
Río Negro is a province of Argentina, located in northern Patagonia. Neighboring provinces are from the south clockwise Chubut, Neuquén, Mendoza, La Pampa and Buenos Aires. To the east lies the Atlantic Ocean.

Chubut is a province in southern Argentina, situated between the 42nd parallel south, the 46th parallel south, the Andes range to the west, and the Atlantic ocean to the east. The province's name derives from the Tehuelche word chupat, meaning "transparent". their description of the Chubut River.

Viedma is the capital and fourth largest city of the Río Negro Province, in northern Patagonia, Argentina. The city has approximately 62,000 inhabitants (2022), and is located on the southern margin of the Negro River, about 30 kilometres off the Atlantic Coast, and 960 km from the city of Buenos Aires on the National Route 3.
Neuquén is the capital city of the Argentine province of Neuquén and of the Confluencia Department, located in the east of the province. It occupies a strip of land west of the confluence of the Limay and Neuquén rivers which form the Río Negro, making it part of the ecoregion of Alto Valle del Río Negro. The city and surrounding area have a population of more than 340,000, making it the largest city in Patagonia. Along with the cities of Plottier and Cipolletti, it is part of the Neuquén – Plottier – Cipolletti conurbation.

Paraná is the capital city of the Argentine province Entre Ríos, located on the eastern shore of the Paraná River, opposite the city of Santa Fe, capital of the neighbouring Santa Fe Province. The city has a population of 247,863.

Trevelin is a town in the western part of the Patagonian Argentine province of Chubut. The town lies on the eastern banks of the Percy River. It is located in the department of Futaleufú, 22 kilometres (14 mi) south of Esquel, and had 6,395 inhabitants at the time of the 2001 census [INDEC] and 7,908 inhabitants in the 2010 census [INDEC].

Esquel is a town in the northwest of Chubut Province in Argentine Patagonia. It is located in Futaleufú Department, of which it is the government seat. The town's name derives from one of two Tehuelche words: one meaning "marsh" and the other meaning "land of burrs", which refers to the many thorny plants including the pimpinella, and the other meaning herbaceous plants whose fruits, when ripe, turn into prickly burrs that stick to the animals' skins and wool or people's clothes as a way of propagation.

The Valdes Peninsula is a peninsula into the Atlantic Ocean in the Viedma Department of north-east Chubut Province, Argentina. Around 3,625 km2 in size, it is an important nature reserve which was listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1999.

Base Orcadas is an Argentine scientific station in Antarctica, and the oldest of the stations in Antarctica still in operation. It is located on Laurie Island, one of the South Orkney Islands, at 4 meters (13 ft) above sea level and 170 meters (558 ft) from the coastline. Established by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition in 1903 and transferred to the Argentine government in 1904, the base has been permanently populated since, being one of six Argentine permanent bases in Argentina's claim to Antarctica, and the first permanently inhabited base in Antarctica.

Posadas is the capital city of the Argentine province of Misiones, in its south, at the far north-west of the country on the left bank of the Paraná River, opposite Encarnación, Paraguay. The city has an area of 965 square kilometres (373 sq mi) and a population of 324,756, and the Greater Posadas area has a population of over 359,609 according to a 2017 estimate.

Junín is a city in the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina, and administrative seat of the partido of Junín. It has a population of 85,420 and is located 260 km (162 mi) west of the city of Buenos Aires. It is mostly known for being the hometown of former first lady of Argentina Eva Perón.

Pehuajó is a city in the Pehuajó Partido in the province of Buenos Aires, Argentina. The partido has about 38,400 inhabitants as per the 2001 census [INDEC]. The name of this relatively small city is well known in Argentina because of María Elena Walsh's song Manuelita, about an adventurous turtle (tortoise); a dilapidated concrete statue of María Elena Walsh's Manuelita lies just outside the city, beside Ruta Nacional 5.

Cuyo is the wine-producing, mountainous region of central-west Argentina. Historically it comprised the provinces of San Juan, San Luis and Mendoza. The modern New Cuyo includes both Cuyo proper and the province of La Rioja. New Cuyo is a political and economic macroregion, but culturally La Rioja is part of the North-West rather than of Cuyo.

Cipolletti is a city in north of the Patagonian province of Río Negro, Argentina. With a population of 87,492 inhabitants at the 2010 census [INDEC], Cipolletti is the third-most populated settlement in the province, after San Carlos de Bariloche and General Roca.

Choele Choel is the capital of the department of Avellaneda in the Argentine province of Río Negro, and the most important settlement within the Valle Medio agricultural area of the Río Negro River in Patagonia.
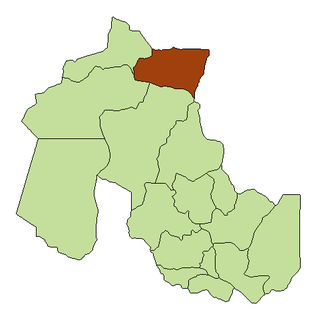
La Quiaca is a small city in the north of the province of Jujuy, Argentina, on the southern bank of the La Quiaca River, opposite the town of Villazón, Bolivia. It lies at the end of National Route 9, 289 km (180 mi) from San Salvador de Jujuy, and at an altitude of 3,442 m (11,293 ft) above mean sea level.

San Antonio Oeste is a port city in the Argentine province of Río Negro, and head of the department of San Antonio.
Las Lomitas is a city in northern Argentina. It is located in the Patiño Department in the center of Formosa Province. It has a population of 12,399 inhabitants as of the 2010 census [INDEC]. This represented a 20% increase in the population compared to the 2001 census [INDEC] which only had 10,354 inhabitants.
Río Colorado is a town and municipality in the Río Negro Province of Argentina. It is the administrative centre of the Pichi Mahuida Department.

Due to its vast size and range of altitudes, Argentina possesses a wide variety of climatic regions, ranging from the hot subtropical region in the north to the cold subantarctic in the far south. The Pampas region lies between those and featured a mild and humid climate. Many regions have different, often contrasting, microclimates. In general, Argentina has four main climate types: warm, moderate, arid, and cold in which the relief features, and the latitudinal extent of the country, determine the different varieties within the main climate types.


















