
Vitex agnus-castus is a plant native of the Mediterranean region. It is one of the few temperate-zone species of Vitex, which is on the whole a genus of tropical and subtropical flowering plants. Theophrastus mentioned the shrub several times, as agnos (ἄγνος) in Enquiry into Plants. It has been long believed to be an anaphrodisiac – leading to its name as "chaste tree" – but its effectiveness for such action remains unproven.

A reusable bottle is a bottle that can be reused, as in the case as by the original bottler or by end-use consumers. Reusable bottles have grown in popularity by consumers for both environmental and health safety reasons. Reusable bottles are one example of reusable packaging.

Enantioselective synthesis, also called asymmetric synthesis, is a form of chemical synthesis. It is defined by IUPAC as "a chemical reaction in which one or more new elements of chirality are formed in a substrate molecule and which produces the stereoisomeric products in unequal amounts."

2,2-Dimethoxypropane (DMP) is an organic compound with the formula (CH3)2C(OCH3)2. A colorless liquid, it is the product of the condensation of acetone and methanol. DMP is used as a water scavenger in water-sensitive reactions. Upon acid-catalyzed reaction, DMP reacts quantitatively with water to form acetone and methanol. This property can be used to accurately determine the amount of water in a sample, alternatively to the Karl Fischer method.

Rauvolfia serpentina, the Indian snakeroot, devil pepper, or serpentine wood, is a species of flower in the milkweed family Apocynaceae. It is native to the Indian subcontinent and East Asia.

4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.
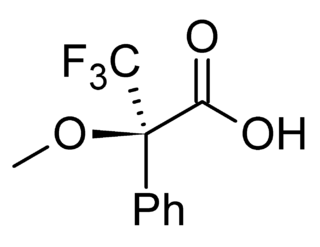
In analytical chemistry, a chiral derivatizing agent (CDA), also known as a chiral resolving reagent, is a derivatization reagent that is a chiral auxiliary used to convert a mixture of enantiomers into diastereomers in order to analyze the quantities of each enantiomer present and determine the optical purity of a sample. Analysis can be conducted by spectroscopy or by chromatography. Some analytical techniques such as HPLC and NMR, in their most commons forms, cannot distinguish enantiomers within a sample, but can distinguish diastereomers. Therefore, converting a mixture of enantiomers to a corresponding mixture of diastereomers can allow analysis. The use of chiral derivatizing agents has declined with the popularization of chiral HPLC. Besides analysis, chiral derivatization is also used for chiral resolution, the actual physical separation of the enantiomers.

Hexafluorophosphate is an anion with chemical formula of [PF6]−. It is an octahedral species that imparts no color to its salts. [PF6]− is isoelectronic with sulfur hexafluoride, SF6, and the hexafluorosilicate dianion, [SiF6]2−, and hexafluoroantimonate [SbF6]−. In this anion, phosphorus has a valence of 5. Being poorly nucleophilic, hexafluorophosphate is classified as a non-coordinating anion.

Astragalus mongholicus, synonyms including Astragalus propinquus and Astragalus membranaceus, commonly known as Mongolian milkvetch in English; 'Хунчир' in Mongolian; huáng qí, běi qí or huáng huā huáng qí, in Mongolia, is a flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. It is one of the 50 fundamental herbs used in traditional Mongolian medicine. It is a perennial plant and it is not listed as being threatened.
Alkylpyrazines are chemical compounds based on pyrazine with different substitution patterns. Some alkylpyrazines are naturally occurring highly aromatic substances which often have a very low odor threshold and contribute to the taste and aroma of various foods including cocoa, baked goods, coffee and wines. Alkylpyrazines are also formed during the cooking of some foods via Maillard reactions.

Aucubin is an iridoid glycoside. Iridoids are commonly found in plants and function as defensive compounds. Iridoids decrease the growth rates of many generalist herbivores.

Afzelechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Bergenia ligulata. It exists as at least 2 major epimers.

Syringetin is an O-methylated flavonol, a type of flavonoid. It is found in red grape, in Lysimachia congestiflora and in Vaccinium uliginosum. It is one of the phenolic compounds present in wine.

Californidine is an alkaloid with the molecular formula C20H20NO4+. It has been isolated from extracts of the California poppy (Eschscholzia californica), from which it gets its name, and from other plants of the genus Eschscholzia.

Zanthoxylum gilletii, the East African satinwood, is a tree species in the genus Zanthoxylum found in Africa. The fruits are used to produce the spice uzazi.

Casticin is a methoxylated flavonol, meaning the core flavonoid structure has methyl groups attached. Found in Artemisia annua, the flavonoid has been shown to enhance the antimalarial activity of artemisinin though casticin itself has no direct antimalarial effects. It has been shown to have anti-mitotic activity. It is also found in Vitex agnus-castus.

Bacoside A is a mixture of chemical compounds, known as bacosides, isolated from Bacopa monnieri. Its major constituents include the saponins bacoside A3, bacopaside II, jujubogenin isomer of bacopasaponin C, and bacopasaponin C. The mixture has been studied in in vitro experiments and animal models for its potential neuroprotectivity.

Agnuside is a chemical compound found in Vitex agnus-castus. Agnuside is the ester of aucubin and p-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Chiral analysis refers to the quantification of component enantiomers of racemic drug substances or pharmaceutical compounds. Other synonyms commonly used include enantiomer analysis, enantiomeric analysis, and enantioselective analysis. Chiral analysis includes all analytical procedures focused on the characterization of the properties of chiral drugs. Chiral analysis is usually performed with chiral separation methods where the enantiomers are separated on an analytical scale and simultaneously assayed for each enantiomer.

Pericopsis laxiflora is a woody deciduous shrub or tree within the Fabaceae family. Sold commercially as satin wood, it is known in some regions as Kulu Kulu, among the Hausa speaking people, it is called Makarfo, the Yorubas call it Ayan and the Igbos call it Abua-Ocha. It is one of three species in the genus Pericopsis genus that occurs in Africa.


















