Related Research Articles
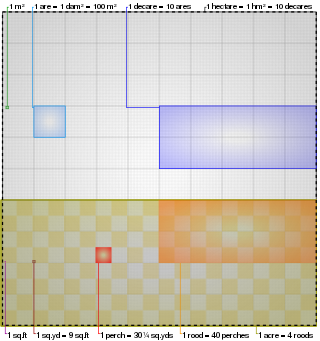
The acre is a unit of land area used in the British imperial and the United States customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong, which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, 1⁄640 of a square mile, 4,840 square yards, or 43,560 square feet, and approximately 4,047 m2, or about 40% of a hectare. Based upon the international yard and pound agreement of 1959, an acre may be declared as exactly 4,046.8564224 square metres. The acre is sometimes abbreviated ac but is usually spelled out as the word "acre".

A furlong is a measure of distance in imperial units and United States customary units equal to one eighth of a mile, equivalent to any of 660 feet, 220 yards, 40 rods, 10 chains or approximately 201 metres. It is now mostly confined to use in horse racing, where in many countries it is the standard measurement of race lengths, and agriculture, where it is used to measure rural field lengths and distances.

The inch is a unit of length in the British imperial and the United States customary systems of measurement. It is equal to 1/36 yard or 1/12 of a foot. Derived from the Roman uncia ("twelfth"), the word inch is also sometimes used to translate similar units in other measurement systems, usually understood as deriving from the width of the human thumb.

The mile, sometimes the international mile or statute mile to distinguish it from other miles, is a British imperial unit and United States customary unit of distance; both are based on the older English unit of length equal to 5,280 English feet, or 1,760 yards. The statute mile was standardised between the Commonwealth of Nations and the United States by an international agreement in 1959, when it was formally redefined with respect to SI units as exactly 1,609.344 metres.

Metrication or metrification is the act or process of converting to the metric system of measurement. All over the world, countries have transitioned from local and traditional units of measurement to the metric system. This process began in France during the 1790s, and is still continuing more than 200 years later, with the modern International System of Units, as the metric system has not been fully adopted in all countries and areas.

United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and most U.S. territories, since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system developed from English units that were in use in the British Empire before the U.S. became an independent country. The United Kingdom's system of measures was overhauled in 1824 to create the imperial system, which was officially adopted in 1826, changing the definitions of some of its units. Consequently, while many U.S. units are essentially similar to their imperial counterparts, there are significant differences between the systems.

The yard is an English unit of length in both the British imperial and US customary systems of measurement equalling 3 feet or 36 inches. Since 1959 it has been by international agreement standardized as exactly 0.9144 meter. A distance of 1,760 yards is equal to 1 mile.

A fathom is a unit of length in the imperial and the U.S. customary systems equal to 6 feet (1.8288 m), used especially for measuring the depth of water. The fathom is neither an international standard (SI) unit, nor an internationally accepted non-SI unit. Historically it was the maritime measure of depth in the English-speaking world but, apart from within the US, charts now use metres.
The ounce is any of several different units of mass, weight, or volume and is derived almost unchanged from the uncia, an Ancient Roman unit of measurement.
The foot (pl. feet), standard symbol: ft, is a unit of length in the British imperial and United States customary systems of measurement. The prime symbol, ′, is a customarily used alternative symbol. In both customary and imperial units, one foot comprises 12 inches, and one yard comprises three feet.
The rod, perch, or pole is a surveyor's tool and unit of length of various historical definitions. In British imperial and US customary units it is defined as 16+1⁄2 feet, equal to exactly 1⁄320 of a mile, or 5+1⁄2 yards, and is exactly 5.0292 meters. The rod is useful as a unit of length because integer multiples of it can form one acre of square measure (area). The 'perfect acre' is a rectangular area of 43,560 square feet, bounded by sides 660 feet long and 66 feet wide or, equivalently, 40 rods by 4 rods. An acre is therefore 160 square rods or 10 square chains.
The chain is a unit of length equal to 66 feet, used in both the US customary and Imperial unit systems. It is subdivided into 100 links. There are 10 chains in a furlong, and 80 chains in one statute mile. In metric terms, it is 20.1168 m long. By extension, chainage is the distance along a curved or straight survey line from a fixed commencing point, as given by an odometer.
A dunam, also known as a donum or dunum and as the old, Turkish, or Ottoman stremma, was the Ottoman unit of area equivalent to the Greek stremma or English acre, representing the amount of land that could be ploughed by a team of oxen in a day. The legal definition was "forty standard paces in length and breadth", but its actual area varied considerably from place to place, from a little more than 900 square metres (9,700 sq ft) in Ottoman Palestine to around 2,500 square metres (27,000 sq ft) in Iraq.

