
Panama is a country located in Central America, bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, between Colombia and Costa Rica. Panama is located on the narrow and low Isthmus of Panama.
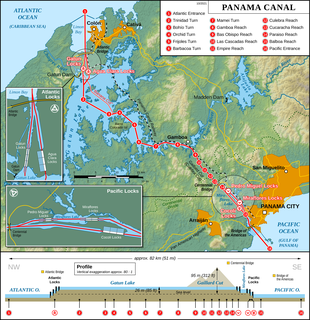
The Panama Canal is an artificial 82 km (51 mi) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. One of the largest and most difficult engineering projects ever undertaken, the Panama Canal shortcut greatly reduces the time for ships to travel between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, enabling them to avoid the lengthy, hazardous Cape Horn route around the southernmost tip of South America via the Drake Passage or Strait of Magellan and the even less popular route through the Arctic Archipelago and the Bering Strait.

The Panama Canal Railway is a railway line linking the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean in Central America. The route stretches 47.6 miles (76.6 km) across the Isthmus of Panama from Colón (Atlantic) to Balboa. Because of the difficult physical conditions of the route and state of technology, the construction was renowned as an international engineering achievement, one that cost US$8 million and the lives of an estimated 5,000 to 10,000 workers. Opened in 1855, the railway preceded the Panama Canal by half a century; the railway was vital in assisting the construction of the canal in the early 1900s. With the opening of the canal, the railroad's route was changed as a result of the creation of Gatun Lake, which flooded part of the original route. Following World War II, the railroad's importance declined and much of it fell into a state of neglect until 1998, when a project to rebuild the railroad to haul intermodal traffic began; the new railroad opened in 2001.
The Gatun Dam is a large earthen dam across the Chagres River in Panama, near the town of Gatun. The dam, constructed between 1907 and 1913, is a crucial element of the Panama Canal; it impounds the artificial Gatun Lake, which in turn carries ships 33 kilometres (21 mi) of their transit across the Isthmus of Panama. In addition, a hydro-electric generating station at the dam generates electricity which is used to operate the locks and other equipment in the canal.

The Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute is located in Panama and is the only bureau of the Smithsonian Institution based outside of the United States. It is dedicated to understanding the past, present, and future of tropical ecosystems and their relevance to human welfare. STRI grew out of a small field station established in 1923 on Barro Colorado Island in the Panama Canal Zone to become one of the world's leading tropical research organizations. STRI's facilities provide for long-term ecological studies in the tropics and are used by some 1,200 visiting scientists from academic and research institutions around the world every year.

The Chagres River, in central Panama, is the largest river in the Panama Canal's watershed. The river is dammed twice, and the resulting reservoirs—Gatun Lake and Lake Alajuela—form an integral part of the canal and its water system. Although the river's natural course runs northwest to its mouth at the Caribbean Sea, its waters also flow, via the canal's locks, into the Gulf of Panama to the south. The Chagres thus has the unusual claim of drainage into two oceans.

Cerros de Amotape National Park is a protected area located in the regions of Piura and Tumbes in northern Peru.

The idea of the Panama Canal dates back to 1513, when Vasco Núñez de Balboa first crossed the isthmus of Panama. The narrow land bridge between North and South America was a fine location to dig a water passage between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. The earliest European colonists recognized this, and several proposals for a canal were made.

Chagres, once the chief Atlantic port on the isthmus of Panama, is now an abandoned village at the historical site of Fort San Lorenzo. The fort's ruins and the village site are located about 8 miles (13 km) west of Colón, on a promontory overlooking the mouth of the Chagres River.
Nuevo Chagres is a seaside town and corregimiento in the Colón Province of Panama, and the capital of the Chagres District. It had a population of 499 as of 2010. Its population as of 1990 was 327; its population as of 2000 was 419.

Gamboa is a small town in corregimiento of Cristóbal in the Colón Province, Panama close to the Panama Canal and the Chagres River. It was one of a handful of permanent Canal Zone townships, built to house employees of the Panama Canal and their dependents. The name Gamboa is the name of a tree of the quince family.
The flame-templed babbler is a species of bird of the family Zosteropidae, in the genus Dasycrotapha. It is one of the most remarkable and distinctive birds with its complex head markings with orange crown tufts, black ears and yellow beak and face. It is endemic to the Philippines, where it is found on the islands of Panay and Negros. Its natural habitat is tropical moist lowland forest. It is threatened by habitat loss. Along with the Negros striped babbler, it is one of the two babbler species extremely sought after by birdwatchers on Negros.
Lò Gò-Xa Mát National Park is a national park in the Southeast region of Vietnam, approximately 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the city of Tây Ninh. It was established by upgrading the status of the former Lò Gò-Xa Mát Nature Reserve. After receiving national park status in 2002, the park was expanded in 2020 to cover an area of 30,022 hectares (115.92 sq mi).

Gatun is a small town on the Atlantic Side of the Panama Canal, located south of the city of Colón at the point in which Gatun Lake meets the channel to the Caribbean Sea. The town is best known as the site of the Panama Canal's Gatun Locks and Gatun Dam, built by the United States between 1906–1914.
Marotandrano Special Reserve is a wildlife reserve in Mandritsara, Mahajanga, Madagascar. It is 10 km from Marotandrano and 42 km from Mandritsara.

The Madden Dam, completed in 1935, impounds the Chagres River in Panama to form Lake Alajuela, a reservoir that is an essential part of the Panama Canal watershed. The lake has a maximum level of 250 feet (76 m) above sea level. It can store one third of the canal's annual water requirements for the operation of the locks. Since the reservoir is not part of the navigational route, there are fewer restrictions on its water level.
The Chagres Formation (Tc) is a geologic formation in the Colón Province of central Panama. The sandstones and siltstones were deposited in a shallow marine environment and preserve fossils dating back to the Middle to Late Miocene period.
The Gatún Formation (Tg) is a geologic formation in the Colón and Panamá Provinces of central Panama. The formation crops out in and around the Panama Canal Zone. The coastal to marginally marine sandstone, siltstone, claystone, tuff and conglomerate formation dates to the latest Serravallian to Tortonian, from 12 to 8.5 Ma. It preserves many fossils, among others, megalodon teeth have been found in the formation.

San Lorenzo Protected Area is a 12,000-ha area in Panama. It includes Fort San Lorenzo and Fort Sherman. At its longest point, is measures 24 kilometres (15 mi) from "Toro Point to the town of Escobal". The widest point of its width measures 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) "from the southeastern corner of Limón Bay to the beaches northeast of the town of Piña". All areas of the SLPA were returned to Panama on June 30, 1999.

Behali Reserved Forest, located in the Biswanath district of Assam is a patch of semi-evergreen forest in the foothills of Eastern Himalayas.














