
Mount Thielsen, is an extinct shield volcano in the Oregon High Cascades, near Mount Bailey. Because eruptive activity ceased 250,000 years ago, glaciers have heavily eroded the volcano's structure, creating precipitous slopes and a horn-like peak. The spire-like shape of Thielsen attracts lightning strikes and creates fulgurite, an unusual mineral. The prominent horn forms a centerpiece for the Mount Thielsen Wilderness, a reserve for recreational activities such as skiing and hiking. Thielsen is one of Oregon's Matterhorns.

Mount Washington is a deeply eroded volcano in the Cascade Range of Oregon. It lies within Deschutes and Linn counties and is surrounded by the Mount Washington Wilderness area.

Gifford Pinchot National Forest is a National Forest located in southern Washington, managed by the United States Forest Service. With an area of 1.32 million acres (5,300 km2), it extends 116 km (72 mi) along the western slopes of Cascade Range from Mount Rainier National Park to the Columbia River. The forest straddles the crest of the South Cascades of Washington State, spread out over broad old-growth forests, high mountain meadows, several glaciers, and numerous volcanic peaks. The forest's highest point is at 12,276 ft (3,742 m) at the top of Mount Adams, the second-tallest volcano in the state after Rainier. Often found abbreviated GPNF on maps and in texts, it includes the 110,000-acre (450 km2) Mount St. Helens National Volcanic Monument, established by Congress in 1982.

Indian Heaven is a volcanic field in Skamania County in the state of Washington, in the United States. Midway between Mount St. Helens and Mount Adams, the field dates from the Pleistocene to the early Holocene epoch. It trends north to south and is dominated by six small shield volcanoes; these shields are topped by small spatter and cinder cones, and the field includes a number of subglacial volcanoes and tuyas. The northernmost peak in the field is Sawtooth Mountain and the southernmost is Red Mountain; its highest point is Lemei Rock at an elevation of 5,925 feet (1,806 m).
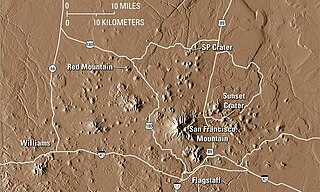
The San Francisco volcanic field is an area of volcanoes in northern Arizona, north of Flagstaff, US. The field covers 1,800 square miles (4,700 km2) of the southern boundary of the Colorado Plateau. The field contains 600 volcanoes ranging in age from nearly 6 million years old to less than 1,000 years, of which Sunset Crater is the youngest. The highest peak in the field is Humphreys Peak, at Flagstaff's northern perimeter: the peak is Arizona's highest at 12,633 feet and is a part of the San Francisco Peaks, an active stratovolcano complex.

Goat Rocks is an extinct stratovolcano in the Cascade Range, located between Mount Rainier and Mount Adams in southern Washington, in the United States. Part of the Cascade Volcanoes, it was formed by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate under the western edge of the North American Plate. The volcano was active from 3.2 million years ago until eruptions ceased between 1 and 0.5 million years ago. Throughout its complex eruptive history, volcanism shifted from silicic explosive eruptions to voluminous, mafic activity.

An active volcano is a volcano that has erupted during the Holocene, is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes.

West Crater is a small lava dome with associated lava flows in southern Washington, United States. Located in Skamania County, it rises to an elevation of 4,131 feet (1,259 m), and forms part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It is also part of the Marble Mountain-Trout Creek Hill volcanic field, a little-known Quaternary volcanic field in the southern Cascades of Washington state. The area can be hiked, and can be accessed by roads in the Gifford Pinchot National Forest.

Black Crater is a shield volcano in the Western Cascades in Deschutes County, Oregon. Located near McKenzie Pass, the volcano has a broad conical shape with gentle slopes. The volcano likely formed during the Pleistocene and has not been active within the last 50,000 years. Eruptive activity at the volcano produced mafic lava flows made of basaltic andesite and olivine basalt; it also formed a number of cinder cones. A normal fault occurs on the western side of the volcano, trending north–south. The volcano has been eroded by glaciers, which carved a large cirque into the northeastern flank of the mountain, forming its current crater.

Marble Mountain-Trout Creek Hill volcanic field (MMTC) is a volcanic field located in Washington, US.

Four Craters Lava Field is a basaltic volcanic field located south east of Newberry Caldera in the U.S. state of Oregon. The volcanic field covers about 30 square kilometers and post-dates Mount Mazama's eruption. Four Holocene cinder cones are the source of the flows in the field and are aligned along a fissure trending N 30° W. The cones rise 75 to 120 meters above the flows and the distance between the northernmost and southernmost cones is about 3.5 kilometers.

The flows of Jordan Craters volcanic field are the youngest of a series of large Quaternary basalt fields in the eastern part of the U.S. state of Oregon. The field is thought to be approximately 3200 years old, based on findings of a lake sediment coring experiment in 1986. It was formed by basaltic pahoehoe emanating from vents throughout the area.
Trout Creek Hill is a small Pleistocene basaltic shield volcano in Washington, United States. Located in Skamania County, Trout Creek Hill rises to an elevation of 2,946 feet (898 m). It is part of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, located in the Marble Mountain-Trout Creek Hill volcanic field.

Indian Heaven Wilderness is a protected area located inside the Gifford Pinchot National Forest of southwestern Washington state. The wilderness consists of 20,782 acres (8,410 ha) of broad, forested plateau, with meadows straddling numerous volcanic peaks and at least 150 small lakes, ponds, and marshes. The wilderness also contains the Indian Heaven volcanic field. Originally known to the Indians as "Sahalee Tyee," the area has been and remains culturally important to Native Americans. During the past 9,000 years, the Yakama, Klickitat, Cascades, Wasco, Wishram, and Umatilla tribes gathered in this area for berry picking, fishing, and hunting.
Mount Mandalagan is a complex volcano located at latitude 10.65° North (10°39'0"N), longitude 123.25° East (123°15'0"E), in the province of Negros Occidental, on the north of the island of Negros of the Philippines. It is located inside the Northern Negros Natural Park.

The volcanic history of the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province presents a record of volcanic activity in northwestern British Columbia, central Yukon and the U.S. state of easternmost Alaska. The volcanic activity lies in the northern part of the Western Cordillera of the Pacific Northwest region of North America. Extensional cracking of the North American Plate in this part of North America has existed for millions of years. Continuation of this continental rifting has fed scores of volcanoes throughout the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province over at least the past 20 million years and occasionally continued into geologically recent times.

The isolated San Martin Tuxtla volcano is a shield volcano which rises above the Gulf of Mexico. It has had eruptions in historical times. It occurs in the Tuxtla volcanic field in Veracruz, Mexico. Lavas from San Martin vary between basanite and alkali basalt. Locally the volcano is also known as Tiltépetl.

Lemei Rock is a shield volcano, and part of the Indian Heaven polygenetic volcanic field in Washington, United States. It is located midway between Mount St. Helens and Mount Adams, and dates from the Pleistocene and Holocene. Lemei Rock is the highest point at 5,925 feet (1,806 m).
















