
Anishinaabe traditional beliefs cover the traditional belief system of the Anishinaabeg peoples, consisting of the Algonquin/Nipissing, Ojibwa/Chippewa/Saulteaux/Mississaugas, Odawa, Potawatomi and Oji-Cree, located primarily in the Great Lakes region of North America.
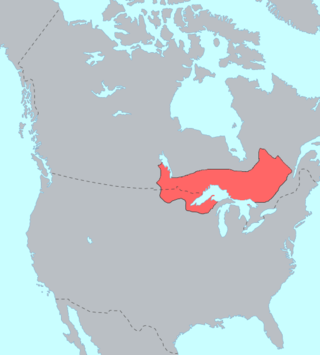
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains. They are Indigenous peoples of the Subarctic and Northeastern Woodlands.
Algonquin is either a distinct Algonquian language closely related to the Ojibwe language or a particularly divergent Ojibwe dialect. It is spoken, alongside French and to some extent English, by the Algonquin First Nations of Quebec and Ontario. As of 2006, there were 2,680 Algonquin speakers, less than 10% of whom were monolingual. Algonquin is the language for which the entire Algonquian language subgroup is named; the similarity among the names often causes considerable confusion. Like many Native American languages, it is strongly verb-based, with most meaning being incorporated into verbs instead of using separate words for prepositions, tense, etc.

Ojibweoh-JIB-way, also known as Ojibwaoh-JIB-wə, Ojibway, Otchipwe, Ojibwemowin, or Anishinaabemowin, is an indigenous language of North America of the Algonquian language family. The language is characterized by a series of dialects that have local names and frequently local writing systems. There is no single dialect that is considered the most prestigious or most prominent, and no standard writing system that covers all dialects.

The Anishinaabe are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe, Odawa, Potawatomi, Mississaugas, Nipissing and Algonquin peoples. The Anishinaabe speak Anishinaabemowin, or Anishinaabe languages that belong to the Algonquian language family.
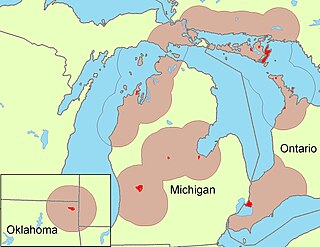
Ottawa or Odawa is a dialect of the Ojibwe language spoken by the Odawa people in southern Ontario in Canada, and northern Michigan in the United States. Descendants of migrant Ottawa speakers live in Kansas and Oklahoma. The first recorded meeting of Ottawa speakers and Europeans occurred in 1615 when a party of Ottawas encountered explorer Samuel de Champlain on the north shore of Georgian Bay. Ottawa is written in an alphabetic system using Latin letters, and is known to its speakers as Nishnaabemwin 'speaking the native language' or Daawaamwin 'speaking Ottawa'.

A wiigwaasabak is a birch bark scroll, on which the Ojibwa (Anishinaabe) people of North America wrote complex geometrical patterns and shapes, also known as a "written language." When used specifically for Midewiwin ceremonial use, these scrolls are called mide-wiigwaas. These enabled the memorization of complex ideas, and passing along history and stories to succeeding generations. Several such scrolls are in museums, including one on display at the Smithsonian Museum in Washington, DC. In addition to birchbark, copper, and slate may have also been used, along with hides, pottery, and other artifacts. Some archaeologists are presently trying to determine the exact origins, dates, and locations of their use. Many scrolls were hidden away in caves and man-made pits.

