
The Department of the Treasury (USDT) is the national treasury and finance department of the federal government of the United States, where it serves as an executive department. The department oversees the Bureau of Engraving and Printing and the U.S. Mint. These two agencies are responsible for printing all paper currency and minting coins, while the treasury executes currency circulation in the domestic fiscal system. The USDT collects all federal taxes through the Internal Revenue Service; manages U.S. government debt instruments; licenses and supervises banks and thrift institutions; and advises the legislative and executive branches on matters of fiscal policy. The department is administered by the secretary of the treasury, who is a member of the Cabinet. The treasurer of the United States has limited statutory duties, but advises the Secretary on various matters such as coinage and currency production. Signatures of both officials appear on all Federal Reserve notes.

The chancellor of the Exchequer, often abbreviated to Chancellor, is a senior minister of the Crown within the Government of the United Kingdom, and head of His Majesty's Treasury. As one of the four Great Offices of State, the chancellor is a high-ranking member of the British Cabinet.

The private finance initiative (PFI) was a United Kingdom government procurement policy aimed at creating "public–private partnerships" (PPPs) where private firms are contracted to complete and manage public projects. Initially launched in 1992 by Prime Minister John Major, and expanded considerably by the Blair government, PFI is part of the wider programme of privatisation and financialisation, and presented as a means for increasing accountability and efficiency for public spending.
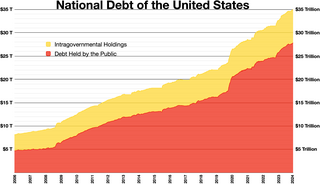
The national debt of the United States is the total national debt owed by the federal government of the United States to Treasury security holders. The national debt at any point in time is the face value of the then-outstanding Treasury securities that have been issued by the Treasury and other federal agencies. The terms "national deficit" and "national surplus" usually refer to the federal government budget balance from year to year, not the cumulative amount of debt. In a deficit year the national debt increases as the government needs to borrow funds to finance the deficit, while in a surplus year the debt decreases as more money is received than spent, enabling the government to reduce the debt by buying back some Treasury securities. In general, government debt increases as a result of government spending and decreases from tax or other receipts, both of which fluctuate during the course of a fiscal year. There are two components of gross national debt:

The State Auditor of North Carolina is a statewide elected office in the U.S. state of North Carolina. The state auditor is a constitutional officer responsible for overseeing and reviewing the financial accounts of all state government agencies. The auditor also conducts performance audits of state agencies, ensures state agencies' accounting conforms with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, evaluates the integrity of computer-generated information, and investigates the misuse of state funds or property. The incumbent is Jessica Holmes, who became state auditor on Dec. 16, 2023.

HM Revenue and Customs is a non-ministerial department of the UK Government responsible for the collection of taxes, the payment of some forms of state support, the administration of other regulatory regimes including the national minimum wage and the issuance of national insurance numbers. HMRC was formed by the merger of the Inland Revenue and HM Customs and Excise, which took effect on 18 April 2005. The department's logo is the St Edward's Crown enclosed within a circle.
A spending review, or occasionally a comprehensive spending review, is a governmental process in the United Kingdom carried out by HM Treasury to set firm expenditure limits and, through public service agreements, define the key improvements that the public can expect from these resources.

The military budget of the United States is the largest portion of the discretionary federal budget allocated to the Department of Defense (DoD), or more broadly, the portion of the budget that goes to any military-related expenditures. The military budget pays the salaries, training, and health care of uniformed and civilian personnel, maintains arms, equipment and facilities, funds operations, and develops and buys new items. The budget funds five branches of the US military: the Army, Navy, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Space Force.

The Comptroller General of the United States is the director of the Government Accountability Office, a legislative-branch agency established by Congress in 1921 to ensure the fiscal and managerial accountability of the federal government.

Sir Daniel Grian Alexander is a former politician who was Chief Secretary to the Treasury between 2010 and 2015. He was the Member of Parliament (MP) for the Inverness, Nairn, Badenoch & Strathspey constituency from 2005 until the general election in May 2015. In his first parliamentary term (2005–2010), Alexander was the Liberal Democrat spokesperson for Work and Pensions (2007–2008), the Chief of Staff to party leader Nick Clegg, and Chair of the Liberal Democrat Manifesto Group (2007–2010).

