Related Research Articles
Royal Caribbean International (RCI), also formerly known as Royal Caribbean Cruise Line (RCCL), is a cruise line brand founded in 1968 in Norway and organised as a wholly owned subsidiary of Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd. (RCCL) since 1997. Based in Miami, Florida, United States, it is the largest cruise line by revenue and second largest by passengers counts. In 2018, Royal Caribbean International controlled 19.2% of the worldwide cruise market by passengers and 14.0% by revenue. It also operates the four largest passenger ships in the world. As of July 2019, the line operates twenty-six ships and has six additional ships on order.
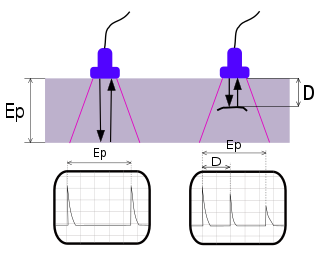
Ultrasonic testing (UT) is a family of non-destructive testing techniques based on the propagation of ultrasonic waves in the object or material tested. In most common UT applications, very short ultrasonic pulse-waves with center frequencies ranging from 0.1-15 MHz, and occasionally up to 50 MHz, are transmitted into materials to detect internal flaws or to characterize materials. A common example is ultrasonic thickness measurement, which tests the thickness of the test object, for example, to monitor pipework corrosion.

The Germanischer Lloyd SE was a classification society based in the city of Hamburg, Germany. It ceased to exist as an independent entity on September 2013 as a result of its merger with Norway's DNV to become the present-day DNV GL.
Polar Class (PC) refers to the ice class assigned to a ship by a classification society based on the Unified Requirements for Polar Class Ships developed by the International Association of Classification Societies (IACS). Seven Polar Classes are defined in the rules, ranging from PC 1 for year-round operation in all polar waters to PC 7 for summer and autumn operation in thin first-year ice.

MV TransAtlantic is a U.S.-flagged container ship owned and operated by TransAtlantic Lines LLC. The 100-metre (330 ft) long ship was built at Wuhu Shipyard in Wuhu, China in 1997 as Steamers Future. Originally owned by Singapore's Keppel Corporation, she has had three owners, been registered under three flags, and been renamed ten times.
Henrik Overgaard Madsen is a businessperson, engineer, Member of the Board of Aker Solutions and was chief executive officer of DNV GL between 2006 and 2015.

Integrated Operations in the High North is a unique collaboration project that during a four-year period starting May 2008 is working on designing, implementing and testing a Digital Platform for what in the Upstream Oil and Gas Industry is called the next or second generation of Integrated Operations. The work on the Digital platform is focussed on capture, transfer and integration of Real-time data from the remote production installations to the decision makers. A risk evaluation across the whole chain is also included. The platform is based on open standards and enables a higher degree of interoperability. Requirements for the digital platform come from use cases defined within the Drilling and Completion, Reservoir and Production and Operations and Maintenance domains. The platform will subsequently be demonstrated through pilots within these three domains.
This is a timeline of the world's largest passenger ships based upon internal volume, initially measured by gross register tonnage and later by gross tonnage. This timeline reflects the largest extant passenger ship in the world at any given time. If a given ship was superseded by another, scrapped, or lost at sea, it is then succeeded. Some records for tonnage outlived the ships that set them - notably the SS Great Eastern, and RMS Queen Elizabeth.

The economy of Greater Oslo plays an important part to Norway's national economy.

Athena is a 7,805 GT factory ship which was built in 1992. In October 2010, she caught fire off the Isles of Scilly. In May 2011 she caught fire while lying at the harbour of Runavík in Skálafjørður, Faroe Islands. It happened at night, and people who lived on the other side of the fjord, where the smoke was headed, were evacuated. Some months later the ship was sold to Smedegaarden in Esbjerg, which took her apart.
Acoustic resonance technology (ART) is an acoustic inspection technology developed by Det Norske Veritas over the past 20 years. ART exploits the phenomenon of half-wave resonance, whereby a suitably excited resonant target exhibits longitudinal resonances at certain frequencies characteristic of the target's thickness. Knowing the speed of sound in the target material, the half-wave resonant frequencies can be used to calculate the target's thickness.

DNV GL is an international accredited registrar and classification society headquartered in Høvik, Norway. The company currently has about 14,500 employees and 350 offices operating in more than 100 countries, and provides services for several industries including maritime, renewable energy, oil & gas, electrification, food & beverage and healthcare. It was created in 2013 as a result of a merger between two leading organizations in the field — Det Norske Veritas (Norway) and Germanischer Lloyd (Germany).
When a ship is purchased for importing and exporting goods, a ship management team is required to maintain and operate the vessels. The function of the management team is to provide the owner with support throughout the occupancy or charter of the vessel. Vessels can range in sizes and function.

Valemax ships are a fleet of very large ore carriers (VLOC) owned or chartered by the Brazilian mining company Vale S.A. to carry iron ore from Brazil to European and Asian ports. With a capacity ranging from 380,000 to 400,000 tons deadweight, the vessels meet the Chinamax standard of ship measurements for limits on draft and beam. Valemax ships are the largest bulk carriers ever constructed, when measuring deadweight tonnage or length overall, and are amongst the longest ships of any type currently in service.
Integrated Software Dependent Systems (ISDS) is an offshore standard (DNV-OS-D203) and recommended practice guideline (DNV-RP-D201) covering systems and software verifications and classification of any integrated system that utilizes extensive software control. The ISDS Recommended Practice (DNV-RP-D201) was launched in 2008 by Det Norske Veritas (DNV), the Norwegian classification society. DNV Offshore Standard OS-D203 launched in April 2010.
Sesam is a software suite for structural and hydrodynamic analysis of ships and offshore structures. It is based on the displacement formulation of the Finite Element Method.
Stiftelsen mean Foundation in Scandinavian languages.

Tore Ulstein is deputy CEO and Chairman of the Board in Ulstein Group and Ulstein Shipping. Tore Ulstein is son of Ulstein Group's previous CEO, Idar Ulstein (1934–2012).
Electro Scan Inc. is a designer and manufacturer of water and sewer machine-intelligent pipeline inspection devices and provider of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) based cloud reporting. The company utilizes electric currents to detect leaks in non-conductive sewer pipes. The company is based in Sacramento, California, with additional offices in London, England and Toronto, Canada.
References
- ↑ http://www.tu.no/industri/article126912.ece Breivoll Inspection Technologies wins 2007 engineering award
- ↑ http://www.forskningsradet.no/en/Funding/naeringsphd/1235469223842 Archived 2012-02-18 at the Wayback Machine Description of the Norwegian Industrial Ph.D. program