The Oji-Cree are a First Nation in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Manitoba, residing in a narrow band extending from the Missinaibi River region in Northeastern Ontario at the east to Lake Winnipeg at the west.
The Severn Ojibwa or the Oji-Cree language is the indigenous name for a dialect of the Ojibwe language spoken in a series of Oji-Cree communities in northern Ontario and at Island Lake, Manitoba, Canada. Ojibwa is a member of the Algonquian language family, itself a member of the Algic language family.
The Anishinaabe, like most Algonquian-speaking groups in North America, base their system of kinship on clans or totems. The Ojibwe word for clan was borrowed into English as totem. The clans, based mainly on animals, were instrumental in traditional occupations, intertribal relations, and marriages. Today, the clan remains an important part of Anishinaabe identity. Each clan are not allowed to harm their representation animal in any way or form. It is an bad omen if you do so.
The Ojibwe language is spoken in a series of dialects occupying adjacent territories, forming a language complex in which mutual intelligibility between adjacent dialects may be comparatively high but declines between some non-adjacent dialects. Mutual intelligibility between some non-adjacent dialects, notably Ottawa, Severn Ojibwe, and Algonquin, is low enough that they could be considered distinct languages. There is no single dialect that is considered the most prestigious or most prominent, and no standard writing system that covers all dialects. The relative autonomy of the regional dialects of Ojibwe is associated with an absence of linguistic or political unity among Ojibwe-speaking groups.
The Central Algonquian languages are commonly grouped together as a subgroup of the larger Algonquian family, itself a member of the Algic family. Though the grouping is often encountered in the literature, it is an areal grouping, not a genetic grouping. In other words, the languages are grouped together because they were spoken near one another, not because they are more closely related to one another than to other Algonquian languages. Within the Algonquian family, only Eastern Algonquian is a valid genealogical group.
Ojibway, Ojibwa, or Ojibwe may refer to:
Chapleau Ojibway First Nation is an Ojibwa First Nation located near Chapleau Township, Sudbury District, Ontario, Canada. The First Nation have reserved for themselves the 67 ha Chapleau 61A Indian Reserve, 64.7 ha Chapleau 74 Indian Reserve and the 799.3 ha Chapleau 74A Indian Reserve. In September, 2007, their total registered population 39, of which their on-reserve population was 30.
Ma-mong-a-ze-da was an 18th-century Ojibwa chief from Shagawamikong. He was a member of the Caribou doodem "Adik Reindeer Clan" and his ancestors came from Grand Portage on the north shore of Lake Superior. His father was his mother's second husband as she had been married to a chief of the Dakota people previously during a period of peace between the Ojibwa and Dakota. When war resumed the couple was obliged to divorce with the husband and children joining the Dakota and the wife marrying an Ojibwa man. In this way, Mamongazeda's older half-brother Wapasha became a chief of the Dakota while he became a chief of the Ojibwa. In addition to being an accomplished war leader, Mamongazeda was persuasive diplomat and strong ally of the French. During the French and Indian War, Mamongazeda raised a party of Lake Superior Ojibwa to fight with the French, and were part of Montcalm's army at the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. He lived to a very old age and was succeeded by his son, the famous chief and warrior, Waubojeeg.
Chippewa is an Algonquian language spoken from upper Michigan westward to North Dakota in the United States. It represents the southern component of the Ojibwe language.
Eastern Ojibwe is a dialect of the Ojibwe language spoken north of Lake Ontario and east of Georgian Bay in Ontario, Canada. Eastern Ojibwe-speaking communities include Rama and Curve Lake. Ojibwe is an Algonquian language.
Northwestern Ojibwe is a dialect of the Ojibwe language, spoken in Ontario and Manitoba, Canada. Ojibwe is a member of the Algonquian language family.
Western Ojibwa is a dialect of the Ojibwe language, a member of the Algonquian language family. It is spoken by the Saulteaux, a subnation of the Ojibwe people, in southern Manitoba and southern Saskatchewan, Canada, west of Lake Winnipeg. Saulteaux is generally used by its speakers, and Nakawēmowin is the general term in the language itself.
Ottawa is a dialect of the Ojibwe language spoken in a series of communities in southern Ontario and a smaller number of communities in northern Michigan. Ottawa has a phonological inventory of seventeen consonants and seven oral vowels; in addition, there are long nasal vowels the phonological status of which are discussed below. An overview of general Ojibwa phonology and phonetics can be found in the article on Ojibwe phonology. The Ottawa writing system described in Modern orthography is used to write Ottawa words, with transcriptions in the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) used as needed.






