Baptists form a major branch of evangelical Protestantism distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers, and doing so by complete immersion. Baptist churches also generally subscribe to the doctrines of soul competency, sola fide, sola scriptura and congregationalist church government. Baptists generally recognize two ordinances: baptism and communion.

The Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) is a mainline Protestant Christian denomination in the United States and Canada. The denomination started with the Restoration Movement during the Second Great Awakening, first existing during the 19th century as a loose association of churches working towards Christian unity, then slowly forming quasi-denominational structures through missionary societies, regional associations, and an international convention. In 1968, the Disciples of Christ officially adopted a denominational structure at which time a group of churches left to remain nondenominational.

The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC), alternatively the Great Commission Baptists (GCB), is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. In 1845 the Southern Baptists separated from the Triennial Convention in order to support slavery, which the southern churches regarded as "an institution of heaven". During the 19th and most of the 20th century, it played a central role in Southern racial attitudes, supporting racial segregation and the Lost Cause of the Confederacy while opposing interracial marriage. In 1995, the organization apologized for its history. Since the 1940s, it has spread across the United States, having member churches across the country and 41 affiliated state conventions.

The American Baptist Churches USA (ABCUSA) is a Baptist Christian denomination established in 1907 originally as the Northern Baptist Convention, and from 1950 to 1972 as the American Baptist Convention. It traces its history to the First Baptist Church in America (1638) and the Baptist congregational associations which organized the Triennial Convention in 1814.
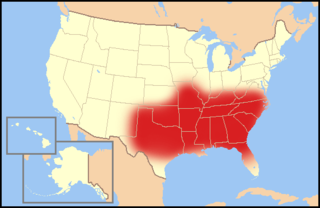
The Bible Belt is a region of the Southern United States and one Midwestern state, the state of Missouri, in all of which socially conservative Protestant Christianity plays a strong role in society. Church attendance across the denominations is generally higher than the nation's average. The region contrasts with the religiously diverse Midwest and Great Lakes, and the Mormon corridor in Utah and southern Idaho.
The American Baptist Association (ABA) is an Independent Baptist Christian denomination in the United States. The headquarters is in Texarkana, Texas. The principal founder was Ben M. Bogard, a pastor of Antioch Missionary Baptist Church in Little Rock, Arkansas. ABA headquarters, including its bookstore and publishing house, Bogard Press, is based in Texarkana, Texas.
Two-Seed-in-the-Spirit Predestinarian Baptists are part of a larger sub-group of Baptists that is commonly referred to as "anti-mission" Baptists. This sub-group includes the Duck River and Kindred Baptists, Old Regular Baptists, some Regular Baptists and some United Baptists. Only a minuscule minority of Primitive Baptists adhere to the Two-Seed doctrine. The primary centers of Two-Seedism were in Northern Alabama, Arkansas, Eastern Tennessee, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Indiana, and Texas. As of 2002, five churches or congregations of this faith and order still existed in Alabama, Indiana, Tennessee, and Texas.
The National Association of Free Will Baptists (NAFWB) is a national body of Free Will Baptist churches in the United States and Canada, organized on November 5, 1935 in Nashville, Tennessee. The Association traces its history in the United States through two different lines: one beginning in the South in 1727 and another in the North in 1780. The "Palmer line," however, never developed as a formal denomination. It consisted of only about three churches in North Carolina. The NAFWB is the largest of the Free Will Baptist denominations.

The Baptist General Convention of Texas (BGCT), more commonly known as the Texas Baptists, is a Baptist Christian denomination in the U.S. state of Texas. It is affiliated with the Southern Baptist Convention and the Baptist World Alliance. Texas Baptist offices are located in the city of Dallas, though convention staff are located across the state. According to a denomination census released in 2023, it claimed 2,038,53 members and 5,375 churches

