
An analgesic or painkiller is any member of the group of drugs used to achieve analgesia, relief from pain. They are distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily affect, and in some instances completely eliminate, sensation.
An anxiolytic is a medication, or other intervention, that reduces anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiogenic agents, which increase anxiety. Together these categories of psychoactive compounds or interventions may be referred to as anxiotropic compounds or agents. Some recreational drugs such as alcohol induce anxiolysis initially; however, studies show that many of these drugs are anxiogenic. Anxiolytic medications have been used for the treatment of anxiety disorder and its related psychological and physical symptoms. Light therapy and other interventions have also been found to have an anxiolytic effect.

Pentazocine, sold under the brand name Talwin among others, is a painkiller used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is believed to work by activating (agonizing) κ-opioid receptors (KOR) and blocking (antagonizing) μ-opioid receptors (MOR). As such it is called an opioid as it delivers its effects on pain by interacting with the opioid receptors. It shares many of the side effects of other opioids like constipation, nausea, itching, drowsiness and respiratory depression, but unlike most other opioids it fairly frequently causes hallucinations, nightmares and delusions. It is also, unlike most other opioids, subject to a ceiling effect, which is when at a certain dose no more pain relief, or side effects, is obtained by increasing the dose any further.
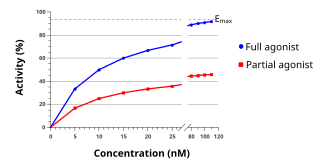
An agonist is a chemical that binds to a receptor and activates the receptor to produce a biological response. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist.

Opioids are substances that, when reaching opioid receptors, have effects similar to those of morphine. Medically they are primarily used for pain relief, including anesthesia. Other medical uses include suppression of diarrhea, replacement therapy for opioid use disorder, reversing opioid overdose, restless leg syndrome, and suppressing cough. Extremely potent opioids such as carfentanil are approved only for veterinary use. Opioids derived from opium are used recreationally by some, at first for their euphoric effects and then to react to withdrawal.

A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers. In pharmacology, antagonists have affinity but no efficacy for their cognate receptors, and binding will disrupt the interaction and inhibit the function of an agonist or inverse agonist at receptors. Antagonists mediate their effects by binding to the active site or to the allosteric site on a receptor, or they may interact at unique binding sites not normally involved in the biological regulation of the receptor's activity. Antagonist activity may be reversible or irreversible depending on the longevity of the antagonist–receptor complex, which, in turn, depends on the nature of antagonist–receptor binding. The majority of drug antagonists achieve their potency by competing with endogenous ligands or substrates at structurally defined binding sites on receptors.

Buprenorphine is an opioid used to treat opioid use disorder, acute pain, and chronic pain. It can be used under the tongue (sublingual), in the cheek (buccal), by injection (intravenous), as a skin patch (transdermal), or as an implant. For opioid use disorder, it is typically started when withdrawal symptoms have begun and for the first two days of treatment under direct observation of a health-care provider. The combination formulation of buprenorphine/naloxone (Suboxone) is recommended to discourage misuse by injection. Maximum pain relief is generally within an hour with effects up to 24 hours.

Dextropropoxyphene is an analgesic in the opioid category, patented in 1955 and manufactured by Eli Lilly and Company. It is an optical isomer of levopropoxyphene. It is intended to treat mild pain and also has antitussive and local anaesthetic effects. The drug has been taken off the market in Europe and the US due to concerns of fatal overdoses and heart arrhythmias. It is still available in Australia, albeit with restrictions after an application by its manufacturer to review its proposed banning. Its onset of analgesia is said to be 20–30 minutes and peak effects are seen about 1.5–2.0 hours after oral administration.

Nalbuphine, sold under the brand names Nubain among others, is an opioid analgesic which is used in the treatment of pain. It is given by injection into a vein, muscle, or fat.
An opioid antagonist, or opioid receptor antagonist, is a receptor antagonist that acts on one or more of the opioid receptors.

