
Staffordshire is a landlocked ceremonial county in the West Midlands of England. It borders Cheshire to the north-west, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the south-east, the West Midlands county and Worcestershire to the south, and Shropshire to the west. The largest settlement is the city of Stoke-on-Trent, and the county town is Stafford.

The Wyrley and Essington Canal, known locally as "the Curly Wyrley", is a canal in the English Midlands. As built it ran from Wolverhampton to Huddlesford Junction near Lichfield, with a number of branches: some parts are currently derelict. Pending planned restoration to Huddlesford, the navigable mainline now terminates at Ogley Junction near Brownhills. In 2008 it was designated a Local Nature Reserve.

Cannock Chase, often referred to locally as The Chase, is a mixed area of countryside in the county of Staffordshire, England. The area has been designated as the Cannock Chase National Landscape, an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, and much of it is managed by Forestry England for its important ecology and for recreational use. The Chase gives its name to the Cannock Chase local government district. It is a former Royal forest.

Cannock is a town in the Cannock Chase district in the county of Staffordshire, England. It had a population of 29,018. Cannock is not far from the towns of Walsall, Burntwood, Stafford and Telford. The cities of Lichfield and Wolverhampton are also nearby.

Rugeley is a market town and civil parish in the Cannock Chase District, in Staffordshire, England. It lies on the north-eastern edge of Cannock Chase next to the River Trent; it is situated 8 miles (13 km) north of Lichfield, 10 miles (16 km) south-east of Stafford, 5 miles (8.0 km) north-east of Hednesford and 11 miles (18 km) south-west of Uttoxeter. At the 2021 Census, the population was 26,156.
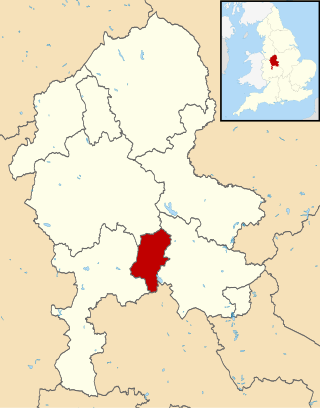
Cannock Chase is a local government district in Staffordshire, England. It is named after and covers a large part of Cannock Chase, a designated National Landscape. The council is based in the town of Cannock. The district also contains the towns of Hednesford and Rugeley, as well as a number of villages and surrounding rural areas.

Hednesford is a market town and civil parish in the Cannock Chase district of Staffordshire, England. The Cannock Chase area of natural beauty is to the north of the town. Hednesford is also 1 mile (1.6 km) to the north of Cannock and 5 miles (8.0 km) to the south of Rugeley. The population at the 2011 census was 17,343.

Cheadle is a market town and civil parish in the Staffordshire Moorlands District of Staffordshire, England, with a population of 12,000 at the 2021 census. It is located between Uttoxeter, Leek, Ashbourne and Stoke-on-Trent.

Great Wyrley is a village and civil parish in the South Staffordshire district of Staffordshire, England. It forms a built up area with nearby Cheslyn Hay, Churchbridge, Landywood and Little Wyrley. It lies 6 miles north of Walsall and a similar distance from Wolverhampton. Cannock is directly north of the village. It had a population of 11,060 at the 2011 census.

Huntington is a civil parish and former mining village in Staffordshire, on the outskirts of Cannock Chase. It lies on the A34 road just north of Cannock and is surrounded by woodland. The village had an estimated population of 3,720 in 2004, increasing to 4,536 at the 2011 Census. The population in Huntington on the 2021 census was 4,715, a 3.94% increase from the decade before.

Hednesford railway station serves the town of Hednesford in Staffordshire, England. The station forms a part of the Chase Line and is operated by West Midlands Railway.

Norton Canes is an industrial village, civil parish and ward of Cannock Chase District, in Staffordshire, England.

The North Staffordshire Coalfield was a coalfield in Staffordshire, England, with an area of nearly 100 square miles (260 km2), virtually all of it within the city of Stoke on Trent and the borough of Newcastle-under-Lyme, apart from three smaller coalfields, Shaffalong and Goldsitch Moss Coalfields near Leek and the Cheadle Coalfield. Coal mining in North Staffordshire began early in the 13th century, but the industry grew during the Industrial Revolution when coal mined in North Staffordshire was used in the local Potteries ceramics and iron industry.

The Cheadle Coalfield is a coalfield in the United Kingdom. Centred on the town of Cheadle, Staffordshire and its outlying villages it lies to the east of Stoke-on-Trent and the much larger North Staffordshire Coalfield. The area has been mined for many years, with documentary evidence from Croxden Abbey citing coal mining in the 13th century.
The Rugeley power stations were a series of two coal-fired power stations located on the River Trent at Rugeley in Staffordshire. The first power station on the site, Rugeley A power station was opened in 1961, but has since been closed and demolished. Rugeley B power station was commissioned in 1970, and closed on 8 June 2016. The cooling towers of which were demolished on 6 June 2021. It had an output of 1,000 megawatts (MW) and had a 400 kilovolt (kV) connection to the national grid. The B station provided enough electricity to power roughly half a million homes.

Coal mining in the United Kingdom dates back to Roman times and occurred in many different parts of the country. Britain's coalfields are associated with Northumberland and Durham, North and South Wales, Yorkshire, the Scottish Central Belt, Lancashire, Cumbria, the East and West Midlands and Kent. After 1972, coal mining quickly collapsed and had practically disappeared by the 21st century. The consumption of coal—mostly for electricity—fell from 157 million tonnes in 1970 to 587,000 tonnes in 2023 Employment in coal mines fell from a peak of 1,191,000 in 1920 to 695,000 in 1956, 247,000 in 1976, 44,000 in 1993, 2,000 in 2015, and to 360 in 2022.

The South Staffordshire coalfield is one of several coalfields in the English Midlands. It stretches for 25 miles / 40 km from the Lickey Hills in the south to Rugeley in the north. The coalfield is around 10 miles (16 km) wide; its eastern and western margins are fault-bounded.
Valley Colliery, commonly known as Valley Pit, was a deep coal mine and training centre located in Hednesford, Staffordshire, UK.

The coal industry in Wales played an important role in the Industrial Revolution in Wales. Coal mining in Wales expanded in the 18th century to provide fuel for the blast furnaces of the iron and copper industries that were expanding in southern Wales. The industry had reached large proportions by the end of that century, and then further expanded to supply steam-coal for the steam vessels that were beginning to trade around the world. The Cardiff Coal Exchange set the world price for steam-coal and Cardiff became a major coal-exporting port. The South Wales Coalfield was at its peak in 1913 and was one of the largest coalfields in the world. It remained the largest coalfield in Britain until 1925. The supply of coal dwindled, and pits closed in spite of a UK-wide strike against closures. Aberpergwm Colliery is the last deep mine in Wales.

The Cannock Chase Railways were mineral lines which served the collieries and many parts of Staffordshire. The branch lines and sidings branched off the local mainlines including the Grand Junction Railway, Chase Line, South Staffordshire Line and Rugby–Birmingham–Stafford line. The main junction on the railways was Norton Junction. This junction connected the lines from Walsall and Hednesford to Wolverhampton and Rugeley Trent Valley for the local collieries and the mines in the towns of Brownhills, Burntwood, Chasetown, Penkridge and Cannock.

















