Bituminous coal, or black coal, is a type of coal containing a tar-like substance called bitumen or asphalt. Its coloration can be black or sometimes dark brown; often there are well-defined bands of bright and dull material within the seams. It is typically hard but friable. Its quality is ranked higher than lignite and sub-bituminous coal, but lesser than anthracite. It is the most abundant rank of coal, with deposits found around the world, often in rocks of Carboniferous age. Bituminous coal is formed from sub-bituminous coal that is buried deeply enough to be heated to 85 °C (185 °F) or higher.
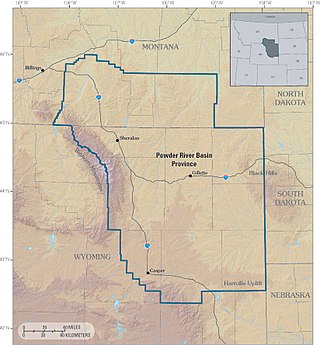
The Powder River Basin is a geologic structural basin in southeast Montana and northeast Wyoming, about 120 miles (190 km) east to west and 200 miles (320 km) north to south, known for its extensive coal reserves. The former hunting grounds of the Oglala Lakota, the area is very sparsely populated and is known for its rolling grasslands and semiarid climate.

Sub-bituminous coal is a lower grade of coal that contains 35–45% carbon. The properties of this type are between those of lignite, the lowest grade of coal, and those of bituminous coal, the second-highest grade of coal. Sub-bituminous coal is primarily used as a fuel for steam-electric power generation.

Peabody Energy is a coal mining company headquartered in St. Louis, Missouri. Its primary business consists of the mining, sale, and distribution of coal, which is purchased for use in electricity generation and steelmaking. Peabody also markets, brokers, and trades coal through offices in China, Australia, and the United States.

Centralia Coal Mine was an open-pit coal mine, owned by the Canadian-based TransAlta Corporation. The mine shut down in 2006. Also referred to as the TransAlta Centralia Mining (TCM) operation, the coal mine was located approximately 5 miles (8 km) northeast of the city of Centralia, in Lewis County, in the US state of Washington. Together with Centralia Power Plant, it was bought in May 2000 by TransAlta for $554 million – $101 million for the mine and $453 million for the power plant.
Coal mining regions are significant resource extraction industries in many parts of the world. They provide a large amount of the fossil fuel energy in the world economy.
Arch Resources, previously known as Arch Coal, is an American coal mining and processing company. The company mines, processes, and markets bituminous and sub-bituminous coal with low sulfur content in the United States. Arch Resources is the second-largest supplier of coal in the United States, behind Peabody Energy. As of 2011 the company supplied 15% of the domestic market. Demand comes mainly from generators of electricity.

The Black Thunder Coal Mine is a surface coal mine in the U.S. state of Wyoming, located in the Powder River Basin which contains one of the largest deposits of coal in the world. In 2022, the mine produced 62,180,000 short tons (56,410,000 t) of coal, over 25% of Wyoming's total coal production.
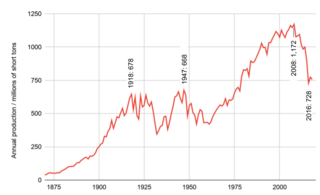
Coal mining is an industry in transition in the United States. Production in 2019 was down 40% from the peak production of 1,171.8 million short tons in 2008. Employment of 43,000 coal miners is down from a peak of 883,000 in 1923. Generation of electricity is the largest user of coal, being used to produce 50% of electric power in 2005 and 27% in 2018. The U.S. is a net exporter of coal. U.S. coal exports, for which Europe is the largest customer, peaked in 2012. In 2015, the U.S. exported 7.0 percent of mined coal.