Gunter's chain is a distance measuring device used for surveying. It was designed and introduced in 1620 by English clergyman and mathematician Edmund Gunter (1581–1626). It enabled plots of land to be accurately surveyed and plotted, for legal and commercial purposes.
A morgen was a unit of measurement of land area in Germany, the Netherlands, Poland, Lithuania and the Dutch colonies, including New Netherland, South Africa, and Taiwan. The size of a morgen varies from 1⁄2 to 2+1⁄2 acres. It was also used in Old Prussia, in the Balkans, Norway and Denmark, where it was equal to about two-thirds acre (2,700 m2).

The Dutch units of measurement used today are those of the metric system. Before the 19th century, a wide variety of different weights and measures were used by the various Dutch towns and provinces. Despite the country's small size, there was a lack of uniformity. During the Dutch Golden Age, these weights and measures accompanied the Dutch to the farthest corners of their colonial empire, including South Africa, New Amsterdam and the Dutch East Indies. Units of weight included the pond, ons and last. There was also an apothecaries' system of weights. The mijl and roede were measurements of distance. Smaller distances were measured in units based on parts of the body – the el, the voet, the palm and the duim. Area was measured by the morgen, hont, roede and voet. Units of volume included the okshoofd, aam, anker, stoop, and mingel. At the start of the 19th century the Dutch adopted a unified metric system, but it was based on a modified version of the metric system, different from the system used today. In 1869, this was realigned with the international metric system. These old units of measurement have disappeared, but they remain a colourful legacy of the Netherlands' maritime and commercial importance and survive today in a number of Dutch sayings and expressions.

The hectare is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), that is, 10,000 square meters, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is about 0.405 hectares and one hectare contains about 2.47 acres.
A rood is a historic English and international inch-pound measure of area, as well as an archaic English measure of length.

The imperial and US customary measurement systems are both derived from an earlier English system of measurement which in turn can be traced back to Ancient Roman units of measurement, and Carolingian and Saxon units of measure.
A number of units of measurement were used in South Africa to measure quantities like length, mass, capacity, etc. The Imperial system of measurements was made standard in 1922 and the metric system was adopted in 1970.
References
- ↑ Matthews, E.L.; G. M. Swift; G. Hartog (1924). "South Africa: Union of South Africa". Journal of Comparative Legislation and International Law. Third Series. 6 (2): 111–134. JSTOR 752924.
- ↑ Jacob de Gelder (1824). Allereerste Gronden der Cijferkunst [Introduction to Numeracy] (in Dutch). 's Gravenhage and Amsterdam: de Gebroeders van Cleef. pp. 163–176. Retrieved 2011-03-02.
- ↑ "Cape Foot". Sizes. Retrieved 2011-12-25.
- ↑ "Instructions for the Conversions of Areas to Metric". Law Society of South Africa. November 2007. Archived from the original on 2018-03-20. Retrieved 2010-03-10.
- ↑ Tomasz Zakiewicz (April 2005). "The Cape Geodetic Standards and Their Impact on Africa" (PDF). FIG, Cairo. Retrieved 2012-01-04.