The king cobra is a venomous snake endemic to Asia. The sole member of the genus Ophiophagus, it is not taxonomically a true cobra, despite its common name and some resemblance. With an average length of 3.18 to 4 m and a record length of 5.85 m (19.2 ft), it is the world's longest venomous snake. The species has diversified colouration across habitats, from black with white stripes to unbroken brownish grey. The king cobra is widely distributed albeit not commonly seen, with a range spanning from the Indian Subcontinent through Southeastern Asia to Southern China. It preys chiefly on other snakes, including those of its own kind. This is the only ophidian that constructs an above-ground nest for its eggs, which are purposefully and meticulously gathered and protected by the female throughout the incubation period.

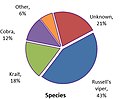
Echis carinatus, known as the saw-scaled viper, Indian saw-scaled viper, little Indian viper, and by other common names, is a viper species found in parts of the Middle East and Central Asia, and especially the Indian subcontinent. It is the smallest member of the "big four" Indian snakes that are responsible for causing the most snakebite cases and deaths, due to various factors including their frequent occurrence in highly populated regions, and their inconspicuous nature. Like all vipers, the species is venomous. Two subspecies are currently recognized, including the nominate subspecies described here.

Snake venom is a highly toxic saliva containing zootoxins that facilitates in the immobilization and digestion of prey. This also provides defense against threats. Snake venom is injected by unique fangs during a bite, whereas some species are also able to spit venom.

Russell's viper is a venomous snake in the family Viperidae native to the Indian subcontinent and one of the big four snakes in India. It was described in 1797 by George Shaw and Frederick Polydore Nodder, and named after Patrick Russell, who wrote about it in his 1796 work An account of Indian serpents, collected on the coast of Coromandel.

The common krait, also known as Bengal krait, is a species of highly venomous elapid snake of the genus Bungarus native to the Indian subcontinent. It is a member of the "Big Four" species that inflict the most snakebites on humans in Pakistan, India and Bangladesh.

The banded krait is a species of elapids endemic to Asia, from Indian Subcontinent through Southeast Asia to Southern China. With a maximum length exceeding 2 m, it is the longest krait with a distinguishable gold and black pattern. While this species is generally considered timid and docile, resembling other members of the genus, its venom is highly neurotoxic which is potentially lethal to humans. Although toxicity of the banded krait based upon murine LD50 experiments is lower than that of many other kraits, its venom yield is the highest due to its size.

The Indian cobra, also known commonly as the spectacled cobra, Asian cobra, or binocellate cobra, is a species of cobra, a venomous snake in the family Elapidae. The species is native to the Indian subcontinent, and is a member of the "big four" species that are responsible for the most snakebite cases in India.

The Caspian cobra, also called the Central Asian cobra, ladle snake, Oxus cobra, or Russian cobra, is a species of highly venomous snake in the family Elapidae. The species is endemic to Central Asia. Described by Karl Eichwald in 1831, it was for many years considered a subspecies of the Indian cobra until genetic analysis revealed it to be a distinct species.

Echis is a genus of vipers found in the dry regions of Africa, the Middle East, India, Sri Lanka and Pakistan. They have a characteristic threat display, rubbing sections of their body together to produce a "sizzling" warning sound. The name Echis is the Latin transliteration of the Greek word for "viper" (ἔχις). Like all vipers, they are venomous. Their common name is "saw-scaled vipers" and they include some of the species responsible for causing the most snakebite cases and deaths in the world. Twelve species are currently recognized.

Snake Cell Andhra Pradesh is a voluntary non-profit organisation working for the Conservation of Reptiles. It rescues snakes from residential areas of Hyderabad and Secunderabad.
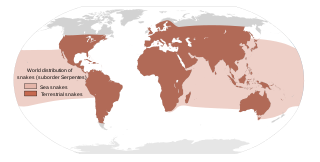
Most snakebites are caused by non-venomous snakes. Of the roughly 3,700 known species of snake found worldwide, only 15% are considered dangerous to humans. Snakes are found on every continent except Antarctica. There are two major families of venomous snakes, Elapidae and Viperidae. 325 species in 61 genera are recognized in the family Elapidae and 224 species in 22 genera are recognized in the family Viperidae, In addition, the most diverse and widely distributed snake family, the colubrids, has approximately 700 venomous species, but only five genera—boomslangs, twig snakes, keelback snakes, green snakes, and slender snakes—have caused human fatalities.
Ten Deadliest Snakes with Nigel Marven is a twelve-part wildlife documentary series from 2013 to 2017. It began airing on Eden Channel in 2013. Seasons 1 and 2 were also broadcast on Animal Planet Europe, while season 3 was premiered on Nat Geo Wild UK and later screened on Nat Geo Wild Europe & Africa in 2017. It is presented by Nigel Marven, who travels around the world and in each hour-long episode he counts down his list of ten deadliest snakes in each different country or continent. The series is produced by Image Impact.