The history of coal mining in the United States starts with the first commercial use in 1701, within the Manakin-Sabot area of Richmond, Virginia. Coal was the dominant power source in the late 1800s and early 1900s, and although in rapid decline it remains a significant source of energy in 2024.
The Cordero Rojo Mine is a coal mining complex located in the state of Wyoming in the United States, in the coal-rich Powder River Basin. The mine is of open pit construction and employs several dragline excavators. Two coal-processing facilities are located on-site, and crushed coal is shipped by rail to electric utility customers in the south and west of the United States. The mine employs between 430 and 540 people.
Foundation Coal Holdings, Inc. was a large American coal mining company. Until its July 31, 2009 merger with Alpha Natural Resources to form the third largest American coal company, the company was publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol FCL. With corporate offices in Linthicum Heights, Maryland, the former Foundation Coal operates coal mines in Pennsylvania, West Virginia and Wyoming, and was, prior to its merger with Alpha Natural Resources, the fourth-largest American coal producer by tonnage.
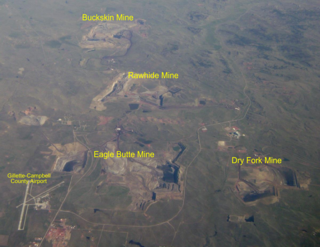
The Eagle Butte mine is a coal mine located 7 miles (11 km) north of Gillette, Wyoming in the United States in the coal-rich Powder River Basin. The mine is an open pit, "truck and shovel", mine producing a low-sulfur, sub-bituminous coal from the Roland and Smith seams that is used for domestic energy generation. Coal produced by the mine is shipped to its customers via railroad. The mine is owned and operated by Eagle Specialty Materials LLC after being acquired from Blackjewel LLC in 2019.

The Rawhide Mine is a coal mine located 10 miles (16.1 km) north of Gillette, Wyoming in the United States in the coal-rich Powder River Basin. The mine is an open pit mine that utilizes a combination of cast blast/dozer push and truck/shovel mining methods to strip an average of 165 feet (50.3m) of overburden off of approximately 105 (32.0m) feet of coal. Rawhide produces a low-sulfur, sub-bituminous coal from the Roland and Smith seams. This coal is used for domestic energy generation and shipped to customers via railroad. The mine is currently owned and operated by Peabody Energy.

The Dry Fork mine is a coal mine located 8 miles north of Gillette, Wyoming in the United States in the coal-rich Powder River Basin. The mine is an open pit mine that utilizes truck and shovel mining method to mine a low-sulfur, sub-bituminous coal that is used for domestic energy generation and shipped to customers via railroad. In 2011, the mine began supplying coal to the newly constructed Dry Fork power station that was constructed adjacent to the mine. The mine is currently owned and operated by Western Fuels Association.

The Wyodak mine is a coal mine in Wyodak, Wyoming, United States, located about 6 miles (9.7 km) east of Gillette in the coal-rich Powder River Basin.
Alpha Metallurgical Resources is a large American producer of metallurgical coal for the industrial production of steel and iron and low-sulfur thermal coal to fuel steam boilers for the production of electrical power. In November, 2018 the company was acquired by Contura Energy. The company also provides industry services relating to equipment repairs, road construction and logistics, with domestic operations and coal reserves within the states of Virginia, West Virginia, Kentucky, Wyoming, Utah, Illinois, Tennessee, and Pennsylvania. Alpha Natural Resources does not produce all of the coal it sells; much of the coal sold by Alpha Natural Resources is purchased from independent mining operations and then resold in the worldwide market.

Coal mining in Wyoming has long been a significant part of the state's economy. Wyoming has been the largest producer of coal in the United States since 1986, and in 2018, coal mines employed approximately 1% of the state's population. In 2013, there were 17 active coal mines in Wyoming, which produced 388 million short tons, 39 percent of all the coal mined in the US, and more than three times the production of second-place West Virginia. Market forces, including the low price of natural gas from the fracking boom—coal's main competition—contributed to the steep drop in coal production in the 2000s as electricity generation switched from coal to gas.

The North Antelope Rochelle Mine is the largest coal mine in the world. Located in Campbell County, Wyoming, about 65 miles (105 km) south of Gillette, it produced 85.3 million tons of coal in 2019.

Coal has been mined in Saskatchewan ever since the 1850s when it was used as a source of heat for the early Pioneers in the treeless Great Plains. Today, coal is still mined in Saskatchewan, but it is primarily used to generate electricity.