
A Beowulf cluster is a computer cluster of what are normally identical, commodity-grade computers networked into a small local area network with libraries and programs installed which allow processing to be shared among them. The result is a high-performance parallel computing cluster from inexpensive personal computer hardware.
MOSIX is a proprietary distributed operating system. Although early versions were based on older UNIX systems, since 1999 it focuses on Linux clusters and grids. In a MOSIX cluster/grid there is no need to modify or to link applications with any library, to copy files or login to remote nodes, or even to assign processes to different nodes – it is all done automatically, like in an SMP.
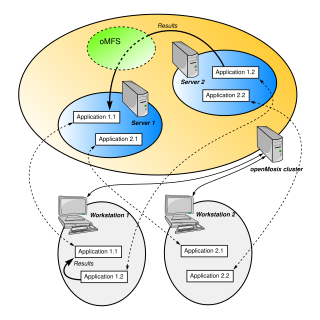
openMosix was a free cluster management system that provided single-system image (SSI) capabilities, e.g. automatic work distribution among nodes. It allowed program processes to migrate to machines in the node's network that would be able to run that process faster. It was particularly useful for running parallel applications having low to moderate input/output (I/O). It was released as a Linux kernel patch, but was also available on specialized Live CDs. openMosix development has been halted by its developers, but the LinuxPMI project is continuing development of the former openMosix code.
OpenSSI is an open-source single-system image clustering system. It allows a collection of computers to be treated as one large system, allowing applications running on any one machine access to the resources of all the machines in the cluster.
Kerrighed is an open source single-system image (SSI) cluster software project. The project started in October 1998 at the Paris research group The French National Institute for Research in Computer Science and Control. From 2006 to 2011, the project was mainly developed by Kerlabs. In January, 2012 the Linux clustering mission of Kerlabs was adopted by a new company: We Cluster, Inc. headquartered in Pacific Grove, California. January 18, 2012: Kerrighed 3.0 has been ported to Ubuntu 12.04 with Linux Kernel v3.2.

Scientific Linux (SL) was a Linux distribution produced by Fermilab, CERN, DESY and by ETH Zurich. It is a free and open-source operating system based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
The Linux-HA project provides a high-availability (clustering) solution for Linux, FreeBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris and Mac OS X which promotes reliability, availability, and serviceability (RAS).
Apache Hadoop is a collection of open-source software utilities that facilitates using a network of many computers to solve problems involving massive amounts of data and computation. It provides a software framework for distributed storage and processing of big data using the MapReduce programming model. Hadoop was originally designed for computer clusters built from commodity hardware, which is still the common use. It has since also found use on clusters of higher-end hardware. All the modules in Hadoop are designed with a fundamental assumption that hardware failures are common occurrences and should be automatically handled by the framework.

The Linux Foundation (LF) is a non-profit technology consortium founded in 2000 as a merger between Open Source Development Labs and the Free Standards Group to standardize Linux, support its growth, and promote its commercial adoption. Additionally, it hosts and promotes the collaborative development of open source software projects. It is a major force in promoting diversity and inclusion in both Linux and the wider open source software community.

A computer cluster is a set of computers that work together so that they can be viewed as a single system. Unlike grid computers, computer clusters have each node set to perform the same task, controlled and scheduled by software.
BioSLAX is a Live CD/Live DVD/Live USB comprising a suite of more than 300 bioinformatics tools and application suites. It has been released by the Bioinformatics Resource Unit of the Life Sciences Institute (LSI), National University of Singapore (NUS) and is bootable from any PC that allows a CD/DVD or USB boot option and runs the compressed Slackware flavour of the Linux Operating System (OS), also known as Slax. Slax was created by Tomáš Matějíček in the Czech Republic using the Linux Live Scripts which he also developed. The BioSLAX derivative was created by Mark De Silva, Lim Kuan Siong and Tan Tin Wee.
OpenWrt is an open-source project for embedded operating systems based on Linux, primarily used on embedded devices to route network traffic. The main components are Linux, util-linux, musl, and BusyBox. All components have been optimized to be small enough to fit into the limited storage and memory available in home routers.

OpenShift is a family of containerization software products developed by Red Hat. Its flagship product is the OpenShift Container Platform — an on-premises platform as a service built around Linux containers orchestrated and managed by Kubernetes on a foundation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux. The family's other products provide this platform through different environments: OKD serves as the community-driven upstream, OpenShift Online is the platform offered as software as a service, and OpenShift Dedicated is the platform offered as a managed service.
Docker is a set of platform as a service (PaaS) products that use OS-level virtualization to deliver software in packages called containers. The service has both free and premium tiers. The software that hosts the containers is called Docker Engine. It was first started in 2013 and is developed by Docker, Inc.
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration system for automating software deployment, scaling, and management. Google originally designed Kubernetes, but the Cloud Native Computing Foundation now maintains the project.

Proxmox Virtual Environment is an open-source software server for virtualization management. Is a hosted hypervisor Type-1 that runs on x64 versions of Windows and Linux operating systems and others. It is a Debian-based Linux distribution with a modified Ubuntu LTS kernel and allows deployment and management of virtual machines and containers. Proxmox VE includes a web console and command-line tools, and provides a REST API for third-party tools. Two types of virtualization are supported: container-based with LXC, and full virtualization with KVM. It includes a web-based management interface.

The ONOS project is an open source community hosted by The Linux Foundation. The goal of the project is to create a software-defined networking (SDN) operating system for communications service providers that is designed for scalability, high performance and high availability.

OpenIO offers object storage for a wide range of high-performance applications. OpenIO was founded in 2015 by Laurent Denel (CEO), Jean-François Smigielski (CTO) and five other co-founders; it has leveraged open source software, developed since 2006, based on a grid technology that enables dynamic behaviour and supports heterogenous hardware. In October 2017 OpenIO completed a $5 million funding round. In July 2020 OpenIO has been acquired by OVH.
Container Linux is a discontinued open-source lightweight operating system based on the Linux kernel and designed for providing infrastructure to clustered deployments, while focusing on automation, ease of application deployment, security, reliability and scalability. As an operating system, Container Linux provided only the minimal functionality required for deploying applications inside software containers, together with built-in mechanisms for service discovery and configuration sharing.











