Related Research Articles

Francis II was King of France from 1559 to 1560. He was also King of Scotland as the husband of Mary, Queen of Scots, from 1558 until his death in 1560.

The French Wars of Religion were a series of civil wars between French Catholics and Protestants from 1562 to 1598. Between two and four million people died from violence, famine or disease directly caused by the conflict, and it severely damaged the power of the French monarchy. One of its most notorious episodes was the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572. The fighting ended with a compromise in 1598, when Henry of Navarre, who had converted to Catholicism in 1593, was proclaimed King Henry IV of France and issued the Edict of Nantes, which granted substantial rights and freedoms to the Huguenots. However, Catholics continued to disapprove of Protestants and of Henry, and his assassination in 1610 triggered a fresh round of Huguenot rebellions in the 1620s.

The House of Guise was a prominent French noble family that was involved heavily in the French Wars of Religion. The House of Guise was the founding house of the Principality of Joinville.

Henri I de Lorraine, Duke of Guise, Prince of Joinville, Count of Eu, sometimes called Le Balafré ('Scarface'), was the eldest son of François, Duke of Guise, and Anna d'Este. His maternal grandparents were Ercole II d'Este, Duke of Ferrara, and Renée of France. Through his maternal grandfather, he was a descendant of Lucrezia Borgia and Pope Alexander VI.

Louis de Bourbon, 1st Prince of Condé was a prominent Huguenot leader and general, the founder of the Condé branch of the House of Bourbon. Coming from a position of relative political unimportance during the reign of Henri II, Condé's support for the Huguenots, along with his leading role in the conspiracy of Amboise and its aftermath, pushed him to the centre of French politics. Arrested during the reign of Francis II then released upon the latter's premature death, he would lead the Huguenot forces in the first three civil wars of the French Wars of Religion before being executed after his defeat at the Battle of Jarnac in 1569.

The Amboise conspiracy, also called Tumult of Amboise, was a failed attempt by a Huguenot faction in France to gain control over the young King Francis II and to reverse the policies of the current administration of Francis, Duke of Guise and Charles, Cardinal of Lorraine through their arrest, and potentially execution. Malcontent factions of Huguenots had been chafing under the French crown since the reign of Henry II and with the arrival of a new young king, saw their chance to take power for themselves. However the plot was uncovered ahead of time, and the Guise were ready for them. As such hundreds would be arrested, and many killed. Louis I, Prince of Condé was suspected of involvement, however he was able to flee south, and it was only after some months that the Guise were able to put him on trial. Shortly thereafter, the sickly Francis II died, their hold on the administration collapsed, and with it the conviction of Condé. This tumult would be one of the key steps in the collapse of crown authority that led to the first French War of Religion.

Jacques de Savoie, duc de Nemours was a French military commander, governor and Prince Étranger. Having inherited his titles at a young age, Nemours fought for king Henri II during the latter Italian Wars, seeing action at the siege of Metz and the stunning victories of Renty and Calais in 1554 and 1558. Already a commander of French infantry, he received promotion to commander of the light cavalry after the capture of Calais in 1558. A year prior he had accompanied François, Duke of Guise on his entry into Italy, as much for the purpose of campaigning as to escape the king's cousin Antoine of Navarre who was threatening to kill him for his extra-marital pursuit of Navarre's cousin.

Claude II de Lorraine, duc d'Aumale was a Prince étranger, military commander and French governor, during the latter Italian Wars and the early French Wars of Religion. The son of the first Duke of Guise he started his career in a pre-eminent position in French politics as a son of one of the leading families in the court of Henri II of France. Upon the death of his father in 1550, Aumale inherited the governorship of Burgundy from his father, and the duchy of Aumale from his brother who assumed the titles of Guise. Aumale was made colonel-general of the light horse by the new king and fought in Italy, Alsace and Picardie between 1551 and 1559. While leading the light cavalry during the defence of Metz he was captured, and held for the next two years, until his mother in law Diane de Poitiers paid his ransom. He achieved success at the siege of Volpiano and played an important role in the capture of Calais for which he was rewarded with the governorship of French Piedmont.
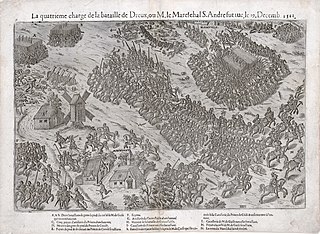
The Battle of Dreux was fought on 19 December 1562 between Catholics and Huguenots. The Catholics were led by Anne de Montmorency while Louis I, Prince of Condé, led the Huguenots. Though commanders from both sides were captured, the French Catholics won the battle which would constitute the first major engagement of the French Wars of Religion and the only major engagement of the first French War of Religion.

The Peace of Saint-Germain-en-Laye was signed on 8 August 1570 by Charles IX of France, Gaspard II de Coligny and Jeanne d'Albret, and ended the 1568 to 1570 Third Civil War, part of the French Wars of Religion.

The Battle of Saint-Denis was fought on 10 November 1567 between a royalist army and Huguenot rebels during the second of the French Wars of Religion. Although their 74 year old commander, Anne de Montmorency, was killed in the fighting, the royalists forced the rebels to withdraw, allowing them to claim victory.

