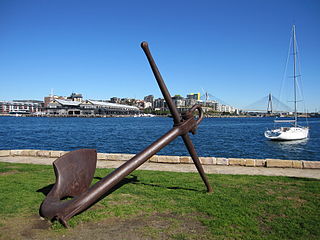Skidmore, Owings & Merrill LLP (SOM) is an American architectural, urban planning and engineering firm. It was founded in 1936 by Louis Skidmore and Nathaniel Owings in Chicago. In 1939, they were joined by engineer John Merrill. The firm opened its second office, in New York City, in 1937 and has since expanded, with additional offices in San Francisco, Los Angeles, Washington, D.C., London, Melbourne, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Seattle, and Dubai.

Beatrix Cadwalader Farrand was an American landscape gardener and landscape architect. Her career included commissions to design about 110 gardens for private residences, estates and country homes, public parks, botanic gardens, college campuses, and the White House. Only a few of her major works survive: Dumbarton Oaks in Washington, D.C., the Abby Aldrich Rockefeller Garden on Mount Desert, Maine, the restored Farm House Garden in Bar Harbor, the Peggy Rockefeller Rose Garden at the New York Botanical Garden, and elements of the campuses of Princeton, Yale, and Occidental.

Landscape architecture is the design of outdoor areas, landmarks, and structures to achieve environmental, social-behavioural, or aesthetic outcomes. It involves the systematic design and general engineering of various structures for construction and human use, investigation of existing social, ecological, and soil conditions and processes in the landscape, and the design of other interventions that will produce desired outcomes.

Humphry Repton was the last great designer of the classic phase of the English landscape garden, often regarded as the successor to Capability Brown. His style is thought of as the precursor of the more intricate and eclectic styles of the 19th century. His first name is often incorrectly spelt "Humphrey".

A landscape architect is a person who is educated in the field of landscape architecture. The practice of landscape architecture includes: site analysis, site inventory, site planning, land planning, planting design, grading, storm water management, sustainable design, construction specification, and ensuring that all plans meet the current building codes and local and federal ordinances.

Landscape design is an independent profession and a design and art tradition, practiced by landscape designers, combining nature and culture. In contemporary practice, landscape design bridges the space between landscape architecture and garden design.

The English landscape garden, also called English landscape park or simply the English garden, is a style of "landscape" garden which emerged in England in the early 18th century, and spread across Europe, replacing the more formal, symmetrical French formal garden which had emerged in the 17th century as the principal gardening style of Europe. The English garden presented an idealized view of nature. Created and pioneered by William Kent and others, the "informal" garden style originated as a revolt against the architectural garden and drew inspiration from landscape paintings by Salvator Rosa, Claude Lorrain, and Nicolas Poussin.

Laurie Olin is an American landscape architect. He has worked on landscape design projects at diverse scales, from private residential gardens to public parks and corporate/museum campus plans.

The Landscape Institute (LI) is a UK based professional body for the landscape profession. Its membership includes landscape architects, urban designers, landscape planners, landscape scientists and landscape managers. The LI also has a category for academic members.

Sir Geoffrey Allan Jellicoe was an English architect, town planner, landscape architect, garden designer, landscape and garden historian, lecturer and author. His strongest interest was in landscape and garden design.

John St. Bodfan Gruffydd was a Welsh landscape architect.

Span Developments Limited was a British property development company formed in the late 1950s by Geoffrey Townsend working in long and close partnership with Eric Lyons as consultant architect. During its most successful period in the 1960s, Span built over 2,000 homes in London, Surrey, Kent and East Sussex – mainly two- and three-bedroom single-family homes and apartment buildings.
Karl Linn was an American landscape architect, psychologist, educator, and community activist, best known for inspiring and guiding the creation of "neighborhood commons" on vacant lots in East Coast inner cities during the 1960s through 1980s. Employing a strategy he called "urban barnraising," he engaged neighborhood residents, volunteer professionals, students, youth teams, social activists, and community gardeners in envisioning, designing, and constructing instant, temporary, and permanent gathering spaces in neighborhoods, on college campuses, and at sites of major conferences and events. "Linn is considered 'Father of American Participatory Architecture' by many academic colleagues and architectural and environmental experts of the National Endowment for the Arts."