The United States budget comprises the spending and revenues of the U.S. federal government. The budget is the financial representation of the priorities of the government, reflecting historical debates and competing economic philosophies. The government primarily spends on healthcare, retirement, and defense programs. The non-partisan Congressional Budget Office provides extensive analysis of the budget and its economic effects. It has reported that large budget deficits over the next 30 years are projected to drive federal debt held by the public to unprecedented levels—from 98 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) in 2020 to 195 percent by 2050.

The New Zealand Treasury is the central public service department of New Zealand charged with advising the Government on economic policy, assisting with improving the performance of New Zealand's economy, and managing financial resources. The Minister responsible for the Treasury is the Minister of Finance of New Zealand; however, from 1996 to 2002, there existed a more specific position of Treasurer of New Zealand. The role was created for Winston Peters by the Fourth National Government under Jim Bolger after the 1996 election, and abolished by Helen Clark’s government in 2002.

The Department of the Treasury, also known as The Treasury, is the national treasury and financial department of the federal government of the Commonwealth of Australia. The treasury is responsible for executing economic and fiscal policy, market regulation and the delivery of the federal budget with the department overseeing 16 agencies. The Treasury is one of only two departments that have existed continuously since Federation in 1901, the other being the Department of the Attorney-General.

The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) is the revenue service for the United States federal government, which is responsible for collecting U.S. federal taxes and administering the Internal Revenue Code, the main body of the federal statutory tax law. It is an agency of the Department of the Treasury and led by the Commissioner of Internal Revenue, who is appointed to a five-year term by the President of the United States. The duties of the IRS include providing tax assistance to taxpayers; pursuing and resolving instances of erroneous or fraudulent tax filings; and overseeing various benefits programs, including the Affordable Care Act.
The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget (CRFB) is a non-profit public policy organization based in Washington, D.C. that addresses federal budget and fiscal issues. It was founded in 1981 by former United States Representatives Robert Giaimo (D-CT) and Henry Bellmon (R-OK), and its board of directors includes former Members of Congress and directors of the Office of Management and Budget, the Congressional Budget Office and the Federal Reserve.

The Office for Budget Responsibility (OBR) is a non-departmental public body funded by the UK Treasury, that the UK government established to provide independent economic forecasts and independent analysis of the public finances. It was formally created in May 2010 following the general election and was placed on a statutory footing by the Budget Responsibility and National Audit Act 2011. It is one of a growing number of official independent fiscal watchdogs around the world.
Whole of Government Accounts (WGA) is the annual publication by the United Kingdom Government of the consolidated financial statements of over 5,500 organisations across the public sector. It aims to provide more complete data for fiscal planning by producing consolidated financial statements which are produced in accordance with the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), the system of accounts used internationally by the private sector.
In the United States, the debt ceiling or debt limit is a legislative limit on the amount of national debt that can be incurred by the U.S. Treasury, thus limiting how much money the federal government may pay by borrowing more money, on the debt it already borrowed. The debt ceiling is an aggregate figure that applies to gross debt, which includes debt in the hands of the public and intra-government accounts. About 0.5 percent of the debt is not covered by the ceiling. Because expenditures are authorized by separate legislation, the debt ceiling does not directly limit government deficits. In effect, it can only restrain the Treasury from paying for expenditures and other financial obligations after the limit has been reached, but which have already been approved and appropriated.
The history of the United States debt ceiling deals with movements in the United States debt ceiling since it was created in 1917. Management of the United States public debt is an important part of the macroeconomics of the United States economy and finance system, and the debt ceiling is a limitation on the federal government's ability to manage the economy and finance system. The debt ceiling is also a limitation on the federal government's ability to finance government operations, and the failure of Congress to authorize an increase in the debt ceiling has resulted in crises, especially in recent years.

The Ministry of Finance, abbreviated MOF, is a ministry of the Government of Somalia that is charged with the responsibility for government expenditure and revenue raising. The ministry's role is to develop economic policy and prepare the federal budget. The Ministry of Finance also oversees financial legislation and regulation. Each year in October, the Minister of Finance presents the Somali federal budget to the Parliament.















