Leasowe is a village in the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral in Merseyside, England. Historically within Cheshire, Leasowe was part of the old County Borough of Wallasey. It is now within the Leasowe and Moreton East Ward of the Metropolitan Borough of Wirral, as well as the Wallasey parliamentary constituency.

The Liverpool Royal Infirmary was a hospital in Pembroke Place in Liverpool, England. The building is now used by the University of Liverpool.

The Mater Misericordiae University Hospital, commonly known as the Mater ( "matter"), is a major teaching hospital, based at Eccles Street, Phibsborough, on the northside of Dublin, Ireland. It is managed by Ireland East Hospital Group.

St Bartholomew's Hospital, commonly known as Barts, is a teaching hospital located in the City of London. It was founded in 1123 and is currently run by Barts Health NHS Trust.

The Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital (RNOH) is a specialist orthopaedic hospital located in the London Borough of Harrow, United Kingdom, and a part of Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital NHS Trust. It provides the most comprehensive range of neuro-musculoskeletal health care in the UK, including acute spinal injury, complex bone tumour treatment, orthopaedic medicine and specialist rehabilitation for chronic back pain. The RNOH is a major teaching centre and around 20% of orthopaedic surgeons in the UK receive training there.

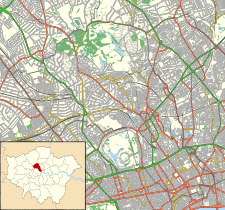
The London Fever Hospital was a voluntary hospital financed from public donations in Liverpool Road in London. It was one of the first fever hospitals in the country.

Cromer and District Hospital opened in 1932 in the suburb of Suffield Park in the town of Cromer within the English county of Norfolk. The hospital is run by the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and provides an important range of acute consultant and nurse-led services to the residents of the district of North Norfolk.

Pilgrim Hospital is a hospital in the east of Lincolnshire on the A16, north of the town of Boston near the mini-roundabout with the A52. It is situated virtually on the Greenwich Meridian and adjacent to Boston High School. The fenland area of Lincolnshire is covered by this hospital, being the county's second largest hospital after Lincoln County Hospital. It is managed by United Lincolnshire Hospitals NHS Trust.

St Leonard's Hospital is a hospital in Hoxton, North London.

Epsom and Ewell Cottage Hospital is a small hospital in West Park Road, Horton Lane, Epsom, Surrey. It is managed by CSH Surrey.
Chailey Heritage School is a special school located in North Chailey, East Sussex, England. It is owned and operated by the Chailey Heritage Foundation. The school is for children and young adults, aged between 3 and 19, with complex physical disabilities and associated learning difficulties. The school has a sixth form. It is a charity. There is boarding accommodation on the site. NHS services are based at the same location.

Richmond Royal Hospital, on Kew Foot Road in Richmond, London, England, is a mental health facility operated by South West London and St George's Mental Health NHS Trust, which has its headquarters at Springfield Hospital in Tooting. The hospital's original block is Grade II listed.

Hounslow Hospital was a small hospital for geriatric and long-stay patients situated in an industrial area of Hounslow, girdled by two motorways and Heathrow Airport. It was run by the Ealing, Hammersmith and Hounslow Area Health Authority.

Highgate Hospital was a name used to refer to the infirmary building which opened in 1869 on the St Pancras side of Dartmouth Park Hill in Highgate, London.

Susan Bell McGahey was the matron of the Royal Prince Alfred Hospital from 1891 to 1904. McGahey was also co-founder of the Australasian Trained Nurses' Association in 1899 and president of the International Council of Nurses from 1904 to 1909.

The Grove Hospital, originally the Grove Fever Hospital, was a hospital for infectious diseases opened in Tooting Grove, London.

The David Lewis Northern Hospital was located in Great Howard Street, Liverpool. It was first established in 1834 and closed in 1978.

Annie Sophia Jane McIntosh CBE, RRC was a British nurse and nursing leader. She was a Matron of St Bartholomew's Hospital, London (1910–1927), promoted the fledgling College of Nursing Ltd, and served on several wartime committees.
Bethnal Green Hospital was an acute care hospital, in Bethnal Green, close to Cambridge Heath in the London Borough of Tower Hamlets, England. It opened in 1900, and it closed in 1990.