
Cadbury Castle is a Bronze and Iron Age hillfort in the civil parish of South Cadbury in the English county of Somerset. It is a scheduled monument and has been associated with King Arthur's legendary court at Camelot.

Dunkery Beacon at the summit of Dunkery Hill is the highest point on Exmoor and in Somerset, England. It is also the highest point in southern England outside of Dartmoor.

Dolebury Warren is a 90.6 hectares biological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) and ancient monument near the villages of Churchill and Rowberrow in North Somerset, part of South West England. It is owned by the National Trust, who acquired the freehold in 1983, and managed by the Avon Wildlife Trust.

Plainsfield Camp is a possible Iron Age earthwork on the Quantock Hills near Aisholt in Somerset, England.

Dowsborough Camp is an Iron Age hill fort on the Quantock Hills near Nether Stowey in Somerset, England. It has been designated as a Scheduled Monument. The fort and associated round barrow has been added to the Heritage at Risk Register due to vulnerability to vehicle damage and erosion.

Cleeve Toot is an Iron Age univallate hillfort above Goblin Combe, Cleeve, Somerset, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument.
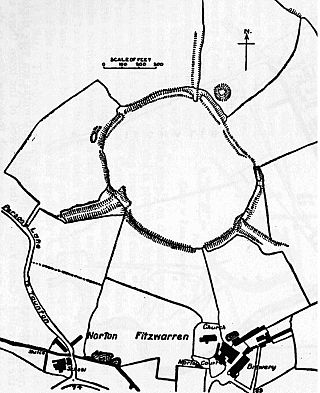
Norton Camp is a Bronze Age hill fort at Norton Fitzwarren near Taunton in Somerset, England.

Bats Castle is an Iron Age hillfort at the top of a 213 metres (699 ft) high hill in the parish of Carhampton south south west of Dunster in Somerset, England.

Black Ball Camp is an Iron Age hillfort South West of Dunster, Somerset, England on the northern summit of Gallox Hill. It is a Scheduled Monument.
Blacker's Hill is an Iron Age hill fort at Chilcompton, 4.5 kilometres (3 mi) south west of Radstock, Somerset, England. It has been designated as a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

Cow Castle is an Iron Age hillfort 5.75 kilometres (4 mi) West South West of Exford, Somerset, England within the Exmoor National Park. It is a Scheduled Monument. It has been added to the heritage at Risk register because of the risk from bracken.

Kenwalch's Castle is probably an Iron Age hill fort that may have been converted into a Roman fortress, near Penselwood, Somerset, England, 6.6 kilometres (4 mi) east south east of Bruton at grid reference ST747335. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. It is believed to be named after Cenwalh of Wessex.

Sweetworthy is the site of two Iron Age hill forts or enclosures at Luccombe, 4 kilometres (2 mi) south of Porlock, Somerset, England. They are on the north-facing slope of Dunkery Hill. One has a single rampart and external ditch, enclosing 0.25 hectares. The rampart is still visible and the ditch on the east side is used as a trackway. There was a defended settlement above the main site.

Kelsborrow Castle is an Iron Age hill fort in Cheshire, northern England. Hill forts were fortified hill-top settlements constructed across Britain during the Iron Age. It is one of only seven hill forts in the county of Cheshire and was probably in use for only a short time. In the 19th century, a bronze palstave was recovered from the site. It is protected as a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

King's Castle is an Iron Age Hillfort 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) east of Wiveliscombe in Somerset, England. It is surrounded by two banks with a ditch between them. The inner wall ranges up to 2.5 metres (8.2 ft) high and the outer wall gets up to 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) high. Arrowheads, scrapers, and borers from as far back as the Neolithic period have been found at the site. A coin hoard of 1139 coins was found in a pot buried 0.30 metres (1 ft) deep.
Grabbist Hillfort is an Iron Age oval hillfort or defended enclosure, west of Dunster in Somerset, England.

Mounsey Castle is an Iron Age irregular triangular earthwork of 1.75 hectares north west of Dulverton, Somerset, England. It has been scheduled as an ancient monument. It has been added to the Heritage at Risk Register.

Long Wood Enclosure is an enclosure which may have been a univallate Iron Age hill fort, in the West Somerset district of Somerset, England. The hill fort is situated approximately 3.5 kilometres (2.2 mi) southwest of the village of Dunster. It has been scheduled as an ancient monument.
West Somerset was a local government district in the English county of Somerset. It merged with Taunton Deane to form Somerset West and Taunton on 1 April 2019.

















