Mindanao is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao has a population of 26,252,442 people, while the entire island group has an estimated population of 27,021,036 according to the 2021 census.
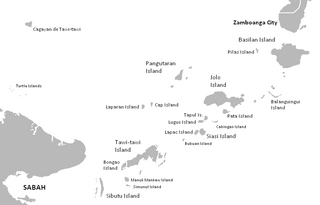
The Sulu Archipelago is a chain of islands in the Pacific Ocean, in the southwestern Philippines. The archipelago forms the northern limit of the Celebes Sea and southern limit of the Sulu Sea. The Sulu Archipelago islands are within the Mindanao island group, consisting of the provinces of Basilan, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi; hence the archipelago is sometimes referred to as Basulta, derived from the first syllables of the three provinces.

Sulu, officially the Province of Sulu, is a province of the Philippines in the Sulu Archipelago and part of the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM).

Tawi-Tawi, officially the Province of Tawi-Tawi, is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM). The capital of Tawi-Tawi is Bongao.

The Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao was an autonomous region of the Philippines, located in the Mindanao island group of the Philippines, that consisted of five predominantly Muslim provinces: Basilan, Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi. It was the only region that had its own government. The region's de facto seat of government was Cotabato City, although this self-governing city was outside its jurisdiction.

Cotabato City, officially the City of Cotabato, is a third class independent component city in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 325,079 people, making it as the most populated city under the independent component city status.

Mapun, officially the Municipality of Mapun, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Tawi-Tawi, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 30,038 people.

Laguindingan Airport, also referred to as Laguindingan International Airport, is an international airport in Northern Mindanao that serves the cities of Cagayan de Oro, Iligan, and Marawi, as well as the provinces of Misamis Oriental, Lanao del Norte and Bukidnon. The airport is Mindanao's second-busiest airport after Francisco Bangoy International Airport in Davao City. It It is classified as a Class 1 principal airport by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP), a body of the Department of Transportation (DOTr) responsible for implementing policies on civil aviation to assure safe, economic and efficient air travel, and the handling of operations at airports.

Cotabato Airport, also known as Awang Airport, is an airport serving the general area of Cotabato City, North Cotabato and Maguindanao del Norte and Maguindanao del Sur, located in the province of Maguindanao del Norte in the Philippines. It is classified as a Class 1 principal airport by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines, a body of the Department of Transportation that is responsible for the operations of all airports in the Philippines except the major international airports.

Puerto Princesa International Airport is an airport serving the general area of Puerto Princesa, located in the province of Palawan in the Philippines. It is classified as an international airport by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines.

Tuguegarao Airport is an airport serving the general area of Tuguegarao, the capital city of the province of Cagayan in the Philippines. Located along Maharlika Highway, the airport is accessible from adjacent municipalities in Cagayan and northern Isabela. It is classified as a major commercial domestic airport by the Air Transportation Office.

Sanga-Sanga Airport, also known as Tawi-Tawi Airport, is the airport serving the general area of Bongao, the capital of the province of Tawi-Tawi in the Philippines. The airport is classified as a Class 2 principal airport by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP), a body of the Department of Transportation (DOTr) that is responsible for the operations of not only the airport but also of all other airports in the Philippines except the major international airports. It is not an international airport, contrary to its classification by the Tawi-Tawi provincial government. It is located in Sanga-Sanga Island. The airport was formerly referred by the International Air Transport Association (IATA) with the code SGS until the end of 2011, when its IATA code was finally changed to TWT.

Bangsamoro, officially the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, is an autonomous region in the Philippines, located in the southeastern portion of the island of Mindanao.
Malabang Airport is an airport located in the coastal town of Malabang, Lanao del Sur, Philippines. The Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines classifies this 16.05-hectare facility as a community airport.

An autonomous region of the Philippines is a first-level administrative division that has the authority to control a region's culture and economy. The Constitution of the Philippines allows for two autonomous regions: in the Cordilleras and in Muslim Mindanao. Currently, Bangsamoro, which largely consists of the Muslim-majority areas of Mindanao, is the only autonomous region in the country.

The International Monitoring Team (IMT) was a monitoring team composed of 60 members headquartered in Cotabato City, Mindanao of the Philippines to monitor the implementation of peace between the Government of the Philippines (GPH) and one of the largest rebels in the region, the Moro Islamic Liberation Front (MILF) in the Moro conflict. The team is led by Malaysia, followed by Brunei Darussalam, Indonesia, Japan, Libya, Norway and subsequently the European Union.
Wao Airport is an airport serving the general area of Wao, located in the province of Lanao del Sur, Philippines. The Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines classifies this recently constructed facility as a community airport.
Dickson Peñas Hermoso is a Filipino government official and former military official who serves as the head of the Ministry of Transportation and Communications of Bangsamoro. He was also known for being part of the Philippine Army's 6th Infantry Division which was involved in the Moro conflict.
Bangsamoro Airport Authority (BAA) is a regional civil aviation body under the Bangsamoro autonomous region's Ministry of Transportation and Communications. It is tasked to oversee the landside operation of airports in Bangsamoro. It is also run under the supervision of the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP), the civil aviation authority of the Philippines, which maintains the airside operations of all airports in the country including those in Bangsamoro.