BitchX is a free IRC client that has been regarded as the most popular ircII-based IRC client. The initial implementation, written by "Trench" and "HappyCrappy", was a script for the IrcII chat client. It was converted to a program in its own right by panasync. BitchX 1.1 final was released in 2004. It is written in C and is a TUI application utilizing ncurses. GTK+ toolkit support has been dropped. It works on all Unix-like operating systems, and is distributed under a BSD license. It is originally based on ircII-EPIC and eventually it was merged into the EPIC IRC client. It supports IPv6, multiple servers and SSL and a subset of UTF-8 with an unofficial patch.

Qt is cross-platform software for creating graphical user interfaces as well as cross-platform applications that run on various software and hardware platforms such as Linux, Windows, macOS, Android or embedded systems with little or no change in the underlying codebase while still being a native application with native capabilities and speed.

ChatZilla is an IRC client that is part of SeaMonkey. It was previously an extension for Mozilla-based browsers such as Firefox, introduced in 2000. It is cross-platform open source software which has been noted for its consistent appearance across platforms, CSS appearance customization and scripting.
The Visual Component Library (VCL) is a visual component-based object-oriented framework for developing the user interface of Microsoft Windows applications. It is written in Object Pascal.

wxWidgets is a widget toolkit and tools library for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs) for cross-platform applications. wxWidgets enables a program's GUI code to compile and run on several computer platforms with minimal or no code changes. A wide choice of compilers and other tools to use with wxWidgets facilitates development of sophisticated applications. wxWidgets supports a comprehensive range of popular operating systems and graphical libraries, both proprietary and free, and is widely deployed in prominent organizations.

Psi is a free instant messaging client for the XMPP protocol which uses the Qt toolkit. It runs on Linux, Windows, macOS and OS/2.

Fast Light Toolkit is a cross-platform widget library for graphical user interfaces (GUIs), developed by Bill Spitzak and others. Made to accommodate 3D graphics programming, it has an interface to OpenGL, but it is also suitable for general GUI programming.

PyQt is a Python binding of the cross-platform GUI toolkit Qt, implemented as a Python plug-in. PyQt is free software developed by the British firm Riverbank Computing. It is available under similar terms to Qt versions older than 4.5; this means a variety of licenses including GNU General Public License (GPL) and commercial license, but not the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL). PyQt supports Microsoft Windows as well as various flavours of UNIX, including Linux and MacOS.

The FOX toolkit is an open-source, cross-platform widget toolkit, i.e. a library of basic elements for building a graphical user interface (GUI). FOX stands for Free Objects for X.

A graphical user interface builder, also known as GUI designer or sometimes RAD IDE, is a software development tool that simplifies the creation of GUIs by allowing the designer to arrange graphical control elements using a drag-and-drop WYSIWYG editor. Without a GUI builder, a GUI must be built by manually specifying each widget's parameters in source-code, with no visual feedback until the program is run. Such tools usually called the term RAD IDE.

Scintilla is a free, open source library that provides a text editing component function, with an emphasis on advanced features for source code editing.
Crazy Eddie's GUI (CEGUI) is a graphical user interface (GUI) library for the programming language C++. It was designed for the needs of video games, but is usable for non-game tasks, such as applications and tools. It is designed for user flexibility in look-and-feel, and to be adaptable to the user's choice in tools and operating systems.
Ircle was an IRC client developed by Onno Tijdgat for the Macintosh computer platform. Ircle was shareware, with free upgrades. The client was scriptable with AppleScript, supported multiple channels and servers, and up to ten simultaneous connections. It was discontinued in 2009. Since 2012, Ircle was not compatible with most recent versions of OS X, and no updates were available. In December 2017 the Ircle home page displayed a poll, to end Q2 2018, to determine whether a new version should be released on OS X and iOS. The results of the poll were 311 votes in favor of a new Mac OS version, 43 votes for an iOS version, and 117 votes for both a Mac OS and iOS version, out of 528 votes cast.
KVIrc is a graphical IRC client for Linux, Unix, Mac OS and Windows. The name is an acronym of K Visual IRC in which the K stands for a dependency to KDE, which became optional from version 2.0.0. The software is based on the Qt framework and its code is released under a modified GNU General Public License.

Quassel IRC, or Quassel, is a graphical, distributed, cross-platform IRC client, introduced in 2008. It is released under the GNU General Public License version 2 and version 3, for GNU and Unix-like operating systems, macOS, and Microsoft Windows. It has also been ported to OS/2 Warp due to its cross-platform nature. Since the release of Kubuntu 9.04 Quassel is Kubuntu's default IRC client. Quassel uses the Qt application framework.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Perl programming language:
LeafChat is a free IRC client for Microsoft Windows and Unix-like operating systems, licensed under the GNU GPL-3.0-or-later. A donation is requested.

IceChat is a full-featured graphical IRC client for Windows. Its current version is open-source and released under the GPLv2 license.
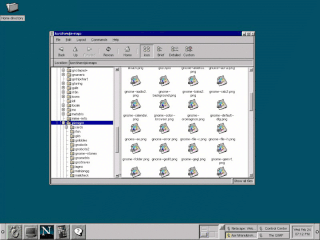
GNOME 1 is the first major release of the GNOME desktop environment. Its primary goal was to provide a consistent user-friendly environment in conjunction with the X Window System. It was also a modern and free and open source software alternative to older desktop environments such as the Common Desktop Environment (CDE), but also to the K Desktop Environment (KDE). Each desktop environment was built-upon then proprietary-licensed widget toolkits, whereas GNOME's goal from the onset, was to be freely-licensed, and utilize the GTK toolkit instead.














