Related Research Articles
Brahmo Samaj is the societal component of Brahmoism, which began as a monotheistic reformist movement that appeared during the Bengal Renaissance.
Bengali Brahmos are those who adhere to Brahmoism, the philosophy of Brahmo Samaj which was founded by Raja Rammohan Roy. A recent publication describes the disproportionate influence of Brahmos on India's development post-19th Century as unparalleled in recent times.

Sir Romesh Chandra Mitra or Romesh Chunder Mitter was an Indian judge and the first Indian officiating Chief Justice of the Calcutta High Court. Sir Romesh Mitra Girls school was founded in his honour in 1897. The school located in Bhowanipore is affiliated to the Central Board of Secondary Education.

Keshub Chandra Sen was a Hindu philosopher and social reformer who attempted to incorporate Christian theology within the framework of Hindu thought. Born a Hindu in the Bengal Presidency of British India, he became a member of the Brahmo Samaj in 1857 but established his own breakaway "Bharatvarshiya Brahmo Samaj" in 1866 while the Brahmo Samaj remained under the leadership of Debendranath Tagore. In 1878, his followers abandoned him after the underage child marriage of his daughter which exposed his campaign against child marriage as hollow. Later in his life he came under the influence of Ramakrishna and founded a syncretic "New Dispensation" inspired by Christianity, Vaishnavbhakti, and other Hindu practices.

SirSurendranath Banerjee, often known as Rashtraguru was Indian nationalist leader during the British Rule. He founded a nationalist organization called the Indian National Association to bring Hindus and Muslims together for political action. He was one of the founding members of the Indian National Congress. Surendranath supported Montagu–Chelmsford Reforms, unlike Congress, and with many liberal leaders he left Congress and founded a new organisation named Indian National Liberation Federation in 1919.

Hare School is one of the oldest schools in Kolkata, India, teaching grades one to twelve under the West Bengal Board of Secondary Education and the West Bengal Council of Higher Secondary Education. It is a state government-administered boys school and was established by the Scottish watch-maker, David Hare. The establishment date is not agreed upon, but the official year of establishment is 1818. Thus the school is declared as the oldest western type school in Asia. The school is situated opposite the Presidency University, and is also adjacent to the University of Calcutta and Hindu School. The combined campuses of the Hare School and Presidency College is one of the largest in Kolkata.
Pandit Sitanath Tattwabhushan was the official theologian and philosopher of the Sadharan Brahmo Samaj. His hymns still form the basis of Brahmo rites and liturgies.

Romesh Chunder Dutt was an Indian civil servant, economic historian, translator of Ramayana and Mahabharata. He was one of the prominent proponents of Indian economic nationalism.
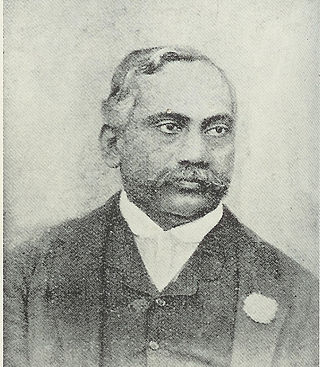
Manmohun Ghose was the first practicing barrister of Indian origin. He is notable for his contributions towards the fields of women's education, for arousing the patriotic feeling of his countrymen and for being one of the earliest persons in the country in organised national politics. At the same time his Anglicised habits often made him a target of ridicule in Calcutta.He was one of the co-founders of Indian National Congress.