The National Baptist Convention of America International, Inc., more commonly known as the National Baptist Convention of America or sometimes the Boyd Convention, is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is a predominantly African-American Baptist denomination, and is headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky. The National Baptist Convention of America has members in the United States, Canada, the Caribbean, and Africa. The current president of the National Baptist Convention of America is Dr. Samuel C. Tolbert Jr. of Lake Charles, Louisiana.
{{Infobox Christian denomination | icon = | icon_width = | icon_alt = | name = The Samavesam of Telugu Baptist Churches | native_name = | native_name_lang = | image = | image width = | alt = | caption = | abbreviation = STBC | type = | main_classification = Protestant | orientation = Evangelical | scripture = Bible | theology = | polity =Congregational | governance = General Council | leader_title = President | leader_name = Chilaka Nissi Praneeth | leader_title1 = Add General Secretary | leader_name1 = C.D.Prakash Rao | leader_title2 = Associate Secretary | leader_name2 = G.Joseph | leader_title3 = Director for Evangelism | leader_name3 = Rev.J.Vijay Kumar | fellowships_type = | fellowships = | fellowships_type1 = | fellowships1 = | division_type = | division = | division_type1 = | division1 = | division_type2 = | division2 = | division_type3 = | division3 = | associations = | area = Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and [[Telangana][SPl GPA Holder Rajkumar Rodricks from Telangana to protect Missionary Properties]] | language =Telugu | headquarters = Markapuram | origin_link = | founder = American Baptist Foreign Mission Society | founded_date = | founded_place = | separated_from = | parent = | merger = | absorbed = | separations = | merged_into = | defunct = | congregations_type = | congregations = | members = 740,000 | ministers_type = | ministers = | missionaries = | churches =830 | hospitals = | nursing_homes = | aid = | primary_schools = 14 | secondary_schools = 14 | tax_status = | tertiary = | other_names = | publications = | website = | slogan = | logo = | footnotes = }}
Landmarkism is a Baptist ecclesiology that emerged in the mid-19th century in the American South. It upholds the perpetuity theory of Baptist origins, which asserts an unbroken continuity and exclusive legitimacy of the Baptist movement since the apostolic period. Landmarkists hold a firm belief in the exclusive validity of Baptist churches and view non-Baptist liturgical forms and practices as invalid. This perspective caused significant controversy and division within the Baptist community, leading to intense debates and numerous schisms.
Approximately 15.3% of Americans identify as Baptist, making Baptists the second-largest religious group in the United States, after Roman Catholics. Baptists adhere to a congregationalist structure, so local church congregations are generally self-regulating and autonomous, meaning that their broadly Christian religious beliefs can and do vary. Baptists make up a significant portion of evangelicals in the United States and approximately one third of all Protestants in the United States. Divisions among Baptists have resulted in numerous Baptist bodies, some with long histories and others more recently organized. There are also many Baptists operating independently or practicing their faith in entirely independent congregations.
The American Baptist Home Mission Society is a Christian missionary society. Its main predecessor the Home Mission Society was established in New York City in 1832 to operate in the American frontier, with the stated mission "to preach the Gospel, establish churches and give support and ministry to the unchurched and destitute." In the 19th century, the Society was related to the Triennial Convention of Baptists. Today it is part of that Convention's successor, the American Baptist Churches, USA, and is the successor by merger of several 19th century Baptist organizations related to missions and education, including publications (1824), women (1877), and education (1888)

The Assemblies of God USA (AG), officially The General Council of the Assemblies of God, is a Pentecostal Christian denomination in the United States founded in 1914 during a meeting of Pentecostal ministers at Hot Springs, Arkansas, who came from a variety of independent churches and networks of churches. The Assemblies of God is a Finished Work Pentecostal denomination and is the U.S. branch of the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, the world's largest Pentecostal body. With a constituency of 2,928,143 in 2022, the Assemblies of God was the ninth largest Christian denomination and the second largest Pentecostal denomination in the United States.

Missionary Baptists are a group of Baptists that grew out of the missionary / anti-missionary controversy that divided Baptists in the United States in the early part of the 19th century, with Missionary Baptists following the pro-missions movement position. Those who opposed the innovations became known as anti-missions or Primitive Baptists. Since arising in the 19th century, the influence of Primitive Baptists waned as "Missionary Baptists became the mainstream". Missionary Baptists do not constitute a distinct denomination, and many affiliate with the Southern Baptist Convention.
Doss Nathan Jackson was a Baptist pastor from the United States who was fundamental in the founding of the North American Baptist Association. He was a debater and conference speaker, publisher and a prolific writer of Christian literature and theological works including Studies in Baptist Doctrine and History.

The Baptist Missionary Association Theological Seminary is an institution in Jacksonville, Texas, owned and operated by the Baptist Missionary Association of America. It is located off Texas State Highway 135 on the northeast side of Jacksonville.
The Council of Baptist Churches in Northeast India is a Baptist Christian denomination in North East India. It is a member of the Asia Pacific Baptist Federation. It is also a member body of the North East India Christian Council, the regional council of the National Council of Churches in India. Its presently led by Mr. Norbu Lama as President and Rev. Prof. Akheto Sema as General Secretary.

The National Baptist Convention, USA, Inc., more commonly known as the National Baptist Convention, is a Baptist Christian denomination headquartered at the Baptist World Center in Nashville, Tennessee and affiliated with the Baptist World Alliance. It is also the largest predominantly and traditionally African American church in the United States and the second largest Baptist denomination in the world.










