
Hetepheres II was a Queen of Ancient Egypt during the 4th Dynasty.

Djedefre was an ancient Egyptian king (pharaoh) of the 4th Dynasty during the Old Kingdom. He is well known by the Hellenized form of his name Rhatoisēs (Ῥατοίσης) by Manetho. Djedefre was the son and immediate throne successor of Khufu, the builder of the Great Pyramid of Giza; his mother is not known for certain. He is the king who introduced the royal title Sa-Rê and the first to connect his cartouche name with the sun god Ra.
Hetepheres is the name of several queens, princesses and noble women from the Fourth dynasty of Egypt.

Huni was an ancient Egyptian king and the last pharaoh of the Third Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom period. Following the Turin king list, he is commonly credited with a reign of 24 years, ending c. 2613 BC.

Khaba was a pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, active during the 3rd Dynasty of the Old Kingdom period. The exact time during which Khaba ruled is unknown but may have been around 2670 BC, and almost definitely towards the end of the dynasty.

Zawyet El Aryan is a town in the Giza Governorate, located between Giza and Abusir. To the west of the town, just in the desert area, is a necropolis, referred to by the same name. Almost directly east across the Nile is Memphis. In Zawyet El Aryan, there are two pyramid complexes and five mastaba cemeteries.

The Layer Pyramid is a ruined step pyramid dating to the 3rd Dynasty of Egypt and located in the necropolis of Zawyet El Aryan. Its ownership is uncertain and may be attributable to pharaoh Khaba. The pyramid architecture, however, is very similar to that of the Buried Pyramid of king Sekhemkhet and for this reason is firmly datable to the 3rd Dynasty.

Hetepheres I was a queen of Egypt during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt who was a wife of one king, the mother of the next king, the grandmother of two more kings, and the figure who tied together two dynasties.

Nebka is the throne name of an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of the Third Dynasty during the Old Kingdom period, in the 27th century BCE. He is thought to be identical with the Hellenized name Νεχέρωχις recorded by the Egyptian priest Manetho of the much later Ptolemaic period.

Prince Ankhhaf was an Egyptian prince and served as an overseer during the reign of the Pharaoh Khufu, who is thought to have been Ankhhaf's half-brother. One of Ankhaf's titles is also as a Vizier, but it is unknown which pharaoh he would have held this title under. He lived during Egypt's 4th Dynasty.
Minkhaf I was an ancient Egyptian prince of the 4th Dynasty. He was a son of Pharaoh Khufu, half-brother of Pharaoh Djedefre and elder brother of Pharaoh Khafre. His mother may have been Queen Henutsen. Minkhaf had a wife and at least one son, but their names are not known. Minkhaf served as vizier possibly under Khufu or Khafre.
Meritites I was an ancient Egyptian queen of the 4th Dynasty. Her name means "Beloved of her Father". Several of her titles are known from a stela found at Giza. She was buried in the middle Queen’s Pyramid in Giza.
Djedefhor or Hordjedef was a noble Egyptian of the 4th Dynasty. He was the son of Pharaoh Khufu and his name means "Enduring Like Horus".

Kawab is the name of an ancient Egyptian prince of the 4th Dynasty. He was the eldest son of King Khufu and Queen Meritites I. Kawab served as vizier and was buried in the double mastaba G 7110–7120 in the east field which is part of the Giza Necropolis.
Khentetka or Khentetenka was a Queen of Egypt; the wife of King Djedefre during the 4th Dynasty.

Meresankh II was a Queen of Egypt who lived during 4th Dynasty.

The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis.

Bikheris is the Hellenized name of an ancient Egyptian pharaoh, who may have ruled during the 4th Dynasty around 2570 BC. Next to nothing is known about this ruler and some Egyptologists even believe him to be fictitious.
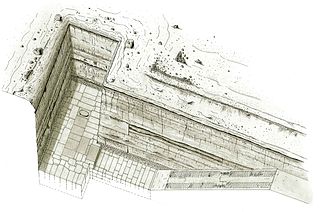
The Unfinished Northern Pyramid of Zawyet El Aryan, also known as Pyramid of Baka and Pyramid of Bikheris is the term archaeologists and Egyptologists use to describe a large shaft part of an unfinished pyramid at Zawyet El Aryan in Egypt. Archaeologists are generally of the opinion that it belongs to the early or the mid-4th Dynasty during the Old Kingdom period. The pyramid owner is not known for certain and most Egyptologists, such as Miroslav Verner, think it should be a king known under his hellenized name, Bikheris, perhaps from the Egyptian Baka. On the contrary, Wolfgang Helck and other egyptologists doubt this attribution.

Setka is the name of an ancient Egyptian crown prince. He is known for his statuette in the shape of a seated scribe. He is also the subject of a theory that claims he was pharaoh of Egypt for a very short time.