Butorphanol is a morphinan-type synthetic agonist–antagonist opioid analgesic developed by Bristol-Myers. Butorphanol is most closely structurally related to levorphanol. Butorphanol is available as the tartrate salt in injectable, tablet, and intranasal spray formulations. The tablet form is only used in dogs, cats and horses due to low bioavailability in humans.

Hydrocodone/paracetamol, also known as hydrocodone/acetaminophen, is the combination of the pain medications hydrocodone and paracetamol (acetaminophen). It is used to treat moderate to severe pain. It is taken by mouth. Recreational use is common in the United States.
Diprenorphine, also known as diprenorfin, is a non-selective, high-affinity, weak partial agonist of the μ- (MOR), κ- (KOR), and δ-opioid receptor (DOR) that is employed in veterinary medicine as an opioid antagonist. It is used to reverse the effects of super-potent opioid analgesics such as etorphine and carfentanil that are used for tranquilizing large animals. The drug is not approved for use in humans.
Methylnaltrexone, used in form of methylnaltrexone bromide, is a medication that acts as a peripherally acting μ-opioid receptor antagonist that acts to reverse some of the side effects of opioid drugs such as constipation without significantly affecting pain relief or precipitating withdrawals. Because MNTX is a quaternary ammonium cation, it cannot cross the blood–brain barrier, and so has antagonist effects throughout the body, counteracting effects such as itching and constipation, but without affecting opioid effects in the brain such as pain relief. However, since a significant fraction of opioid analgesia can be mediated by opioid receptors on peripheral sensory neurons, particularly in inflammatory conditions such as arthritis, traumatic or surgical pain, MNTX may increase pain under such circumstances.
Dezocine is a marketed opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan group. First synthesized in 1970, it acts as a modulator of mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptors. Dezocine is a mixed agonist/antagonist of opioid receptors. It is related to other benzomorphans such as pentazocine, with a similar profile of effects that include analgesia and euphoria. Unlike many other benzomorphans however, it is a silent antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor, and in accordance, does not produce side effects such as dysphoria or hallucinations at any dose.
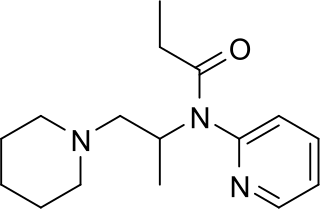
Propiram is a partial mu opioid receptor agonist and weak mu antagonist analgesic from the ampromide family of drugs related to other drugs such as phenampromide and diampromide. It was invented in 1963 in the United Kingdom by Bayer but was not widely marketed, although it saw some limited clinical use, especially in dentistry. Propiram reached Phase III clinical trials in the United States and Canada.
"Pain ladder", or analgesic ladder, was created by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a guideline for the use of drugs in the management of pain. Originally published in 1986 for the management of cancer pain, it is now widely used by medical professionals for the management of all types of pain.
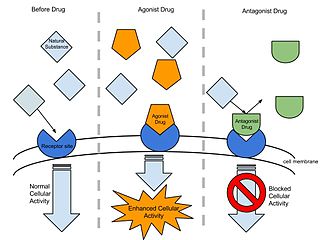
In pharmacology the term agonist-antagonist or mixed agonist/antagonist is used to refer to a drug which under some conditions behaves as an agonist while under other conditions, behaves as an antagonist.
An equianalgesic chart is a conversion chart that lists equivalent doses of analgesics. Equianalgesic charts are used for calculation of an equivalent dose between different analgesics. Tables of this general type are also available for NSAIDs, benzodiazepines, depressants, stimulants, anticholinergics and others as well.

Buprenorphine/naloxone, sold under the brand name Suboxone among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication that includes buprenorphine and naloxone. It is used to treat opioid use disorder, and reduces the mortality of opioid use disorder by 50%. It relieves cravings to use and withdrawal symptoms. Buprenorphine/naloxone is available for use in two different forms, under the tongue or in the cheek.














