing, which is fishing for survival and livelihood.
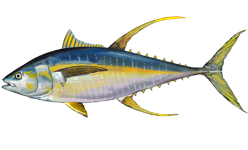
The yellowfin tuna, also known as the Albacore tuna, is a species of tuna found in pelagic waters of tropical and subtropical oceans worldwide.

Pelagic fish live in the pelagic zone of ocean or lake waters—being neither close to the bottom nor near the shore—in contrast with demersal fish that live on or near the bottom, and reef fish that are associated with coral reefs.

A fish aggregatingdevice (FAD) is a man-made object used to attract pelagic fish such as marlin, tuna and mahi-mahi. They usually consist of buoys or floats tethered to the ocean floor. Various types of FADs have been employed in the traditional fishing cultures of Island Southeast Asia, Japan, and Malta for centuries. Modern FADs are increasingly being used in modern commercial and sport fishing.

Marlin fishing or billfishing is offshore saltwater game fishing targeting several species of fast-swimming pelagic predatory fish with elongated rostrum collectively known as billfish, which include those from the families Istiophoridae and Xiphiidae (swordfish). It is considered by some fishermen to be a pinnacle of big-game fishing, due to the size, speed and power of the billfish and their relative elusiveness.

The environmental impact of fishing includes issues such as the availability of fish, overfishing, fisheries, and fisheries management; as well as the impact of industrial fishing on other elements of the environment, such as bycatch. These issues are part of marine conservation, and are addressed in fisheries science programs. According to a 2019 FAO report, global production of fish, crustaceans, molluscs and other aquatic animals has continued to grow and reached 172.6 million tonnes in 2017, with an increase of 4.1 percent compared with 2016. There is a growing gap between the supply of fish and demand, due in part to world population growth.

The little tunny, also known as the false albacore, little tuna, bonita, or erroneously as the blue bonito, is a species of tuna in the family Scombridae. It can be found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean and Black seas; in the western Atlantic, it ranges from Brazil to the New England states. The little tunny is a pelagic fish that can be found regularly in both offshore and inshore waters, and it is classified as a highly migratory species. The little tunny is best identified by the "worm-like" markings on its back and the dark spots appearing between its pectoral and ventral fins.
This page is a list of fishing topics.
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.
Land-based game fishing is a form of big-game sport fishing in which anglers attempt to catch oceanic game fish from shore rather than from ocean-going boats. The locations for such activities are generally rock platforms, though wharfs, jetties and beaches are also common. Some species such as sharks can be targeted in shallow littoral water, however most other species prefer deeper pelagic water, and this limits the areas where these types can be fished from the shore. Tackle used is usually comparable to that used on boats, but some differences are necessary, such as changes in rod length. Different tackle is used according to location and species targeted.

Forage fish, also called prey fish or bait fish, are small pelagic fish that feed on planktons and other small aquatic organisms. They are in turn preyed upon by various predators including larger fish, seabirds and marine mammals, this making them keystone species in their aquatic ecosystems.

The fishing industry in the Maldives is the island's second main industry. According to national tradition in the words of former President Maumoon Abdul Gayoom, "Fishing is the lifeblood of our nation, it is inborn. From the soil on which we live, to the sea around us, it remains an integral part of our existence. Fishing, and our country and its people, [are] one and shall remain inseparable forever." The Maldives has an abundance of aquatic life and species of fish. Common are tuna, groupers, dolphin fish, barracuda, rainbow runner, trevally and squirrelfish and many more. Aside from being of essential importance to the economy, fishing is also a popular recreational activity in the Maldives, not only among locals but by tourists. The islands have numerous fishing resorts which cater for these activities.

Fishing down the food web is the process whereby fisheries in a given ecosystem, "having depleted the large predatory fish on top of the food web, turn to increasingly smaller species, finally ending up with previously spurned small fish and invertebrates".

A bait ball, or baitball, occurs when small fish swarm in a tightly packed spherical formation about a common centre. It is a last-ditch defensive measure adopted by small schooling fish when they are threatened by predators. Small schooling fish are eaten by many types of predators, and for this reason they are called bait fish or forage fish.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to fish:


















