
Tripura is a state in Northeast India. The third-smallest state in the country, it covers 10,491 km2 (4,051 sq mi); and the seventh-least populous state with a population of 36.71 lakh. It is bordered by Assam and Mizoram to the east and by Bangladesh to the north, south and west. Tripura is divided into 8 districts and 23 sub-divisions, where Agartala is the capital and the largest city in the state. Tripura has 19 different tribal communities with a majority of the Bengali population. Bengali, English and Kokborok are the state's official languages.

Agartala is the capital and the largest city of the Indian state of Tripura, situated on the banks of Hoara River, about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) east of the border with Bangladesh and about 2,499 km (1,52 mi) from the National Capital New Delhi. According to 2022 census, Agartala is the third-most populous city in Northeast India with a population of about 5.7 lakh. It is India's third international internet gateway and being developed under the Smart Cities Mission.

The Tripuri are an ethnic group originating in the Indian state of Tripura. They are the inhabitants of the Twipra/Tripura Kingdom in North-East India and Bangladesh. The Tripuri people through the Manikya dynasty ruled the Kingdom of Tripura for many years until the kingdom joined the Indian Union on 15 October 1949.

The Pushbanta Palace also known as Kunjaban Palace is one of former royal palace of Tripura, it was built by Maharaja Birendra Kishore Manikya in 1917. It was the Raj Bhavan of Tripura till 2018, which later shifted. The palace is being developed as a national-level cultural museum.
The Twipra Kingdom was one of the largest historical kingdoms of the Tripuri people in Northeast India.

The Manikya dynasty was the ruling house of the Twipra Kingdom and later the princely Tripura State, what is now the Indian state of Tripura. Ruling since the early 15th century, the dynasty at its height controlled a large swathe of the north-east of the Indian subcontinent. After coming under British influence, in 1761 they transitioned from feudal monarchs into rulers of a princely state, though the Manikyas maintain control of the region until 1949, when it ascended in union with India.
Maharaja Bir Bikram Kishore Manikya Debbarma Bahadur was a king of Tripura State.

Kirit Pradyot Manikya Deb Barman Bahadur is the current head of the Tripuri royal family and is the titular king. He was born in New Delhi, and now resides in Agartala, Tripura. He also served as the editor of TNT-The Northeast Today. He is the current chairman of The Indigenous Progressive Regional Alliance also known as TIPRA Motha. He is known as 'Bubagra' among his people and is one of the active voices for the rights of Indigenous Tripuri people of Tripura.

Neermahal also known as Twijilikma Nuyung is a former royal palace of Tripura Kingdom, built by Maharaja Bir Bikram Kishore Manikya bahadur in 1930. It is also the largest water palace in India. The palace is situated in the middle of Rudrasagar Lake, in Melaghar 53 kilometers away from Agartala, the capital of Tripura.

The Ujjayanta Palace also known as Nuyungma, is the former royal palace of Tripura kingdom built by Maharaja Radha Kishore Manikya in 1901; and the name was given by Rabindranath Tagore. It housed the State Legislative Assembly up to 2011. At present, it is the State Museum of Tripura, which is located in the capital Agartala.
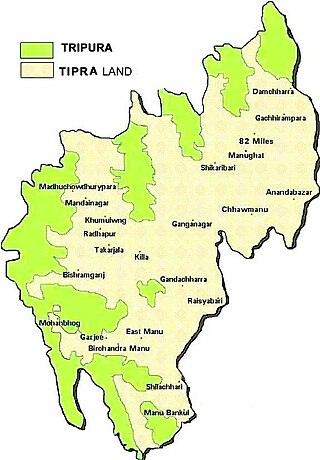
Tipraland is the name of a proposed state in India for the indigenous Tripuri people in the tribal areas of the Tripura state. They demand the Tripura Tribal Areas Autonomous District Council and some surrounding areas to be made into a separate state from Tripura. The proposed state covers 68% of the total geographical area of the Tripura and is home to over one-third of the total population of Tripura.

Maharaja Radha Kishore Manikya of the Manikya Dynasty reigned as the king of Tripura State from 1897 to 1909. He has been described as one of the architects of modern Tripura.

Maharaja Bir Chandra Manikya Bahadur of the Manikya Dynasty was the king of Tripura from 1862 to 1896.

A temple dedicated to the Hindu God Lakshminarayan located in the Ujjayanta Palace ground in the city of Agartala, Tripura state, India.

Gomati district is a district of Tripura, India. This district was created in January 2012 when four new districts were created in Tripura, taking the number of districts in the state from four to eight. Udaipur is its headquarters.

Tripura State, also known as Hill Tipperah, was a princely state in India during the period of the British Raj and for some two years after the departure of the British. Its rulers belonged to the Manikya dynasty and until August 1947 the state was in a subsidiary alliance, from which it was released by the Indian Independence Act 1947. The state acceded to the newly independent Indian Union on 13 August 1947, and subsequently merged into the Indian Union in October 1949.
Pratap Manikya was a Maharaja of Tripura during the late 15th century.
Mahendra Manikya was the Maharaja of Tripura from 1712 to 1714.

The Tipra Motha Party (TMP), also known as the Tipraha Indigenous Progressive Regional Alliance, is a regional political party and previously a social organization in Tripura, India. The TIPRA is led by Pradyot Bikram Manikya Deb Barma.














