Environment
The sea has a moderating effect on the climate, so temperatures do not fall much below 0 °C (32 °F) in winter, and are not as high in the summer as in area further inland. The Kaliakra cliffs in the north of Bulgaria are rich in flora, including many species in common with the neighboring Steppic and Mediterranean Regions. The western Black Sea Region is the Via Pontica, Europe's second largest bird migration route. The migrating birds use the coastal lakes, marshes and lagoons behind the shoreline, and some spend the winter in these wetlands. The Danube Delta is the best known of the wetlands.
In Bulgaria and Romania the region is threatened by development of agriculture, industry, urbanization and tourism. The Black Sea itself, a very deep inland sea, is poor in oxygen and supports very little marine life in the deeper regions. However, it had a productive fishery until the 1960s, when stocks crashed in part because of over-fishing and in part from pollution and invasion by exotic species.
A Special Protection Area (SPA) is a designation under the European Union Directive on the Conservation of Wild Birds. Under the Directive, Member States of the European Union (EU) have a duty to safeguard the habitats of migratory birds and certain particularly threatened birds. Together with Special Areas of Conservation (SACs), the SPAs form a network of protected sites across the EU, called Natura 2000. Each SPA has an EU code – for example the North Norfolk Coast SPA has the code UK9009031.
Natura 2000 is a network of nature protection areas in the territory of the European Union. It is made up of Special Areas of Conservation and Special Protection Areas designated under the Habitats Directive and the Birds Directive, respectively. The network includes both terrestrial and Marine Protected Areas.

Varna Province, formerly known as Varna okrug, is a province in eastern Bulgaria, one of the 28 Bulgarian provinces. It comprises 12 municipalities with a population of 494,216 inhabitants as of April 2016. The province is named after its administrative centre, Varna.

Byala is a small town and seaside resort in Eastern Bulgaria, located on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast in Varna Province. It is the administrative centre of the homonymous Byala Municipality and lies in a semi-mountainous region in the easternmost branches of Stara Planina about 50 km south of the city of Varna and 70 km north of Burgas. As of December 2009, the town has a population of 2,171 inhabitants.

The Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, also known as the Bulgarian Riviera, covers the entire eastern bound of Bulgaria stretching from the Romanian Black Sea resorts in the north to European Turkey in the south, along 378 km of coastline. White and golden sandy beaches occupy approximately 130 km of the 378 km long coast. The region is an important center of tourism during the summer season (May–October), drawing millions of foreign and local tourists alike and constituting one of the country's most popular tourist destinations. Prior to 1989 the Bulgarian Black Sea coast was internationally known as the Red Riviera. Since the fall of the Iron Curtain, however, its nickname has been changed to the Bulgarian Riviera.

Kaliakra is a long and narrow headland in the Southern Dobruja region of the northern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, 12 kilometres (7 mi) east of Kavarna, 60 kilometres (37 mi) northeast of Varna and 65 kilometres (40 mi) southwest of Mangalia. The coast is steep with vertical cliffs reaching 70 metres (230 ft) down to the sea. Kaliakra is a nature reserve, where dolphins and cormorants can be observed. It sits on the Via Pontica, a major bird migration route from Africa into Eastern and Northern Europe. Many rare and migrant birds can be seen here in spring and autumn and, like much of this coastline, is home to several rare breeding birds. The rest of the reserve also has unusual breeding birds; saker falcon, lesser grey shrike and a host of others.

The Kamchiya is a 191-kilometre (119 mi) river in eastern Bulgaria, the longest river on the Balkan Peninsula to flow directly into the Black Sea. From it longest source, Golyama Kamchiya, it has a total length of (244.5-kilometre. The river Kamchiya proper starts from the confluence of the two rivers springing from Eastern Stara Planina, Golyama Kamchiya and Luda Kamchiya, flows eastward to the Black Sea and empties into it 25 km south of Varna, in the Resort of Kamchiya.

Lake Pomorie is the northernmost of the coastal Burgas Lakes, located in the immediate proximity of the Black Sea and the Bulgarian town of Pomorie. It has an area of 8.5 km² and has an elongated shape with a length of 6.7 km and width of 1.8–2 km. Divided from the sea by a narrow strip of sand (spit) and an artificial dike, the lake is an ultrasaline natural lagoon.
A Site of Community Importance (SCI) is defined in the European Commission Habitats Directive (92/43/EEC) as a site which, in the biogeographical region or regions to which it belongs, contributes significantly to the maintenance or restoration at a favourable conservation status of a natural habitat type or of a species and may also contribute significantly to the coherence of Natura 2000, and/or contributes significantly to the maintenance of biological diversity within the biogeographic region or regions concerned.
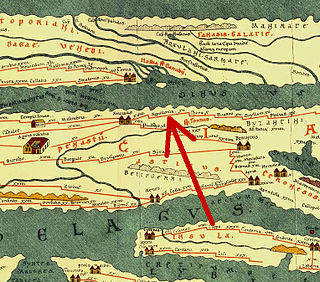
Via Pontica was an ancient Roman road in Thrace along the Black Sea, starting from Byzantium and passing through Deultum, Aquae Calidae, Apollonia, Mesembria, Odessos, Byzone, and Kaliakra ; and then through Kallatis, Tomis, and Istros.

Bolata is a small cove and Nature reserve located in the Northern Bulgarian Black Sea Coast.

Mangalia Marina is a harbour for yachts and small boats(up to 18 m long) located on the Black Sea coast. It is the most modern tourist harbour in Romania.

The Jiwani Coastal Wetland is a wetland located in Balochistan, Pakistan, near the town of Jiwani. The site is one of the 19 Ramsar sites in Pakistan and was inducted in 2001.

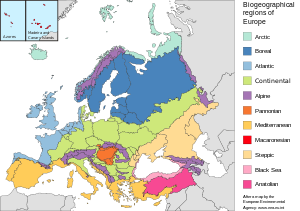
The Boreal Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region of Northern Europe that consists primarily of coniferous forests and wetlands.

The biogeographic regions of Europe are biogeographic regions defined by the European Environment Agency. They were initially limited to the European Union member states, but later extended to cover all of Europe west of the Urals, including all of Turkey. The map of biogeographic regions is deliberately simplified and ignores local anomalies. It is intended primarily as a framework for coordinating and reporting overall results of conservation efforts.

The Atlantic Biogeographic Region is the biogeographic region of Europe bordering the Atlantic Ocean and North Sea.

The Continental Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of Europe that extend in a broad band from east to west through the center of the continent.

The Pannonian Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region, as defined by the European Environment Agency. It covers the lowlands of the Pannonian Basin centered on Hungary.

The Steppic Biogeographic Region is a biogeographic region of Europe, as defined by the European Environment Agency.