The Edsel and Eleanor Ford House is a mansion located at 1100 Lake Shore Drive in Grosse Pointe Shores, northeast of Detroit, Michigan; it stands on the site known as "Gaukler Point", on the shore of Lake St. Clair. The house became the new residence of the Edsel and Eleanor Ford family in 1928. Edsel Ford was the son of Henry Ford and an executive at Ford Motor Company. The estate's buildings were designed by architect Albert Kahn, its site plan and gardens by renowned landscape designer Jens Jensen. The property was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979, and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 2016.

Pietro Porcinai is renowned as one of the most outstanding Italian landscape architects of the twentieth century. He designed a wide variety of projects on the most diverse scales: gardens and public parks, industrial districts, hotels and tourist villages, motorways and agricultural areas. The hundreds of projects implemented in Italy and abroad comprise the most extraordinary “landscaped” gardens, perfectly integrated within the surroundings and so natural as to appear untouched by human hand.

Foodscaping is a modern term for the practice of integrating edible plants into ornamental landscapes. It is also referred to as edible landscaping and has been described as a crossbreed between landscaping and farming. As an ideology, foodscaping aims to show that edible plants are not only consumable but can also be appreciated for their aesthetic qualities. Foodscaping spaces are seen as multi-functional landscapes which are visually attractive and also provide edible returns. Foodscaping is a great way to provide fresh food in an affordable way.

The Field Elm cultivar Ulmus minor 'Dicksonii', commonly known as Dickson's Golden Elm, is a yellow-leaved tree raised in Chester in 1900 by Dickson's Nursery, which distributed it from the autumn of 1907 as 'Golden Cornish Elm'. 'Cornish Elm' was the name often given in error to Guernsey or Wheatley Elm by the local authorities who planted the latter extensively, an error which may have influenced the choice of name by Dickson's nursery. 'Dicksonii' is usually listed as a variety of Guernsey Elm rather than Cornish Elm, Bean giving 'Wheatleyi Aurea' as a synonym, and Hillier 'Sarniensis Aurea' and later U. × sarniensis 'Dicksonii'. Clibrans' nursery of Altrincham, however, described it (1922) as otherwise identical "in habit and constitution" to 'type' Cornish Elm. The Späth nursery of Berlin distributed it from c.1913 as U. campestris cornubiensis Dicksonii. The nursery Messieurs Otin père et fils of Saint-Étienne sold an Ulmus Wheatleyi aurea pyramidalis, with leaves marbled yellow, in 1882, earlier than Dickson's introduction.
John Andrew Brookes, MBE was a garden and landscape designer. He started designing gardens and landscapes in the late 1950s and designed thousands of gardens. He also taught and lectured about horticulture, landscape and interior design.
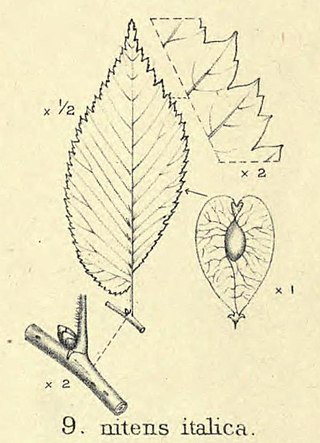
Ulmus minorvar.italica was first described by Augustine Henry in 1913, as a 'variety' of field elm from Italy, Spain, Portugal and Algeria. He called it Ulmus nitens var. italica, 'Mediterranean Elm'. The variety was accepted by Krüssman (1984), despite the wide source-area claimed for it, as a non-clonal cultivar, U. carpinifolia var. italicaHenry. Bean (1988), however, considered it "a variety of rather dubious standing", and it was ignored by Richens (1983), who listed instead a "small-leaved U. minor of Spain" and a "narrow-leaved U. minor of northern and central Italy", as well as "the densely hairy leaved U. minor of southern Italy", the latter being Ulmus minor subsp. canescens, formerly Melville's Ulmus canescens.
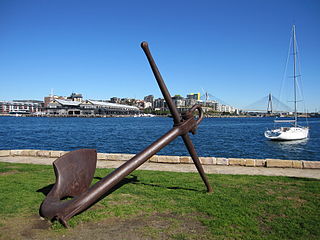
Iloura Reserve is a heritage-listed public reserve on the site of a former timber yard at 10–20 Weston Street, Balmain East, Inner West Council, Sydney New South Wales, Australia. Following the resumption of the timber yard for public space in the 1960s, the present reserve was designed and laid out by landscape architect Bruce Mackenzie and constructed in two stages: stage one in 1970 and stage two in 1981. It is also known as Peacock Point and Illoura. The reserve is owned by the Inner West Council. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 29 November 2013.