
Negros Occidental, officially the Province of Negros Occidental (Hiligaynon: Kapuoran sang Nakatungdang Negros (Negros Occidental; Tagalog: Lalawigan ng Kanlurang Negros, is a province in the Philippines located in the Western Visayas region. Its capital is the city of Bacolod, of which it is geographically situated and grouped under by the Philippine Statistics Authority, but remains politically independent from the provincial government. It occupies the northwestern half of the large island of Negros, and borders Negros Oriental, which comprises the southeastern half. Known as the "Sugarbowl of the Philippines", Negros Occidental produces more than half the nation's sugar output.

Bacolod, officially the City of Bacolod, is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Western Visayas, Philippines. It is the capital of the province of Negros Occidental, where it is geographically situated but governed administratively independent.

Valencia, officially the Municipality of Valencia, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Negros Oriental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 38,733 people.

Silay, officially the City of Silay, is a 3rd class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 130,478 people.

Talisay, officially the City of Talisay, is a 4th class component city in the province of Negros Occidental, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 108,909 people.

The legislative districts of Negros Occidental are the representations of the province of Negros Occidental in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province is currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through its first, second, third, fourth, fifth, and sixth congressional districts.

The Negros Revolution, commemorated and popularly known as the Fifth of November or Negros Day, was a political movement that in 1898 created a government on Negros Island in the Philippines, ending Spanish control of the island and paving the way for a republican government run by the Negrense natives. The newly established Negros Republic lasted for approximately three months. American forces landed on the island unopposed on February 2, 1899, ending the island's independence. Negros was then annexed to the Philippine Islands on 20 April 1901.

Carlos Hilado Memorial State University, also colloquially called by its former acronym CHMSC, is a public, state-owned university, the main campus of which is in Talisay, Negros Occidental, Philippines. It provides preschool, elementary, secondary, higher technological, professional and vocational instruction and training in science, agriculture and industrial fields, as well as short-term or vocational courses.

The Bacolod Metropolitan Area, simply known as Metro Bacolod, is the 8th-most populous and the 6th-most densely populated metropolitan area out of the 12 metropolitan areas in the Philippines. This metropolitan area as defined by the National Economic and Development Authority (NEDA) has an estimated population of 1,435,593 inhabitants as of the 2020 official census by the Philippine Statistics Authority.

The 2011 POC-PSC National Games was held at the cities of Bacolod, Bago, Silay and Talisay - Negros Occidental from May 22–29, 2011.
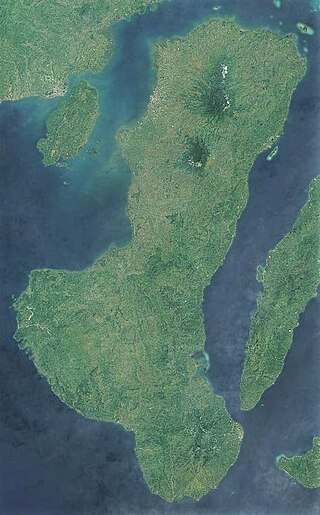
Negros is the fourth largest and third most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of 13,309 km2 (5,139 sq mi). Negros is one of the many islands of the Visayas, in the central part of the country. The predominant inhabitants of the island region are mainly called Negrenses. As of 2020 census, the total population of Negros is 4,656,945 people.

The Northern Negros Natural Park is a protected area of the Philippines located in the northern mountainous forest region of the island of Negros in the Visayas. It is spread over five municipalities and six cities in the province of Negros Occidental and is the province's largest watershed and water source for seventeen municipalities and cities including the Bacolod metropolitan area. The park was established first as a forest reserve spanning 107,727 hectares on 28 April 1935 through Administrative Act No. 789 signed by Governor-General Frank Murphy. On 7 August 1946, the Northern Negros Forest Reserve was reduced to its present area of 80,454.5 hectares with the signing of Proclamation No. 798 by President Manuel Roxas. In 2005, the protected area was converted into a natural park under the National Integrated Protected Areas System (NIPAS) Act by virtue of Proclamation No. 895 signed by President Gloria Arroyo.

Mambukal Resort, officially the Township of Mambukal or simply known as Mambukal, is a resort township located within the boundaries of the municipality of Murcia, Negros Occidental. As a township, it is directly governed by the Provincial Government of Negros Occidental, which also manages Mambukal Mountain Resort in the 6-hectare townsite near Brgy. Minoyan. The resort is owned and managed by the Provincial Government of Negros Occidental under its Economic Enterprise Development Department.

Capitol Central, previously called the Negros Occidental Provincial Capitol Complex, is a government complex and mixed-use estate centered around the Negros Occidental Provincial Capitol, currently co-managed with Ayala Land. Certain portions are leased or sold to Ayala Land, as part of their industrial estate in Bacolod, Philippines.
The Negros Occidental Provincial Board is the Sangguniang Panlalawigan of the Philippine province of Negros Occidental.

The National Electrification Administration is a government-owned and controlled corporation (GOCC) attached to the Department of Energy of the Philippines tasked in the full implementation of the rural electrification program (REP) and reinforce the technical capability and financial viability of the 121 rural electric cooperatives (ECs).

Alfredo Abelardo "Albee" Bantug Benitez is a Filipino businessman and politician serving as the mayor of Bacolod since 2022. He served three consecutive terms as the representative of Negros Occidental's 3rd district from 2010 to 2019. He was one of the richest congressmen in the Philippines.

The Bacolod North Road is a 163.52-kilometer (101.61 mi), two-to-six lane major north–south lateral highway that connects the city of Bacolod to the city of San Carlos in Negros Occidental, Philippines.

Negros Occidental's 3rd congressional district is one of the six congressional districts of the Philippines in the province of Negros Occidental. It has been represented in the House of Representatives of the Philippines since 1916 and earlier in the Philippine Assembly from 1907 to 1916. The district consists of the cities of Silay, Talisay and Victorias, as well as the adjacent municipalities of Enrique B. Magalona and Murcia. It is currently represented in the 18th Congress by Jose Francisco "Kiko" Benitez of the Partido Federal ng Pilipinas (PFP).
Pedro C. Hernaez was a Filipino lawyer, politician, diplomat and Senator.


















