
Hannibal was a Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.

The Second Punic War was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Italy and Iberia, but also on the islands of Sicily and Sardinia and, towards the end of the war, in North Africa. After immense materiel and human losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were once again defeated. Macedonia, Syracuse and several Numidian kingdoms were drawn into the fighting, and Iberian and Gallic forces fought on both sides. There were three main military theatres during the war: Italy, where Hannibal defeated the Roman legions repeatedly, with occasional subsidiary campaigns in Sicily, Sardinia and Greece; Iberia, where Hasdrubal, a younger brother of Hannibal, defended the Carthaginian colonial cities with mixed success before moving into Italy; and Africa, where Rome finally won the war.
This article concerns the period 219 BC – 210 BC.

Year 216 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Varro and Paullus. The denomination 216 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The Battle of Cannae was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and their allies, led by Hannibal, surrounded and practically annihilated a larger Roman and Italian army under the consuls Lucius Aemilius Paullus and Gaius Terentius Varro. It is regarded as one of the greatest tactical feats in military history and one of the worst defeats in Roman history, and it cemented Hannibal's reputation as one of antiquity's greatest tacticians.
Mago Barca was a Barcid Carthaginian who played an important role in the Second Punic War, leading forces of Carthage against the Roman Republic in Iberia and northern and central Italy. Mago was the third son of Hamilcar Barca, was the brother of Hannibal and Hasdrubal, and was the brother-in-law of Hasdrubal the Fair.

The Battle of Lake Trasimene was fought when a Carthaginian force under Hannibal ambushed a Roman army commanded by Gaius Flaminius on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War. The battle took place on the north shore of Lake Trasimene, to the south of Cortona, and resulted in a heavy defeat for the Romans.

Hasdrubal Barca, a latinization of ʿAzrubaʿal son of Hamilcar Barca, was a Carthaginian general in the Second Punic War. He was the brother of Hannibal and Mago Barca.
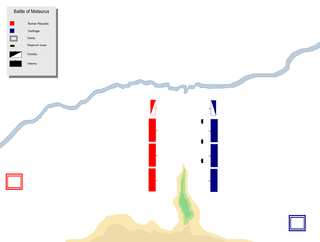
The Battle of the Metaurus was a pivotal battle in the Second Punic War between Rome and Carthage, fought in 207 BC near the Metauro River in Italy. The Carthaginians were led by Hasdrubal Barca, brother of Hannibal, who was to have brought siege equipment and reinforcements for Hannibal. The Roman armies were led by the consuls Marcus Livius, who was later nicknamed the Salinator, and Gaius Claudius Nero.

Gaius Claudius Nero was a Roman general active during the Second Punic War against the invading Carthaginian force, led by Hannibal Barca. During a military career that began as legate in 214 BC, he was praetor in 212 BC, propraetor in 211 BC during the siege of Capua, before being sent to Spain that same year. He became consul in 207 BC.
The Battle of the Upper Baetis was a double battle, comprising the battles of Castulo and Ilorca, fought in 211 BC during the Second Punic War between a Carthaginian force led by Hasdrubal Barca and a Roman force led by Publius Cornelius Scipio and his brother Gnaeus. The immediate result was a Carthaginian victory in which both Roman brothers were killed. Before this defeat, the brothers had spent seven years campaigning against the Carthaginians in Hispania, thus limiting the resources available to Hannibal, who was simultaneously fighting the Romans in Italy.
The Battles of Kroton in 204 and 203 BC were, as well as the raid in Cisalpine Gaul, the last larger scale engagements between the Romans and the Carthaginians in Italy during the Second Punic War. After Hannibal’s retreat to Bruttium due to the Metaurus debacle, the Romans continuously tried to block his forces from gaining access to the Ionian Sea and cut his eventual escape to Carthage by capturing Kroton, the last port which had remained in his hands after years of fighting.

The first Battle of Herdonia was fought in 212 BC during the Second Punic War between Hannibal's Carthaginian army and Roman forces led by Praetor Gnaeus Fulvius Flaccus, brother of the consul. The Roman army was destroyed, leaving Apulia free of Romans for the year.

The second battle of Herdonia took place in 210 BC during the Second Punic War. Hannibal, leader of the Carthaginians, who had invaded Italy eight years earlier, encircled and destroyed a Roman army which was operating against his allies in Apulia. The heavy defeat increased the war's burden on Rome and, piled on previous military disasters, aggravated the relations with her exhausted Italian allies. For Hannibal the battle was a tactical success, but did not halt for long the Roman advance. Within the next three years the Romans reconquered most of the territories and cities lost at the beginning of the war and pushed the Carthaginian general to the southwestern end of the Apennine peninsula. The battle was the last Carthaginian victory of the war; all battles which followed were either inconclusive or Roman victories.

The Roman Republic conquered and occupied territories in the Iberian Peninsula that were previously under the control of native Celtic, Iberian, Celtiberian and Aquitanian tribes and the Carthaginian Empire. The Carthaginian territories in the south and east of the peninsula were conquered in 206 BC during the Second Punic War. Control was gradually extended over most of the Iberian Peninsula without annexations. It was completed after the end of the Roman Republic, by Augustus, the first Roman emperor, who annexed the whole of the peninsula to the Roman Empire in 19 BC.
The Battle of Ager Falernus was a skirmish during the Second Punic War between the armies of Rome and Carthage. After winning the Battle of Lake Trasimene in Italy in 217 BC, the army commanded by Hannibal marched south and reached Campania. The Carthaginians ultimately moved into the district of Falernum, a fertile river valley surrounded by mountains.

The Battle of Canusium also known as the Battle of Asculum was a three-day engagement between the forces of Rome and Carthage. It took place in Apulia during the spring of 209 BC, the tenth year of the Second Punic War. A larger Roman offensive, of which it was a part, aimed to subjugate and to punish cities and tribes that had abandoned the alliance with Rome after the Battle of Cannae, and to narrow the base of the Carthaginian leader, Hannibal, in southern Italy.

The Punica is a Latin epic poem in seventeen books in dactylic hexameter written by Silius Italicus, comprising some twelve thousand lines. It is the longest surviving Latin poem from antiquity. Its theme is the Second Punic War and the conflict between the two great generals Hannibal and Scipio Africanus. The poem was re-discovered in either 1416 or 1417 by the Italian humanist and scholar Poggio Bracciolini.

Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet Africanus, literally meaning "the African," but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa.

















