
Casablanca, also known in Arabic as Dar al-Bayda is the largest city in Morocco. Located on the Atlantic coast of the Chaouia plain in the central-western part of Morocco, the city has a population of about 3.71 million in the urban area, and over 4.27 million in the Greater Casablanca, making it the most populous city in the Maghreb region, and the eighth-largest in the Arab world. Casablanca is considered the economic and business center of Morocco, although the national political capital is Rabat. The leading Moroccan companies and many international corporations doing business in the country have their headquarters and main industrial facilities in Casablanca. Recent industrial statistics show Casablanca holds its recorded position as the primary industrial zone of the nation. Casablanca is Morocco's chief port, with the Port of Casablanca being one of the largest artificial ports in the world, and the second largest port in North Africa, after Tanger-Med. Casablanca also hosts the primary naval base for the Royal Moroccan Navy.

The Bank Al-Maghrib is the central bank of the Kingdom of Morocco. It was founded in 1959 as the successor to the State Bank of Morocco. In 2008 Bank Al-Maghrib held reserves of foreign currency with an estimated worth of US$36 billion. In addition to currency management, the Bank Al-Maghrib also supervises a number of private banks supplying commercial banking services. The bank has a branch in Casablanca, and agencies in 18 other cities in Morocco. The current governor is Abdellatif Jovahri.

The ONA Group was established in 1934 and dissolved in 2010 and succeeded by Societe Nationale d'Investissement. ONA was an industrial, financial and services conglomerate, focused on positions of leadership and value creation in business activities contributing to the growth and sustainable development of Morocco, the Maghreb Region and the African Continent. ONA Group was structured around several activities: Mining, Agribusiness, Distribution, Financial Services, Telecommunication, Renewable Energies, and Growth Drivers, etc.
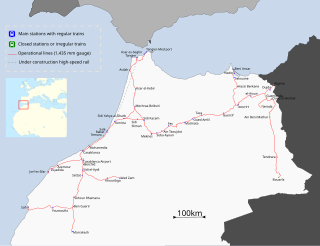
ONCF is Morocco's national railway operator. ONCF is a state-owned company that is under the control of the Ministry of Equipment, Transport and Logistics and is responsible for all passenger and freight traffic on the national railway network. The company is also responsible for building and maintaining the rail infrastructure.

Maroc Telecom is the main telecommunications company in Morocco. Currently employing around 11,178 employees, it is the largest telecommunications network in the country with 8 regional delegations and 220 offices present across Morocco. The company is listed on both the Casablanca Stock Exchange and Euronext Paris.

Attijariwafa Bank is a Moroccan multinational commercial bank and financial services company founded and based in Rabat, Morocco. It is the leading bank in Morocco and is part of Al Mada holding company.
Banque Commerciale du Maroc was a bank founded in 1911, shortly ahead of the establishment of the French protectorate in Morocco. The bank was initially controlled by France's Banque Transatlantique, then from 1941 by the Crédit Industriel et Commercial, and from 1988 by Morocco's ONA Group. In 2004, it merged with Wafa bank to form Attijariwafa Bank.

BMCI is a bank based in Morocco. It is a majority-owned subsidiary of the French financial group BNP Paribas.

The Hassania School of Public Works, is one of Morocco's oldest engineering schools, a member of the Conférence des grandes écoles, and remains to this day the most prestigious Moroccan Grande Ecole in engineering. It is located in Casablanca few miles from the Casablanca Technopark.
Nouaceur is a province in the Moroccan region of Casablanca-Settat. Its population in 2004 was 236,119. Its major town is Bouskoura, although the administrative centre is Nouaceur.

Science and technology in Morocco has significantly developed in recent years. The Moroccan government has been implementing reforms to encourage scientific research in the Kingdom. While research has yet to acquire the status of a national priority in Morocco, the country does have major assets that could transform its R&D sector into a key vehicle for development. The industry remains dominated by the public sector, with the universities employing 58% of researchers. Morocco's own evaluation of its national research system – carried out in 2003 – revealed that the country has a good supply of well trained high quality human resources and that some laboratories are of very high quality. However, the greatest gap at that point of time lied in the link between research and innovation. The educational qualifications of Moroccan researchers have increased significantly since the early 1990s. The University of Al-Karaouine is considered the oldest continuously operating academic degree-granting university in the world.

Water supply and sanitation in Morocco is provided by a wide array of utilities. They range from private companies in the largest city, Casablanca, the capital, Rabat, Tangier, and Tetouan, to public municipal utilities in 13 other cities, as well as a national electricity and water company (ONEE). The latter is in charge of bulk water supply to the aforementioned utilities, water distribution in about 500 small towns, as well as sewerage and wastewater treatment in 60 of these towns.
Inwi is a telecommunication company in Morocco. one of the three major telecom company in Morocco, It is a subsidiary of the group SNI and the Kuwaiti group Zain.
SOMED is a conglomerate company based in Morocco. Its active in a range of sectors such as mining, construction material dealership, tourism, real estate development, food processing and Car dealership. Its capital is composed of Mohammed VI's holding company SNI, Emirati private funds and the Moroccan state.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Casablanca, Morocco.

The International University of Rabat or UIR is a semi-public university founded in 2010 in Morocco. It delivers double-degrees, in collaboration with foreign universities, in law, engineering, aeronautics, energy engineering, architecture, business management and political sciences.

Kamal Mokdad is the General Manager of Banque Centrale Populaire of Morocco.

La Compagnie Marocaine was a French colonial holding company founded in 1902 for the purpose of exploiting Morocco.

The State Bank of Morocco was a quasi-central bank established in 1907 following the Algeciras Conference, to stabilize the Moroccan currency and serve as a vehicle for European and especially French influence in the Sultanate of Morocco. Following the independence of Morocco, it was replaced in 1959 by the newly created Banque du Maroc, known since 1987 as Bank Al-Maghrib.













