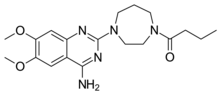
Antiandrogens, also known as androgen antagonists or testosterone blockers, are a class of drugs that prevent androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT) from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the androgen receptor (AR) and/or inhibiting or suppressing androgen production. They can be thought of as the functional opposites of AR agonists, for instance androgens and anabolic steroids (AAS) like testosterone, DHT, and nandrolone and selective androgen receptor modulators (SARMs) like enobosarm. Antiandrogens are one of three types of sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiestrogens and antiprogestogens.

Ergoline is a chemical compound whose structural skeleton is contained in a variety of alkaloids, referred to as ergoline derivatives or ergoline alkaloids. Ergoline alkaloids, one being ergine, were initially characterized in ergot. Some of these are implicated in the condition ergotism, which can take a convulsive form or a gangrenous form. Even so, many ergoline alkaloids have been found to be clinically useful. Annual world production of ergot alkaloids has been estimated at 5,000–8,000 kg of all ergopeptines and 10,000–15,000 kg of lysergic acid, used primarily in the manufacture of semi-synthetic derivatives.
Antihypertensives are a class of drugs that are used to treat hypertension. Antihypertensive therapy seeks to prevent the complications of high blood pressure, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Evidence suggests that reduction of the blood pressure by 5 mmHg can decrease the risk of stroke by 34%, of ischaemic heart disease by 21%, and reduce the likelihood of dementia, heart failure, and mortality from cardiovascular disease. There are many classes of antihypertensives, which lower blood pressure by different means. Among the most important and most widely used medications are thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor antagonists (ARBs), and beta blockers.

Naltrexone, sold under the brand names ReVia and Vivitrol among others, is a medication primarily used to manage alcohol or opioid dependence. An opioid-dependent person should not receive naltrexone before detoxification. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a muscle. Effects begin within 30 minutes. A decreased desire for opioids, though, may take a few weeks.

Prazosin is an alpha-1 blocker medication primarily used to treat high blood pressure, symptoms of an enlarged prostate, and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is a less preferred treatment of high blood pressure. Other uses may include heart failure and Raynaud syndrome. It is taken by mouth.

A selective progesterone receptor modulator (SPRM) is an agent that acts on the progesterone receptor (PR), the biological target of progestogens like progesterone. A characteristic that distinguishes such substances from full receptor agonists and full antagonists is that their action differs in different tissues, i.e. agonist in some tissues while antagonist in others. This mixed profile of action leads to stimulation or inhibition in tissue-specific manner, which further raises the possibility of dissociating undesirable adverse effects from the development of synthetic PR-modulator drug candidates.
Alpha-1 blockers constitute a variety of drugs that block the effect of alpha-1-adrenergic receptors. They are mainly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), hypertension and post-traumatic stress disorder. Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors are present in vascular smooth muscle, the central nervous system, and other tissues. When alpha blockers bind to these receptors in vascular smooth muscle, they cause vasodilation.

Phenoxybenzamine is a non-selective, irreversible alpha blocker.

Tachykinin peptides are one of the largest families of neuropeptides, found from amphibians to mammals. They were so named due to their ability to rapidly induce contraction of gut tissue. The tachykinin family is characterized by a common C-terminal sequence, Phe-X-Gly-Leu-Met-NH2, where X is either an Aromatic or an Aliphatic amino acid. The genes that produce tachykinins encode precursor proteins called preprotachykinins, which are chopped apart into smaller peptides by posttranslational proteolytic processing. The genes also code for multiple splice forms that are made up of different sets of peptides.
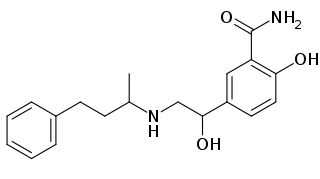
Labetalol is a medication used to treat high blood pressure and in long term management of angina. This includes essential hypertension, hypertensive emergencies, and hypertension of pregnancy. In essential hypertension it is generally less preferred than a number of other blood pressure medications. It can be given by mouth or by injection into a vein.

Integrin α4β1 is an integrin dimer. It is composed of CD49d and CD29. The alpha 4 subunit is 155 kDa, and the beta 1 subunit is 150 kDa.

Tropisetron is a serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonist used mainly as an antiemetic to treat nausea and vomiting following chemotherapy, although it has been used experimentally as an analgesic in cases of fibromyalgia.
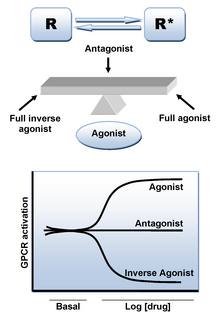
An adrenergic antagonist is a drug that inhibits the function of adrenergic receptors. There are five adrenergic receptors, which are divided into two groups. The first group of receptors are the beta (β) adrenergic receptors. There are β1, β2, and β3 receptors. The second group contains the alpha (α) adrenoreceptors. There are only α1 and α2 receptors. Adrenergic receptors are located near the heart, kidneys, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. There are also α-adreno receptors that are located on vascular smooth muscle.
A sympatholytic drug is a medication that opposes the downstream effects of postganglionic nerve firing in effector organs innervated by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). They are indicated for various functions; for example, they may be used as antihypertensives. They are also used to treat anxiety, such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder and PTSD.
A serotonin antagonist, or serotonin receptor antagonist, is a drug used to inhibit the action at serotonin (5-HT) receptors.

Idazoxan (INN) is a drug which is used in scientific research. It acts as both a selective α2 adrenergic receptor antagonist, and an antagonist for the imidazoline receptor. Idazoxan has been under investigation as an antidepressant, but it did not reach the market as such. More recently, it is under investigation as an adjunctive treatment in schizophrenia. Due to its alpha-2 receptor antagonism it is capable of enhancing therapeutic effects of antipsychotics, possibly by enhancing dopamine neurotransmission in the prefrontal cortex of the brain, a brain area thought to be involved in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia.

Alpha-blockers, also known as α-blockers or α-adrenoreceptor antagonists, are a class of pharmacological agents that act as antagonists on α-adrenergic receptors (α-adrenoceptors).

L-765,314 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the Alpha-1 adrenergic receptor subtype α1B. It has mainly been used to investigate the role of α1B receptors in the regulation of blood pressure. The α1B receptor is also thought to have an important role in the brain; however, L-765,314 does not cross the blood–brain barrier.

Aptazapine (developmental code name CGS-7525A) is a tetracyclic antidepressant (TeCA) which was assayed in clinical trials for the treatment of depression in the 1980s but was never marketed. It is a potent α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist with ~10x the strength of the related compound mianserin and has also been shown to act as a 5-HT2 receptor antagonist and H1 receptor inverse agonist, while having no significant effects on the reuptake of serotonin or norepinephrine. Based on its pharmacological profile, aptazapine may be classified as a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (NaSSA).
A drug class is a set of medications and other compounds that have similar chemical structures, the same mechanism of action, a related mode of action, and/or are used to treat the same disease.