
The 3rd century BC started the first day of 300 BC and ended the last day of 201 BC. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period.

This article concerns the period 309 BC – 300 BC.
During the 290s BC, Hellenistic civilization begins its emergence throughout the successor states of the former Argead Macedonian Empire of Alexander the Great, resulting in the diffusion of Greek culture throughout the Levant and advances in science, mathematics, philosophy, etc. Meanwhile, the Roman Republic is embroiled in war against the Samnites, the Mauryan Empire continues to thrive in Ancient India, and the Kingdom of Qin in Ancient China, the one which in the future will conquer its adversaries and unite China, begins to emerge as a significant power during the Warring States period.

Year 298 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Barbatus and Centumalus. The denomination 298 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Osci were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the language of the Samnites was called Oscan, the Samnites were never referred to as Osci, nor were the Osci called Samnites.

The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanians.

The Social War, also called the Italian War or the Marsic War, was fought from 91 to 87 BC between the Roman Republic and several of its autonomous allies in Italy. The Italian allies wanted Roman citizenship, not only for the status and influence that came with it, but also for the right to vote in Roman elections and laws. They believed that they should be treated equally to the Romans, given that they had formed cultural and linguistic connections with the Roman civilization, and had been their loyal allies for over two centuries. The Romans strongly opposed their demands, and refused to grant them citizenship, thus leaving the socii with fewer rights and privileges.
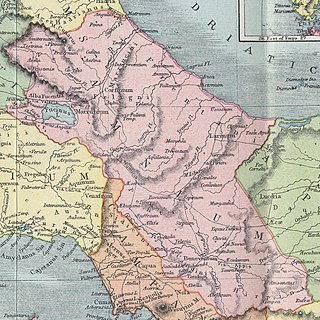
Samnium is a Latin exonym for a region of Southern Italy anciently inhabited by the Samnites. Their own endonyms were Safinim for the country and Safineis for the people. The language of these endonyms and of the population was the Oscan language. However, not all the Samnites spoke Oscan, and not all the Oscan-speakers lived in Samnium.
From its origin as a city-state on the peninsula of Italy in the 8th century BC, to its rise as an empire covering much of Southern Europe, Western Europe, Near East and North Africa to its fall in the 5th century AD, the political history of Ancient Rome was closely entwined with its military history. The core of the campaign history of the Roman military is an aggregate of different accounts of the Roman military's land battles, from its initial defense against and subsequent conquest of the city's hilltop neighbors on the Italian peninsula, to the ultimate struggle of the Western Roman Empire for its existence against invading Huns, Vandals and Germanic tribes. These accounts were written by various authors throughout and after the history of the Empire. Following the First Punic War, naval battles were less significant than land battles to the military history of Rome due to its encompassment of lands of the periphery and its unchallenged dominance of the Mediterranean Sea.

