
Lake Erie is the fourth-largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and also has the shortest average water residence time. At its deepest point Lake Erie is 210 feet (64 m) deep, making it the only Great Lake whose deepest point is above sea level.

The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the Straits of Mackinac. It is surrounded by water on all sides except its southern border, which it shares with Indiana and Ohio. Although the Upper Peninsula is commonly referred to as "the U.P.", it is uncommon for the Lower Peninsula to be called "the L.P."

A sea serpent is a type of sea monster described in various mythologies, most notably Mesopotamian (Tiamat), Judaeo-Christian (Leviathan), Greek, and Norse (Jörmungandr).

Oliver Hazard Perry was an American naval commander, born in South Kingstown, Rhode Island. A prominent member of the Perry family naval dynasty, he was the son of Sarah Wallace Alexander and United States Navy Captain Christopher Raymond Perry, and older brother of Commodore Matthew C. Perry.

Lake Huron is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrologically, it comprises the easterly portion of Lake Michigan–Huron, by area, the second largest in the world, having the same surface elevation as Lake Michigan, to which it is connected by the 5-mile-wide (8.0 km), 20-fathom-deep Straits of Mackinac. It is shared on the north and east by the Canadian province of Ontario and on the south and west by the U.S. state of Michigan. The name of the lake is derived from early French explorers who named it for the indigenous people they knew as Huron (Wyandot) inhabiting the region. Lake Huron and Michigan are considered to be one lake hydrologically The Huronian glaciation was named from evidence collected from Lake Huron region. The northern parts of the lake include the North Channel and Georgian Bay. Saginaw Bay is located in the southwest corner of the lake. The main inlet is the St. Marys River, and the main outlet is through the St. Clair River to Lake Erie. Lake Huron has a fairly large drainage basin covering parts of Michigan and Ontario. Water flows through Lake Huron faster than the other Great Lakes with a retention time of only 22 years.
Cadborosaurus, nicknamed Caddy by journalist Archie Wills, is a sea serpent in the folklore of regions of the Pacific Coast of North America. Its name is derived from Cadboro Bay in Greater Victoria, British Columbia, and the Greek root word "saurus" meaning lizard or reptile.

In Canadian folklore, the Ogopogo is a lake monster said to inhabit Okanagan Lake in British Columbia, Canada. Some scholars have charted the entity's development from First Nations folklore and widespread water monster folklore motifs. The Ogopogo now plays a role in the commercial symbolism and media representation of the region.

The Miami and Erie Canal was a 274-mile (441 km) canal that ran from Cincinnati to Toledo, Ohio, creating a water route between the Ohio River and Lake Erie. Construction on the canal began in 1825 and was completed in 1845 at a cost to the state government of $8 million. At its peak, it included 19 aqueducts, three guard locks, 103 canal locks, multiple feeder canals, and a few man-made water reservoirs. The canal climbed 395 feet (120 m) above Lake Erie and 513 feet (156 m) above the Ohio River to reach a topographical peak called the Loramie Summit, which extended 19 miles (31 km) between New Bremen, Ohio to lock 1-S in Lockington, north of Piqua, Ohio. Boats up to 80 feet long were towed along the canal by mules, horses, or oxen walking on a prepared towpath along the bank, at a rate of four to five miles per hour.
The Erie people were Indigenous people historically living on the south shore of Lake Erie. An Iroquoian group, they lived in what is now western New York, northwestern Pennsylvania, and northern Ohio before 1658. Their nation was almost exterminated in the mid-17th century by five years of prolonged warfare with the powerful neighboring Iroquois for helping the Huron in the Beaver Wars for control of the fur trade. Captured survivors were adopted or enslaved by the Iroquois.
In Canadian folklore, the Manipogo is a lake monster said to live in Lake Manitoba, Manitoba, Canada. The creature was dubbed Manipogo in 1960, the name echoing British Columbia's Ogopogo. There is also a Lake Winnipegosis monster called Winnepogo, thought possibly to be the same creature since the lakes are connected. It is the namesake of the Manipogo Provincial Park.

In American folklore, Chessie is a sea monster said to live in the midst of the Chesapeake Bay. Claims of sightings appear in local media and regionally-themed books from 1936 onward. Over time, the figure developed into an environmental icon associated with the ecological health of the Chesapeake Bay, and continues to play a role in modern popular culture.

In American folklore, Champ or Champy is the name of a lake monster said to live in Lake Champlain, a 125-mile (201 km)-long body of fresh water shared by New York and Vermont, with a portion extending into Quebec, Canada. The legend of the monster is considered a draw for tourism in the Burlington, Vermont and Plattsburgh, New York areas.