Ananda Mohan Bose was an Indian politician, academician, social reformer, and lawyer during the British Raj. He co-founded the Indian National Association, one of the earliest Indian political organizations, and later became a senior leader of the Indian National Congress. In 1874, he became the first Indian Wrangler of the Cambridge University. He was also a prominent religious leader of Brahmoism and with Sivanath Sastri a leading light of Adi Dharm.
The Brahmo Conference Organisation (Sammilan) was founded on 27 January 1881 at Mymensingh Bangladesh to maintain communication between Adi Dharm and Sadharan Brahmo Samaj after the 2nd schism of Brahmoism in 1878. The stated objectives for founding the organisation included
The Tattwabodhinī Sabhā was a group founded in Calcutta on 6 October 1839 as a splinter group of the Brahmo Samaj, reformers of Hinduism and Indian Society. The founding member was Debendranath Tagore, previously of the Brahmo Samaj, eldest son of influential entrepreneur Dwarkanath Tagore, and eventually father to renowned polymath Rabindranath Tagore. In 1859, the Tattwabodhinī Sabhā were dissolved back into the Brāhmo Samāj by Debendranath Tagore.
Sunanda K. Datta-Ray is an Indian journalist. He has been editor of The Statesman and has also written for the International Herald Tribune and Time. He was editor-in-Residence at the East-West Center in Honolulu. He was editorial consultant to Singapore's The Straits Times newspaper. Datta-Ray also worked in Singapore in the mid-1970s with S. R. Nathan. After the Straits Times, Datta-Ray was a supernumerary fellow of Corpus Christi College, Oxford.

Surendranath Law College formerly known as Ripon College) is an postgraduate law college affiliated with the University of Calcutta. It was established in Kolkata in the Indian state of West Bengal in 1885 by a trust formed by the nationalist leader, scholar and educationist Surendranath Banerjee, a year after he founded Surendranath College. This is now regarded one of the oldest Law college of British India.

Krishna Kumar Mitra (1852–1936) was an Indian freedom fighter, journalist and leader of the Brahmo Samaj. He is remembered for his contributions to the Swadeshi movement through his journal Sanjibani.
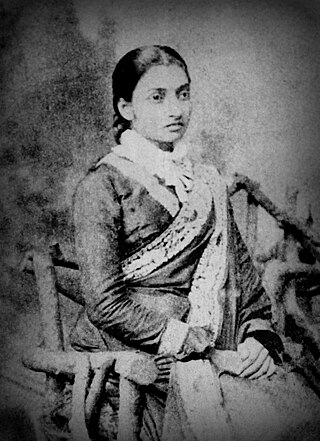
Jnanadanandini Tagore was a social reformer who pioneered various cultural innovations and influenced the earliest phase of women's empowerment in 19th century Bengal. She was married to Satyendranath Tagore, Rabindranath Tagore's elder brother, and a scion of the Jorasanko Tagore Family. She is known today for developing a unique style of sari, the Brahmika sari, based on both the traditional Bengali style, with elements from Gujarati and Parsi style drapes she encountered while living in Bombay.

Rasamay Dutt or Russomoy Dutt was a Bengali educationist of British India during the Bengali Renaissance. He was the co-founder of Hindu School, Kolkata. Bengali poet Toru Dutt was his granddaughter.

Atmaram Pandurang or Atmaram Pandurang Turkhadekar was an Indian physician and social reformer who founded the Prarthana Samaj and was one of the two Indian co-founders of the Bombay Natural History Society. A graduate of Grant Medical College, he was a brother of Dadoba Pandurang, a scholar of Sanskrit and Marathi. Atmaram Pandurang served briefly as sheriff of Bombay in 1879.
References
- ↑ J. N. Gupta, Life and Works of Romesh Chunder Dutt, (1911); The first Indian to enter the Indian Civil Service was Satyendranath Tagore, the second eldest son of Maharshi Debendranath Tagore, who joined the service in 1863, coming out to India in 1864. The batch of 1869 set new standards of excellence for other Indian students to perform well in the ICS, but Tagore's entry into the service six years earlier acted as an inspiration for future generations of Indian students who aspired to be members of the covenanted civil service.
- ↑ "South Asians at the Inns: Middle Temple, 1863-1944" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 July 2018. Retrieved 4 March 2017.
- ↑ Brahmo Sammilan Samaj
- ↑ Gupta, Life and Works of Romesh Chunder Dutt; This matter was later taken up by Sir Courtney Ilbert, the Law Member of the Viceroy's Executive Council, who in his famous Ilbert Bill report passed in 1883 recommended that Indian judges of a certain rank should be given considerable powers to try British subjects of the Crown settled or based in India. A hostile Anglo-Indian press and opinion challenged the recommendations leading to a fierce debate on the right of Indians to be appointed to such high judicial and administrative posts, leading eventually to the scaling down of the recommended powers of the Indian judges in 1884.