CCDC40 is the gene in humans that encodes the protein named coiled-coil domain containing 40. [5]
CCDC40 is the gene in humans that encodes the protein named coiled-coil domain containing 40. [5]
This gene encodes a protein that is necessary for motile cilia function. It functions in correct left-right axis formation by regulating the assembly of the inner dynein arm and the dynein regulatory complexes, which control ciliary beat. Mutations in this gene cause primary ciliary dyskinesia type 15, a disorder due to defects in cilia motility. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011].

The cilium is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion.
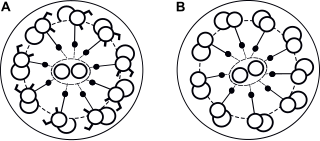
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD) is a rare, autosomal recessive genetic ciliopathy, that causes defects in the action of cilia lining the upper and lower respiratory tract, sinuses, Eustachian tube, middle ear, fallopian tube, and flagella of sperm cells. The alternative name of "immotile ciliary syndrome" is no longer favored as the cilia do have movement, but are merely inefficient or unsynchronized. When accompanied by situs inversus the condition is known as Kartagener syndrome.

Centrosomal protein of 290 kDa is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEP290 gene. CEP290 is located on the Q arm of chromosome 12.

Inversin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the INVS gene.

Dynein axonemal heavy chain 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAH5 gene.

Dynein heavy chain 9, axonemal is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAH9 gene.

Dynein axonemal intermediate chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAI1 gene.

Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 50 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LRRC50 gene.

Radial spoke head protein 9 homolog is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RSPH9 gene.

Radial spoke head protein 4 homolog A, also known as radial spoke head-like protein 3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RSPH4A gene.

Dynein axonemal intermediate chain 2 also known as axonemal dynein intermediate chain 2, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAI2 gene.

Thioredoxin domain-containing protein 3 (TXNDC3), also known as spermatid-specific thioredoxin-2 (Sptrx-2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NME8 gene on chromosome 7.

ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 13B (ARL13B), also known as ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein 2-like 1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARL13B gene.

Dynein axonemal light chain 1, (LC1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAL1 gene.

Kintoun, is a protein that is encoded by the DNAAF2 gene.

Radial spoke head 1 homolog (RSPH1), also known as cancer/testis antigen 79 (CT79) or testis-specific gene A2 protein (TSGA2), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RSPH1 gene.

Coiled-coil domain containing 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC8 gene.

Coiled-coil domain containing 151 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC151 gene.

Dynein axonemal heavy chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNAH1 gene.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires |journal= (help)This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.