
MySQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A relational database organizes data into one or more data tables in which data may be related to each other; these relations help structure the data. SQL is a language that programmers use to create, modify and extract data from the relational database, as well as control user access to the database. In addition to relational databases and SQL, an RDBMS like MySQL works with an operating system to implement a relational database in a computer's storage system, manages users, allows for network access and facilitates testing database integrity and creation of backups.
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling structured data, i.e., data incorporating relations among entities and variables.
A distributed database is a database in which data is stored across different physical locations. It may be stored in multiple computers located in the same physical location ; or maybe dispersed over a network of interconnected computers. Unlike parallel systems, in which the processors are tightly coupled and constitute a single database system, a distributed database system consists of loosely coupled sites that share no physical components.

An object–relational database (ORD), or object–relational database management system (ORDBMS), is a database management system (DBMS) similar to a relational database, but with an object-oriented database model: objects, classes and inheritance are directly supported in database schemas and in the query language. Also, as with pure relational systems, it supports extension of the data model with custom data types and methods.
In computing, Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard application programming interface (API) for accessing database management systems (DBMS). The designers of ODBC aimed to make it independent of database systems and operating systems. An application written using ODBC can be ported to other platforms, both on the client and server side, with few changes to the data access code.
A stored procedure is a subroutine available to applications that access a relational database management system (RDBMS). Such procedures are stored in the database data dictionary.
Oracle Rdb is a relational database management system for the OpenVMS operating system. It was originally released by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1984 as VAX Rdb/VMS.
ADO.NET is a data access technology from the Microsoft .NET Framework that provides communication between relational and non-relational systems through a common set of components. ADO.NET is a set of computer software components that programmers can use to access data and data services from a database. It is a part of the base class library that is included with the Microsoft .NET Framework. It is commonly used by programmers to access and modify data stored in relational database systems, though it can also access data in non-relational data sources. ADO.NET is sometimes considered an evolution of ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) technology, but was changed so extensively that it can be considered an entirely new product.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of relational database management systems. Please see the individual products' articles for further information. Unless otherwise specified in footnotes, comparisons are based on the stable versions without any add-ons, extensions or external programs.

Microsoft Data Access Components is a framework of interrelated Microsoft technologies that allows programmers a uniform and comprehensive way of developing applications that can access almost any data store. Its components include: ActiveX Data Objects (ADO), OLE DB, and Open Database Connectivity (ODBC). There have been several deprecated components as well, such as the Jet Database Engine, MSDASQL, and Remote Data Services (RDS). Some components have also become obsolete, such as the former Data Access Objects API and Remote Data Objects.

Virtuoso Universal Server is a middleware and database engine hybrid that combines the functionality of a traditional relational database management system (RDBMS), object–relational database (ORDBMS), virtual database, RDF, XML, free-text, web application server and file server functionality in a single system. Rather than have dedicated servers for each of the aforementioned functionality realms, Virtuoso is a "universal server"; it enables a single multithreaded server process that implements multiple protocols. The free and open source edition of Virtuoso Universal Server is also known as OpenLink Virtuoso. The software has been developed by OpenLink Software with Kingsley Uyi Idehen and Orri Erling as the chief software architects.
Oracle Data Mining (ODM) is an option of Oracle Database Enterprise Edition. It contains several data mining and data analysis algorithms for classification, prediction, regression, associations, feature selection, anomaly detection, feature extraction, and specialized analytics. It provides means for the creation, management and operational deployment of data mining models inside the database environment.
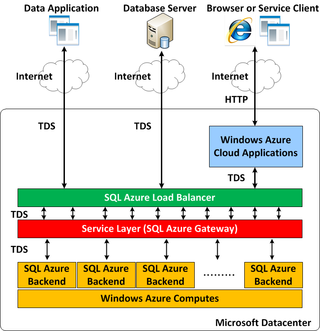
Microsoft Azure SQL Database is a managed cloud database (PaaS) cloud-based Microsoft SQL Servers, provided as part of Microsoft Azure services. The service handles database management functions for cloud based Microsoft SQL Servers including upgrading, patching, backups, and monitoring without user involvement.
A database shard, or simply a shard, is a horizontal partition of data in a database or search engine. Each shard may be held on a separate database server instance, to spread load.
NoSQL is an approach to database design that focuses on providing a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases. Instead of the typical tabular structure of a relational database, NoSQL databases house data within one data structure. Since this non-relational database design does not require a schema, it offers rapid scalability to manage large and typically unstructured data sets. NoSQL systems are also sometimes called "Not only SQL" to emphasize that they may support SQL-like query languages or sit alongside SQL databases in polyglot-persistent architectures.
A cloud database is a database that typically runs on a cloud computing platform and access to the database is provided as-a-service. There are two common deployment models: users can run databases on the cloud independently, using a virtual machine image, or they can purchase access to a database service, maintained by a cloud database provider. Of the databases available on the cloud, some are SQL-based and some use a NoSQL data model.
A blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records (blocks) that are securely linked together via cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Since each block contains information about the previous block, they effectively form a chain, with each additional block linking to the ones before it. Consequently, blockchain transactions are resistant to alteration because, once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be changed retroactively without altering all subsequent blocks and obtaining network consensus to accept these changes. This protects blockchains against nefarious activities such as creating assets "out of thin air", double-spending, counterfeiting, fraud, and theft.
The Yahoo! Cloud Serving Benchmark (YCSB) is an open-source specification and program suite for evaluating retrieval and maintenance capabilities of computer programs. It is often used to compare the relative performance of NoSQL database management systems.

Oracle Cloud is a cloud computing service offered by Oracle Corporation providing servers, storage, network, applications and services through a global network of Oracle Corporation managed data centers. The company allows these services to be provisioned on demand over the Internet.





