Related Research Articles

Le Rhône was the name given to a series of rotary aircraft engines built between 1910 and 1920. Le Rhône series engines were originally sold by the Société des Moteurs Le Rhône and, following a 1914 corporate buyout, by its successor company, Gnome et Rhône. During World War I, more than 22,000 nine cylinder Le Rhône engines were built, with the type far outselling Gnome et Rhône's other main wartime engine series, the Gnome Monosoupape.

The Avro Type E, Type 500, and Type 502 made up a family of early British military aircraft, regarded by Alliott Verdon Roe as his firm's first truly successful design. It was a forerunner of the Avro 504, one of the outstanding aircraft of the First World War.

The Bristol T.B.8, or Bristol-Coanda T.B.8 was an early British biplane built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company and designed by the Romanian Henri Coandă. Fifty four Bristol T.B.8s were built, being mainly used as a trainer. A small number of Bristol T.B.8s were briefly used as bombers at the start of the World War I by the Royal Naval Air Service.

The Morane-Borel monoplane was an early French single-engine, single-seat aircraft. It was flown in several European air races.

The Borel military monoplane was a French single-engine, two-seat aircraft designed shortly before World War I in response to a French Army requirement for an aircraft to seek and destroy enemy balloon airships.

The Borel Hydro-monoplane was a French seaplane produced in 1912.

The Bristol Prier monoplane was an early British aircraft produced in a number of single- and two-seat versions.

The Bristol Gordon England biplanes were a series of early British military biplane aircraft designed by Eric Gordon England for the Bristol Aeroplane Company that first flew in 1912. Designed for easy ground transport, the aircraft could be quickly disassembled.
The Grahame-White Baby was an early British aircraft designed by pioneer aviator Claude Grahame-White in 1910.

The Royal Aircraft Factory B.E.8 was a British two-seat single-engined general purpose biplane of the First World War, designed by John Kenworthy at the Royal Aircraft Factory in 1913. Small numbers were used by the Royal Flying Corps over the Western Front in the first year of the war, with the type being used as a trainer until 1916.

The FBA Type A and the similar Type B and C were a family of reconnaissance flying boats produced in France prior to and during World War I.
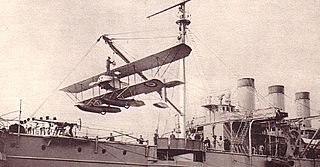
The Caudron J Marine was an amphibious, two-seat, biplane equipped with floats and wheels, similar to the earlier Caudron J floatplane.
The Borel Bo.11 was a French two-seat general purpose monoplane designed and built by Etablissements Borel.

The Royal Aircraft Factory B.E.3 was a single-engined rotary engined biplane developed by the British Royal Aircraft Factory prior to the First World War. The B.E.4 and B.E.7 were virtually identical aircraft that differed only in the engine fitted.

The Paulhan-Tatin Aéro-Torpille No.1,, was a French experimental aircraft built in 1911 as a collaboration between the famous pilot Louis Paulhan and Victor Tatin, a scientist who had experimented with various types of flying models and in 1879 had made the first model aircraft to take off under its own power.

The Ponnier L.1 was an early French biplane single seat scout, built just before World War I. It did not reach production.

The Ponnier D.III was a French monoplane racing aircraft, designed to compete in the 1913 Gordon Bennett Trophy race. It finished a close second.

The Hanriot D.I was a French monoplane racing aircraft, designed in France in 1912 and strongly influenced by Nieuport practice. Examples were built and raced both in France and the UK during 1912.

The Caudron Types M and N were small, fast French sports monoplanes, flown 1911–13 under a wide range of engine powers. There was also a military version.

The Morane-Borel military monoplane was an unsuccessful French single-engine, multi-seat prototype aircraft built in 1911 for the Reims Military Aviation Competition hosted by the French Army. The aircraft only met one of the requirements and was eliminated from the competition.
References
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 193.
- Gunston, Bill (1993). World Encyclopedia of Aircraft Manufacturers. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. p. 54.
- Contemporary diagram published in l'Aérophile, date unknown