
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.

Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufactured sewing threads may be finished with wax or other lubricants to withstand the stresses involved in sewing. Embroidery threads are yarns specifically designed for needlework. Yarn can be made of a number of natural or synthetic materials, and comes in a variety of colors and thicknesses. Although yarn may be dyed different colours, most yarns are solid coloured with a uniform hue.

Worsted is a high-quality type of wool yarn, the fabric made from this yarn, and a yarn weight category. The name derives from Worstead, a village in the English county of Norfolk. That village, together with North Walsham and Aylsham, formed a manufacturing centre for yarn and cloth in the 12th century, when pasture enclosure and liming rendered the East Anglian soil too rich for the older agrarian sheep breeds. In the same period, many weavers from the County of Flanders moved to Norfolk. "Worsted" yarns/fabrics are distinct from woollens : the former is considered stronger, finer, smoother, and harder than the latter.

Mohair is a fabric or yarn made from the hair of the Angora goat. Both durable and resilient, mohair is notable for its high luster and sheen, and is often used in fiber blends to add these qualities to a textile. Mohair takes dye exceptionally well. It feels warm in winter as it has excellent insulating properties, while its moisture-wicking properties allow it to remain cool in summer. It is durable, naturally elastic, flame-resistant and crease-resistant. It is considered a luxury fiber, like cashmere, angora, and silk, and can be more expensive than most sheep's wool.

Wool classing is the production of uniform, predictable, low-risk lines of wool, carried out by examining the characteristics of the wool in its raw state and classing (grading) it accordingly. Wool classing is done by a wool classer.

Cashmere wool, usually simply known as cashmere, is a fiber obtained from cashmere goats, pashmina goats, and some other breeds of goat. It has been used to make yarn, textiles and clothing for hundreds of years. Cashmere is closely associated with the Kashmir shawl, the word "cashmere" deriving from an anglicization of Kashmir, when the Kashmir shawl reached Europe in the 19th century. Both the soft undercoat and the guard hairs may be used; the softer hair is reserved for textiles, while the coarse guard hair is used for brushes and other non-apparel purposes.

Textile manufacturing is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products.

The spinning mule is a machine used to spin cotton and other fibres. They were used extensively from the late 18th to the early 20th century in the mills of Lancashire and elsewhere. Mules were worked in pairs by a minder, with the help of two boys: the little piecer and the big or side piecer. The carriage carried up to 1,320 spindles and could be 150 feet (46 m) long, and would move forward and back a distance of 5 feet (1.5 m) four times a minute.

The Romney, formerly called the Romney Marsh sheep but generally referred to by the local farmers as the Kent, is a breed of sheep originating in England. The Romney is a "long-wool" breed recognized in England by 1800. Exported to other continents, the Romney is an economically important sheep breed, especially to the sheep-meat and wool export trades of New Zealand.

The Targhee is an American breed of domestic sheep. It was developed in the early twentieth century at the U.S. Sheep Experiment Station of the Agricultural Research Service of the United States Department of Agriculture at Dubois, Idaho, and is named after the Targhee National Forest which surrounds it. It is a dual-purpose breed, with heavy, medium-quality wool and good meat production characteristics. It is hardy and well-suited to the ranges of the West where it was developed. It is kept mainly in Montana, Wyoming and South Dakota, and is reared primarily for wool.

A micron (micrometre) is the measurement used to express the diameter of wool fibre. Fine wool fibers have a low micron value. Fibre diameter is the most important characteristic of wool in determining its value.
Spinning count is a measure of fibre fineness and distribution developed by the English. It is defined as the number of hanks of yarn that can be spun from a pound of wool. A hank of wool is 560 yards long. In theory a pound of 62s wool could produce 34720 yards of yarn.

Open-end spinning is a technology for creating yarn without using a spindle. It was invented and developed in Czechoslovakia in Výzkumný ústav bavlnářský / Cotton Research Institute in Ústí nad Orlicí in 1963.
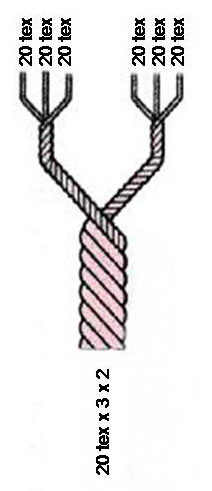
Textile fibers, threads, yarns and fabrics are measured in a multiplicity of units.

Combing is a method for preparing carded fibre for spinning. Combing aligns fibers in parallel before spinning to produce a smoother, stronger, and more lustrous yarn. The process of combing is accompanied by gilling, a process of evening out carded or combed top making it suitable for spinning. Combing separates out short fibres by means of a rotating ring or rectilinear row of steel pins. The fibres in the 'top' it produces have been straightened and lie parallel to each other. When combing wool, the discarded short fibres are called noils, and are ground up into shoddy.
A staple fiber is a textile fiber of discrete length. The opposite is a filament fiber, which comes in continuous lengths. Staple length is a characteristic fiber length of a sample of staple fibers. A fiber is made up of natural substances and is known for being longer than it is wide. It is an essential criterion in yarn spinning, and aids in cohesion and twisting. Compared to synthetic fibers, natural fibers tend to have different and shorter lengths. The quality of natural fibers like cotton is categorized on staple length such as short, medium, long staple, and extra-long. Gossypium barbadense, one of several cotton species, produces extra-long staple fibers. The staple fibers may be obtained from natural and synthetic sources. In the case of synthetics and blends, the filament yarns are cut to a predetermined length.

Alpaca fleece is the natural fiber harvested from an alpaca. There are two different types of alpaca fleece. The most common fleece type comes from a Huacaya. Huacaya fiber grows and looks similar to sheep wool in that the animal looks "fluffy". The second type of alpaca is Suri and makes up less than 10% of the South American alpaca population. Suri fiber is more similar to natural silk and hangs off the body in locks that have a dreadlock appearance. While both fibers can be used in the worsted milling process using light weight yarn or thread, Huacaya fiber can also be used in a woolen process and spun into various weight yarns. It is a soft, durable, luxurious and silky natural fiber.
An S number on the label of wool suits or other tailored apparel, wool fabric, or yarn, indicates the fineness of the wool fiber used in the making of the apparel, as measured by its maximum diameter in micrometres. Fiber fineness is one of the factors determining the quality and performance of a wool product. In recent years it has also become an important marketing device used by many mills, garment makers, and retailers. The S number appears as a plural with an s or 's following the number, such as 100s or 100's.

Bradford Industrial Museum, established 1974 in Moorside Mills, Eccleshill, Bradford, United Kingdom, specializes in relics of local industry, especially printing and textile machinery, kept in working condition for regular demonstrations to the public. There is a Horse Emporium in the old canteen block plus a shop in the mill, and entry is free of charge.

A thread is a long strand of material, often composed of several filaments or fibres, used for joining, creating or decorating textiles. In early humanity Egyptians were known for creating thread using plant fibers, wool and hair. Today, thread can also be made of many different materials including but not limited to cotton, wool, linen, nylon, silk, polyester etc. There are also metal threads, which can be made of fine wire.
