The siege of Rouen was a key military engagement of the first French War of Religion. After having been seized by those opposing the crown on 16 April, the siege, beginning on 28 May and culminating on 26 October brought the important city of Rouen back into the crowns control. The fall of Rouen would set the stage for the main battle of the war at Dreux several months later.

The Peace of Longjumeau was signed on 23 March 1568 by Charles IX of France and Catherine de' Medici. The edict brought to an end the brief second French Wars of Religion with terms that largely confirmed those of the prior edict of Amboise. Unlike the previous edict it would not be sent to the Parlements to examine prior to its publication, due to what the crown had felt was obstructionism the last time. The edict would not however last, and it would be overturned later in the year, being replaced by the Edict of Saint-Maur which outlawed Protestantism at the beginning of the third war of religion.

The surprise of Meaux was a failed coup attempt by leading aristocratic Huguenots which precipitated the second French War of Religion. Dissatisfied with their lot, and under the pretext of fear of extermination, Louis, Prince of Condé and Gaspard II de Coligny plotted to seize the king, Charles IX, while he was staying near Meaux. Alerted by the mustering of the Huguenots, the royal court made a dash for Paris, fighting off attempts to break through to them en route. Their plan foiled, the Huguenots laid siege to the city, beginning the second war. The event would be of lasting importance in the reputation it gave its architects for sedition.

The siege of Orléans was the final key military engagement of the first French War of Religion. Having lost the Battle of Dreux the rebel Huguenots fell back with their remaining forces to the city. François, Duke of Guise, the only non captive royal commander, moved to lay siege to the town, hoping its capitulation would bring about a total victory for the crowns forces. However, despite reducing the suburbs, he would be assassinated at the siege before he could bring it to a conclusion. As a result the captive Louis, Prince of Condé and Anne de Montmorency at Catherine de' Medici's direction were able to negotiate a compromise end to the first war in the Edict of Amboise.

The Edict of July, also known as the first Edict of Saint-Germain was a decree of limited tolerance promulgated by the regent of France, Catherine de' Medici, in July 1561. Whilst it emphasised a continued commitment to banning Huguenot worship in France, it granted pardon for all religious offenses since the reign of Henry II, who had died two years earlier, which was a victory for the Protestant community. A further Protestant victory was in the reaffirmation of the removal of the death penalty for heresy cases. The edict would be overtaken by events, and ultimately left unenforced as France moved first to the landmark Edict of Saint-Germain and then into the Wars of Religion.

The Estates General of 1560–1561 was a national meeting of the three estates of France, the clergy, nobility and commoners convoked by François II, though he would die before it could begin. It represented the first meeting of the estates general in 76 years, the last one having been convened by Charles VIII at Tours. Meeting at Orléans the estates would be tasked with providing solutions to the crowns dire fiscal problems, a legacy of the Habsburg–Valois Wars, and the growing religious problem caused by the Reformation. The estates would however be unable to finish their deliberations, with Catherine de' Medici proroguing the session, and reconvening the estates general at a later date in 1561 at Pontoise, where she sought a more agreeable selection of delegates. Ultimately the work of the estates would solve neither the crowns fiscal insolvency or the religious conflict, which exploded in the first French War of Religion.

The Edict of Amboise (1560) was a decree that created the framework to separate heresy from sedition, promulgated by the young king Francis II on the advice of his council and mother Catherine de' Medici. The edict was the first promulgated in France that lessened the persecution of Huguenots through the provision of amnesty for past religious crimes on the condition the offender returned to the Catholic fold. The edict was published during the Amboise conspiracy whilst the royal court was resident in the Château d'Amboise and their authority over France was shaken. It would be superseded first by the Edict of Romorantin in May of the same year, then the Edict of July and finally the Edict of Saint-Germain

Artus de Cossé, seigneur de Gonnor and Comte de Secondigny (1512–1582), was a Marshal of France, an office he was elevated to in 1567. He served to administer the armies finances during the first of the French Wars of Religion and would lead the royal army in its pursuit of the Prince of Condé during the second civil war. His failure to catch the army led to his dismissal from overall royal command. During the third civil war he would again lead troops, beating a small Protestant force, before being defeated in the final days of the war at Arney-le-Duc. His long history of Politique leanings would push him into the orbit of the Malcontents for which he would be arrested in 1574. In 1576 he would be released and restored to favour before he died in 1582.
Guillaume de Montmorency, Seigneur of Thoré was a French noble, and military commander during the latter French Wars of Religion. Thoré was among those Catholic nobles who were perceived as soft on Protestantism, and as such during the Massacre of Saint Bartholomew he feared for his life. Shortly after the massacre as France descended back into civil war, Thoré, lacking military experience and keen to prove himself militarily joined the siege of La Rochelle.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Campbell 2003.
- 1 2 Thompson 1909, p. 506.
- ↑ Konnert, Mark W. (2006). Local Politics in the French Wars of Religion: The Towns of Champagne, the Duc de Guise, and the Catholic League, 1560-95. London: Routledge. pp. 122–123.
- ↑ d'Aubigné, Agrippa. Histoire Universelle, volume 4 (Alphonse de Ruble ed.). pp. 380–381.
- 1 2 3 Richards 2016, p. 177.