Lake Maumee was a proglacial lake and an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 17,500 calendar years, or 14,000 Radiocarbon Years Before Present (RCYBP) as the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Laurentide Ice Sheet retreated at the end of the Wisconsin glaciation. As water levels continued to rise the lake evolved into Lake Arkona and then Lake Whittlesey.
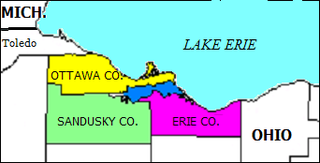
Sandusky Bay is a bay on Lake Erie in northern Ohio, formed at the mouth of the Sandusky River. It was identified as Lac Sandouské on a 1718 French map, with early variations recorded that suggest the name was derived from Native American languages. The Thomas A. Edison Memorial Bridge was constructed across it in the 20th century to connect highways in Erie and Ottawa counties.

The Inner and Outer Hebrides off the western coast of Scotland are made up of a great number of large and small islands. These isolated islands are the source of a number of Hebridean myths and legends. The Hebridean Islands are a part of Scotland that have always relied on the surrounding sea to sustain the small communities which have occupied parts of the islands for centuries, resulting in a number of sea legends relating to these local islands.
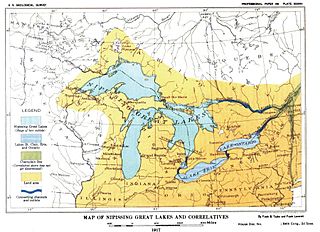
Nipissing Great Lakes was a prehistoric proglacial lake. Parts of the former lake are now Lake Superior, Lake Huron, Georgian Bay and Lake Michigan. It formed about 7,500 years before present (YBP). The lake occupied the depression left by the Labradorian Glacier. This body of water drained eastward from Georgian Bay to the Ottawa valley. This was a period of isostatic rebound raising the outlet over time, until it opened the outlet through the St. Clair valley, at one stage it had two stable outlets both draining to the east.
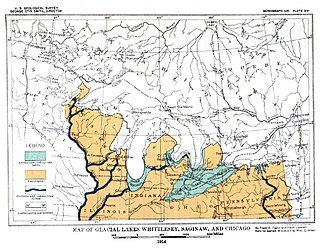
Lake Whittlesey was a proglacial lake that was an ancestor of present-day Lake Erie. It formed about 14,000 years ago. As the Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin Glacier retreated at the end of the last ice age, it left melt-water in a previously-existing depression area that was the valley of an eastward-flowing river known as the Erigan River that probably emptied into the Atlantic Ocean following the route of today's Saint Lawrence River. The lake stood at 735 feet (224 m) to 740 feet (230 m) above sea level. The remanent beach is not horizontal as there is a ‘hinge line’ southwest of a line from Ashtabula, Ohio, through the middle part of Lake St. Clair. The hinge line is where the horizontal beaches of the lake have been warped upwards towards the north by the isostatic rebound as the weight of the ice sheet was removed from the land. The rise is 60 feet (18 m) north into Michigan and the Ubly outlet. The current altitude of the outlet is 800 feet (240 m) above sea level. Where the outlet entered the Second Lake Saginaw at Cass City the elevation is 740 feet (230 m) above sea level. The Lake Whittlesey beach called the Belmore Beach and is a gravel ridge 10 feet (3.0 m) to 15 feet (4.6 m) high and one-eighth mile wide. Lake Whittlesey was maintained at the level of the Ubly outlet only until the ice melted back on the "Thumb" far enough to open a lower outlet. This ice recession went far enough to allow the lake to drop about 20 feet (6.1 m) below the lowest of the Arkona beaches to Lake Warren levels.

Lake Warren was a proglacial lake that formed in the Lake Erie basin around 12,700 years before present (YBP) when Lake Whittlesey dropped in elevation. Lake Warren is divided into three stages: Warren I 690 feet (210 m), Warren II 680 feet (210 m), and Warren III 675 feet (206 m), each defined by the relative elevation above sea level.

Iosco was a Great Lakes freighter that served on the Great Lakes from her construction in 1891 to her foundering on September 2, 1905, when she and her tow, the schooner barge Olive Jeanette sank on Lake Superior. While Olive Jeanette's wreck was located in over 300 feet (91 m) of water about eight miles (13 km) off the Huron Islands in the 1990s, Iosco's wreck has not yet been found.

SS Etruria was a steel hulled lake freighter that served on the Great Lakes of North America from her construction in 1902 to her sinking in 1905. On June 18, 1905, while sailing upbound on Lake Huron with a cargo of coal, she was rammed and sunk by the freighter Amasa Stone 10 miles (16 km) off Presque Isle Light. For nearly 106 years the location of Etruria's wreck remained unknown, until the spring of 2011 when her wreck was found upside down in 310 feet (94 m) of water.

















