
A sifaka is a lemur of the genus Propithecus from the family Indriidae within the order Primates. The name of their family is an onomatopoeia of their characteristic "shi-fak" alarm call. Like all lemurs, they are found only on the island of Madagascar. All species of sifakas are threatened, ranging from endangered to critically endangered.

Galerina is a genus of small brown-spore saprobic fungi, with over 300 species found throughout the world from the far north to remote Macquarie Island in the Southern Ocean. The genus is most noted for some extremely poisonous species which are occasionally confused with hallucinogenic species of Psilocybe. Species are typically small and hygrophanous, with a slender and brittle stem. They are often found growing on wood, and when on the ground have a preference for mossy habitats.

Russula is a very large genus composed of around 750 worldwide species of ectomycorrhizal mushrooms. They are typically common, fairly large, and brightly colored – making them one of the most recognizable genera among mycologists and mushroom collectors. Their distinguishing characteristics include usually brightly coloured caps, a white to dark yellow spore print, brittle, attached gills, an absence of latex, and absence of partial veil or volva tissue on the stem. Microscopically, the genus is characterised by the amyloid ornamented spores and flesh (trama) composed of spherocysts. Members of the related genus Lactarius have similar characteristics but emit a milky latex when their gills are broken. The genus was described by Christian Hendrik Persoon in 1796.

Spalerosophis diadema, known commonly as the Blotched diadem snake and the Blotched royal snake, is a species of large snake in the subfamily Colubrinae of the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to Asia and northern Africa.

The diademed sifaka, or diademed simpona, is an endangered species of sifaka, one of the lemurs endemic to certain rainforests in eastern Madagascar. Along with the indri, this species is one of the two largest living lemurs, with an average weight of 6.5 kg and a total adult length of approximately 105 centimetres (41 inches), half of which is its tail. Russell Mittermeier, one of the contemporary authorities on lemurs, describes the diademed sifaka as "one of the most colorful and attractive of all the lemurs", having a long and silky coat. P. diadema is also known by the Malagasy names simpona, simpony and ankomba joby. The term "diademed sifaka" is also used as a group species designation formerly encompassing four distinct subspecies.

The New Caledonian lorikeet is a potentially extinct lorikeet endemic to the Melanesian island of New Caledonia.
A resting spore is a resistant cell, used to survive adverse environmental conditions. Resting spore is a term commonly applied to both diatoms and fungi.

The plushcap is a species of bird in the tanager family Thraupidae and it is the only member of the genus Catamblyrhynchus.
The Mograbin diadem snake, also known commonly as Werner's diadem snake, is a species of snake in the family Colubridae. The species is endemic to northwestern Africa.

The diadem leaf-nosed bat or diadem roundleaf bat is one of the most widespread species of bat in the family Hipposideridae. It is probably most closely related to Hipposideros demissus from Makira and to Hipposideros inornatus from the Northern Territory in Australia. Hipposideros diadema is found in Australia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Marnaviridae is a family of positive-stranded RNA viruses in the order Picornavirales that infect various photosynthetic marine protists. Members of the family have non-enveloped, icosahedral capsids. Replication occurs in the cytoplasm and causes lysis of the host cell. The first species of this family that was isolated is Heterosigma akashiwo RNA virus (HaRNAV) in the genus Marnavirus, which infects the toxic bloom-forming Raphidophyte alga, Heterosigma akashiwo. As of 2021, there are twenty species across seven genera in this family, as well as many other related virus sequences discovered through metagenomic sequencing that are currently unclassified.

Chaetocerotaceae is a diatom family (Bacillariophyta). This family comprise the three genera Attheya T. West, Bacteriastrum Shadbolt and Chaetoceros Ehrenberg. Chaetoceros is perhaps the largest and most species rich genus of marine planktonic diatoms. The taxonomic status within Chaetocerotaceae at present is somewhat unclear.

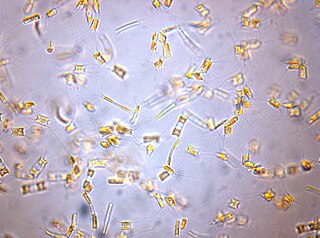
Chaetoceros is a genus of diatoms in the family Chaetocerotaceae, first described by the German naturalist C. G. Ehrenberg in 1844. Species of this genus are mostly found in marine habitats, but a few species exist in freshwater. It is arguably the common and most diverse genus of marine planktonic diatoms, with over 200 accepted species. It is the type genus of its family.

Chaetoceros furcellatus is an Arctic neritic diatom in the genus Chaetoceros. The easiest way to identify this species is by finding the very characteristic resting spores. C. furcellatus is a common and important species in the Barents sea.
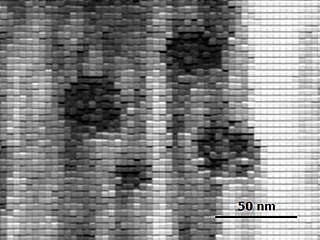
Attheya is a genus of small single celled diatoms. Some of these species were earlier regarded to belong to Chaetoceros, or to Gonioceros, the taxonomic status of some of these species are still debated.

Bacteriastrum is a genus of diatoms in family Chaetocerotaceae. There are more than 30 described species in genus Bacteriastrum, but many of these are not currently accepted, and new species are still added to the genus. The type species for the genus is Bacteriastrum furcatum Shadbolt.

The silky sifaka is a large lemur characterized by long, silky, white fur. It has a very restricted range in northeastern Madagascar, where it is known locally as the simpona. It is one of the rarest mammals on Earth. The silky sifaka is one of nine sifaka species, and one of four former subspecies of diademed sifaka (P. diadema). Studies in 2004 and 2007 compared external proportions, genetics, and craniodental anatomy supporting full species status, which has generally been accepted.

Lophosoria quadripinnata(J.F.Gmel.) C.Chr. is a species of fern that, according to DNA molecular analysis, belongs to the family Dicksoniaceae, where it is placed in the genus Lophosoria. It is found in the Americas spanning from Cuba and Mexico to Chile. In Chile it is present in the area between Talca and Aysén including Juan Fernández Islands. In Argentina it grows only in the humid valleys of western Neuquén and Río Negro Province. Diamondleaf fern is a common name. In Spanish it is known as 'ampe' or palmilla, but one has to remember that there are several species of ferns called "palmillas" that have larger or smaller fronds, and which grow in colder climates. It is a medium-sized plant, growing to about 4–5 feet and even though the rhizome does not grow a trunk, it is clearly related to the other tree ferns due to features that were apparently already present in their common ancestor, like 'pneumathodes', and the rhizome which changed from the dorsiventral symmetry typical of the other ferns, to a radial symmetry typical of tree ferns. Their large and multiple pinnate fronds, with the petiole raised adaxially, and the hairs on the rhizome and lower part of the petioles, also resemble those of tree ferns. To identify the species, use the position and characteristics of the spores found on the fertile fronds. The genus already existed in the Cretaceous Period in southern Gondwana according to fossil remains found in Antarctica. The species is well known as an ornamental plant.

Conus diadema, common name the diadem cone, is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Conidae, the cone snails and their allies.
Chaetoceros pseudocurvisetus is a marine diatom in the genus Chaetoceros. It is an important primary producer in the oceans. C. pseudocurvisetus forms resting spores and resting cells, particularly in the absence of essential nutrients.