The Samnites were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium in south-central Italy. They became involved in several wars with the Roman Republic until the 1st century BC. An Oscan-speaking people, the Samnites probably originated as an offshoot of the Sabines. The Samnites formed a confederation, consisting of four tribes: the Hirpini, Caudini, Caraceni, and Pentri. They allied with Rome against the Gauls in 354 BC, but later became enemies of the Romans and were soon involved in a series of three wars against the Romans. Despite an overwhelming victory over the Romans at the Battle of the Caudine Forks, the Samnites were eventually subjugated. Although severely weakened, the Samnites later helped Pyrrhus and some went over to Hannibal in their wars against Rome. They also fought from 91 BC in the Social War and later in the civil war as allies of the Roman consuls Papirius Carbo and Gaius Marius against Sulla, who defeated them and their leader Pontius Telesinus at the Battle of the Colline Gate. They were eventually assimilated by the Romans, and ceased to exist as distinct people.
The Battle of Sentinum was the decisive battle of the Third Samnite War, fought in 295 BC near Sentinum, in which the Romans overcame a formidable coalition of Samnites, Etruscans, and Umbrians and Senone Gauls. The Romans won a decisive victory that broke up the tribal coalition and paved the way for the Romans' complete victory over the Samnites. The Romans involved in the battle of Sentinum were commanded by consuls Publius Decius Mus and Quintus Fabius Maximus Rullianus.
The Pentri were a tribe of the Samnites, and apparently one of the most important of the subdivisions of that nation. According to Salmon, their name comes from the Celtic pen- <peak>. Their capital city was Bovianum Undecumanorum, modern Bojano, in the very heart of the Samnite territory, and it is therefore probable that they occupied the whole of that rugged and mountainous district which extends from the frontiers of Latium, in the valley of the Liris, to those of the Frentani, towards the Adriatic Sea. But it is impossible to determine their exact limits, or to separate their history from that of the remaining Samnites. It is probable, indeed, that, throughout the long wars of the Romans with the Samnites, the Pentri were the leading tribe of the latter people, and always took part in the war, whether specified or not. The only occasion when we hear of their separating themselves from the rest of their countrymen, is during the Second Punic War, when we are told that all the other Samnites, except the Pentri, declared in favour of Hannibal after the battle of Cannae, 216 BC. This is the last occasion on which we find their name in history; all trace of the distinction between them and the other Samnites seems to have been subsequently lost, and their name is not even mentioned by Strabo or Pliny.
Quintus Poppaedius Silo was a leader of the Italian tribe of the Marsi and one of the leaders of the Italian rebels during the Social War against Rome. Poppaedius was called the 'heart and soul' of the rebellion. He was a friend of Marcus Livius Drusus the Younger.

Gaius Papius Mutilus was a Samnite noble who is best known for being the leader of the southern rebels who fought against the army of Rome in the Social War of 91-88 BC ; was member of the clan Variani/Varriano. His father was Gaius Papius Mutilus, who held the highest Samnite magistracy in Bovianum a number of times in the second half of the 2nd century BC

The socii or foederati were confederates of Rome and formed one of the three legal denominations in Roman Italy (Italia) along with the Roman citizens (Cives) and the Latini. The Latini, who were simultaneously special confederates and semi-citizens, should not be equated with the homonymous Italic people of which Rome was part. This tripartite organisation lasted from the Roman expansion in Italy to the Social War, when all peninsular inhabitants were awarded Roman citizenship.

The Roman expansion in Italy covers a series of conflicts in which Rome grew from being a small Italian city-state to be the ruler of the Italian peninsula. Roman tradition attributes to the Roman kings the first war against the Sabines and the first conquests around the Alban Hills and down to the coast of Latium. The birth of the Roman Republic after the overthrow of the Etruscan monarch of Rome in 509 BC began a series of major wars between the Romans and the Etruscans. In 390 BC, Gauls from the north of Italy sacked Rome. In the second half of the 4th century BC Rome clashed repeatedly with the Samnites, a powerful tribal coalition of the Apennine region. By the end of these wars, Rome had become the most powerful state in central Italy and began to expand to the north and to the south. The last threat to Roman hegemony came during the Pyrrhic war (280-275) when Tarentum enlisted the aid of the Greek king Pyrrhus of Epirus to campaign in the South of Italy. Resistance in Etruria was finally crushed in 265-264, the same year the First Punic War began and brought Roman forces outside of the peninsula for the first time.

Lucius Postumius Megellus was a politician and general during the middle years of the Roman Republic. Reportedly an arrogant and overbearing man, he was elected consul in 305 BC. The Second Samnite War was ongoing, and as consul he led troops against the Samnites. He defeated them at the Battle of Bovianum and took the town of Bovianum, which caused the Samnites to sue for peace, ending the war. Megellus was awarded a triumph.

Gnaeus Fulvius Maximus Centumalus was a military commander and politician from the middle period of the Roman Republic, who became consul in 298 BC. He fought in the final wars against the Etruscans and later led armies in the Third Samnite War. He was appointed dictator in 263 BC with responsibility for overseeing the start of the Roman ship building effort in the First Punic War.
Statius Gellius was a Samnite general who fought against the Romans, in the Second Samnite War. He was defeated and taken prisoner in 305 BC, at the Battle of Bovianum.
Gaius Sulpicius Longus was an accomplished general and statesman of the Roman Republic who served as Consul thrice and dictator once during his career, triumphing once over the Samnites and achieving great political success.










